CTEC 101 Introductory Analog Electronics
advertisement

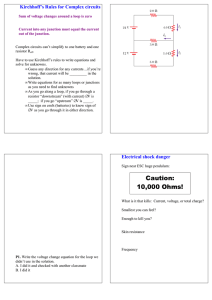
Faculty: Phone#: Fax#: E-mail: Office Hours: Room #: COURSE OUTLINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2004-2005 It is the student's responsibility to retain course outlines for possible future use in support of applications for transfer credit to other educational institutions. PROGRAM: COMPUTER AND NETWORK SUPPORT TECHNICIAN COMPUTER ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY WIRELESS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY COURSE NUMBER/NAME: CTEC 101 - Introductory Analog Electronics CREDITS: 4 PRE-REQUISITES: None PREPARED AND/OR REVIEWED BY: PROGRAM FACULTY PROGRAM COORDINATOR: PAUL MICHAUD APPROVED BY: DEAN (or designate) I September 2004 DATE COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to analog electronic fundamentals. It exposes students to electrical and electronic fundamentals such as current, voltage, resistance and the relevant circuitry and calculations. Students will learn to build small electronic circuits containing analog components. They will be able to test and troubleshoot these circuits using multi- meters and oscilloscopes. Wherever possible examples will relate to modern computer and communications technology. The student is responsible for purchasing an electronics parts kit containing all the components necessary to complete the laboratory experiments. The same kit will be used in other and subsequent courses/ semesters. II LEARNING OUTCOMES Learning outcomes are clear statements of the critical/essential knowledge, skills and attitudes that a student is required to demonstrate to indicate successful completion of the course. Generic/Employability Skills are transferable skills that provide the foundation for a student’s academic, vocational, and personal success. These outcomes include communications, personal, interpersonal, thinking, mathematics, and computer skills. A. Core Outcomes Upon completion of this course, the successful student will be able to: 1. Draw electronic diagrams using correct symbols and build the resultant circuits. 2. Describe insulation, conduction and the key features of a good electrical connections 3. Determine the value and tolerance of a resistor using the resistor colour code 4. Make measurements of voltages, currents and resistance in simple circuits. 5. Perform calculations of voltage, current, power and resistance in simple circuits. 6. Recognize, troubleshoot and analyze series, parallel and series/parallel circuits. 7. Describe various electronic waveforms and perform related calculations. 8. Measure, with an oscilloscope, frequency, time intervals and amplitude of waveforms. 9. Explain the basic characteristics of capacitors/capacitance and inductors/inductance 10. Demonstrate the correct and safe use of electrical/electronic test equipment and devices. 11. Simulate, analyze and chart electronic circuits and data using electronic simulation software and spreadsheets. 12. Compare simulated laboratory results versus actual laboratory results and comment on the possible causes of differences between the two. B. Generic/Employability Skills Outcomes The following generic skills will be acquired and/or enhanced: COMMUNICATION • • • • • • Respond correctly to oral and written instructions. Communicate in written, oral or diagrammatic form using course related electronic terminology in technical reports and discussions. Read and comprehend standard reference materials, manuals and diagrams. Write in clear and concise sentences and paragraphs accurate records of lab work. Read and interpret policy and procedure. Interpret a range of technical and non-technical instructions through dialogue and refined questioning skills. MATHEMATICS • • • • Apply the fundamentals of mathematics when performing calculations using complex electronic expressions and formulae. Transpose formulae to solve related problems. Tabulate and analyze data. Produce graphs from tabulated data. INTERPERSONAL • • • • III Participate effectively in group discussions. Make decisions regarding problem solving. Demonstrate safety awareness with electrical equipment and hand tools. Take responsibility for one's own actions and demonstrate understanding, cooperation, maturity, and a respect for the rights of individuals when working with others. COURSE CONTENT 1. Initial Concepts of Current, voltage and Resistance. • • • • • • Basic atomic theory leading to electron and conventional current flow. The transmission and speed of current flow through a typical wires and cables Voltage, common voltage sources and voltage drop concept. The various voltage references (EMF, Potential Difference, total, drop, 'with respect to'). Simple circuit diagrams with common symbols. Electrical connections, metal plating, oxidation, corrosion, moisture and mechanical versus soldered connections. 2. Resistor Colour Code • The three band resistor colour code with the tolerance and reliability bands. • The four band resistor colour code with the tolerance and reliability bands. • Other coding methods. 3. Meters • • • 4. Ohm's Law and Series Circuits • • • 5. • Calculations and measurements of voltage, current, resistance and power in multiple component parallel circuits. The current dividing concepts of parallel circuits Series-Parallel Combination Circuits. • • 7. Voltage, current, resistance and power in series circuits containing multiple components. The "voltage divider rule". Calculations of power based on combinations of voltage, current and resistance Parallel Circuits • 6. Measurements using voltmeters, current meters and ohmmeters. Comparison of analog vs. digital meters. Measurements of continuity and resistance using a multi-meter. Analysis, calculation, measurement and trouble shooting concepts of series/parallel circuits. Meter and circuit loading errors Variable Resistors as Potentiometers and Rheostats • The construction, configuration and various method of connecting variable resistors as voltage dividing potentiometers and current limiting rheostats. 8. AC Voltages and Waveforms • Analysis of AC voltages and waveforms including the calculations of Peak, Peak-to-Peak, RMS and Average DC voltage levels. Calculation of Period times and frequency. 9. Oscilloscope and Function Generator • 10. Capacitors and Capacitance • 11. The construction and basic properties of inductors. Self-inductance and the effects of inductors/inductance in DC and in simple AC circuits including induced voltage spikes in switching or squarewave/pulse circuits. Software Applications for Electronic Simulation, Calculations and Graphs • IV The construction and basic properties of capacitors. Charge and discharge times plus the behavior and effects of capacitance/capacitors in DC and in the simple coupling/de-coupling of AC circuits. Inductors and Inductance • 12. The use of a Function Generator to produce square, triangular and sine wave and of an oscilloscope to view the waveforms and make measurements of Peak and Peak to Peak voltages, period times, frequency and duty cycle. Familiarization with Electronic Work Bench and MS-Excel to emulate electronic lab experiments and perform calculations and graphing of electronic data. EVALUATION PROCEDURE Formal Tests - There will be a minimum of two tests during the semester. All tests will have equal weighting. A minimum average of 60% must be achieved on these tests. Assignments - Assignments may be given. They will have due dates and must be completed by that date. Evaluation methods are at the discretion of the individual teacher. Lab Exercises - Laboratory attendance within the assigned time periods, is mandatory. Students who have not completed lab exercises by the end of the lab period must complete them in their own time in an open lab. All completed lab work must be signed by a teacher or E.A. Part of the lab grade will be based on the writing skills, neatness and professionalism exhibited in the lab reports. Lab exercises will have due dates that must be adhered to, failure to comply with due dates may result in an overall course failure. Final Grade Calculation: - To pass this course the student must obtain a minimum average of 60% on the tests and 60% on the practical/laboratory portion. Should either mark be lower than 60% the lower mark will become the final grade. If a passing grade is achieved on all components, the following formula is suggested for combining lab and test marks. Changes to the method of evaluation are at the discretion of the individual teacher and will be given in writing. The Marking distribution is as follows: THEORY/TESTS 70% LABS/ASSIGNMENTS 30% TOTAL 100% A minimum final grade of 60% is required for course completion. Please