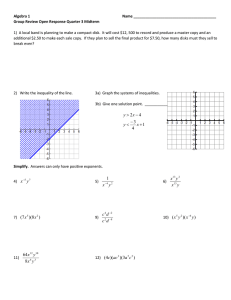
Document

Math-3
Lesson 3-3
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
Quiz 3-1:
Simplify the following:
4
x
x
6 x
2
x
4 x
( x
8
2 )
( x x
6
2 )
( x
( x
2 )
2 )
*
4 x
( x x
6
2 )
4 x
8 x ( x
2 )
( x x
6
2 )
* x x
x
4 x
( x
8
2 )
x x ( x
2
6 x
2 )
4 x
8
x ( x x
2
2 )
6 x
x
2
( x
10 x
1 )( x
8
2 )
Your Turn: Simplify
1.
x
2
(
3 x
28 x
7 )
2. x
3 x
2 x
2
12 x
3 x
3. 2 x
3
2 x
7
BE CAREFUL!!!!! x
7
7 ( x
No, no, no, no, no!!!
9 )
Addition and Subtraction mean:
Combine the terms into one term (if you can)
If you can’t combine them (unlike terms) they still are connected to each other.
Put binomials into a parentheses.
( x
7 ( x
7 )
9 )
Multiplying Fractions
6
7
*
14
9 multiply
6 * 14
7 * 9
2 * 3 * 2 * 7
7 * 3 * 3
4
3
84
63 simplify
6 * 14
7 * 9
6
7
*
14
9 simplify
2 * 3 * 2 * 7
7 * 3 * 3
4
3
Do you multiply first or do you simplify THEN multiply?
Multiplying Rational Expressions
( x
1 )
2 ( x
3 )
* x
2
9
( x
1 )
Simplify before you multiply.
( x
1 )(
2 ( x
x
3
)(
3 )( x x
3 )
1 )
( x
1 )( x
3 )
2 ( x
1 ) multiplying allows you to put all the factors together
in one numerator and one denominator so you can simplify.
DON’T multiply the simplified version of the product,
just leave it in factored form.
Your turn:
Multiply the expressions
3 ( x
4 )
( x
3 )
( x
*
( x
2 )
4 )
( x
*
6 ( x
3 )
2 )
3
6
1
2
( x
3 )
( x
5 )
*
( x
2
( x
16
4 )
)
( x
3 )( x
( x
3 )( x
4 )
( x
5 )
( x
4 )( x
5 )( x
4 )
4 )
Your turn:
Multiply the expressions
( x
3 )( x
( x
3 )( x x
2
4
3
x
2
)
) x
12
9
* x
( x
5 )( x
*
( x
4 )( x
2 x
2 x
15
2
16
3
4
)
)
(
( x
5 ) x
4 )
(Solutions on this slide)
Your turn:
2 x
2 x
2
8 x
2 x
Multiply the expressions
24
3
* x x
2
2
7
2 x x
12
24
(Solutions on this slide)
2 ( (
( ( 3 )(
12 ) )
1 ) )
2 ( x
6 )( x
2 )
( x
1 )( x
6 )
( (
( (
3 )(
6 )(
4
4
) )
) )
2 ( x
2 )
( x
1 )
2 ( x
2
4 x
12 )
( x
1 )( x
6 )
Divide Rational Expressions
2
3
5
7
What do we do? Multiply by the reciprocal
2
3
*
7
5
14
15
Divide Rational Expressions
12 xyz
5 mnp
4 x
2 z
5 mn
Multiply by the reciprocal
12 xyz
5 mnp
5 mn
*
4 x
2 z
12 xy p
1
*
4 x
2
4 * 3 xy p
1
*
4 * x * x
3 p y 1
* x
3 y px
Your turn:
6 abz
7 mp
2
*
14 m
2
4 b
3 z p
6 abz
7 mp
2
4 b
3
14 m
2 z p
7
2 * 3 * a * b
* m * p * p
*
2 * 7 * m * m *
2 * 2 * b * b * b p
3 am pb
2
Dividing Rational Expressions x
2 x
3
x
6
x
8 x
2
?
x
2 x
3 x
6
* x
2 x
8 simplify then multiply!
x
3
( x
3 )( x
2 )
* x
2 x
8
( x
3 )( x
2 )
( x
3 )( x
2 )( x
8 )
1
( x
8 )
( x
Your turn: x
2 x
3
x
6
* x
2 x x
8
6
( x
2
( x x
2 x
3
x
6
x
2 x
8 x
6
3 ) x
6 )
*
( x
2
( x
x
8 )
6 )
( x
3 )
( x
8 )
Your turn: x x
2
2
2 x
35
4 x
12
x
2 x
2
2 x
15
9 x
14 x x
2
2
2 x
4 x
35
12
* x
2 x
2
9 x
14
2 x
15
(
( x x
7 )( x
5 )
6 )( x
2 )
*
(
( x
x
2 )( x
5 )( x
7
3 )
)
( x
7 )( x
7 )
( x
6 )( x
3 )
Your Turn: divide x x
2
2
x
2 x
20
15
x
2 x
5 x
2
5 x
4
Divide
28 x
2 y
3 y
14 x
2
6 x
3 y
2
Your Turn:
Multiply
Multiply divide
4 ( x
5 )
4 x
16 x ( x
1 )
*
2 ( x
5 ) x
2 x
2
3 x
2 x
10
15
* ( x
2
10 x
21 ) x x
2
2
x
2
4 x
5
2 x
4
5 x
25
Compound (or Complex) Fraction
1
3
2
5
1
3
2
5
1 * 5
3 * 2
5
6
1
3
*
5
2
Simplifying a Compound Rational
Function
x
2 x
1
4 x x
1
Convert division to multiplication
x
2 x
1
* x
1
4 x remove common factors in
Numerator/denominator
2
4
1
2
Compound Rational Functions
2 x x
1
3 x
4 x
3
Convert Division into multiplication
=
2 x x
1
3
* x
3 x
4
( 2
Leave as is x
3 )( x
3 )
( x
1 )( x
4 )
Your turn:
1
2 x
1 x
2
Simplify
Sum/difference in Numerator and Denominator
1. Combine the numerator fractions into one fraction. x
3
2
3 x
6
=
2 x
3
3 x
6
1
= x
2
3
18
3 x
2. Combine the denominator fractions into one fraction. x
18
2 x
3
3 x
=
18
3
*
2 x x
3
x
3 (
(
2 x x
18 )
3 ) x
Your turn:
Simplify the complex fraction.
1 x x
2
3
3 x
4
Another Example: Electrical Circuits
Voltage
Source
R
1
R total
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
3
R
2
Parallel Resistors
1
R total
1
R
1
1
R
2
1
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
3
Voltage
Source
R
1
T
R
2
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
1
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
1
R
2
R
3
1
R
T
R
2
R
3
R
1
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
T
R
2
R
3
R
1
R
R
1
2
R
R
3
3
R
1
R
2
Parallel Resistors
1
R total
1
R
1
1
R
2
1
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
3
Voltage
Source
Electrical resistance is measured in “ohms.” Given the following resistances, find the total resistance of the circuit. R
1
5
R
2
10
R
3
15
R
T
R
2
R
3
R
1
R
R
1
2
R
R
3
3
R
1
R
2
10 * 15
5
* 10
5
* 15
* 15
5 * 10
2 .
72
People working together is similar to parallel resistance because they are working “in parallel”.
1
The total time to complete a job is a function of the times required to complete the job by each worker separately.
T t
1
T a
1
T b
Alfonso takes 5 hours to paint a room. Bob takes 6 hours to paint the same room. How long does it take them to paint the room while working together?
1
T t
5
1
1
6
1
T t
6
30
5
30
1
T t
11
30
T t
30
11
2 .
7 hrs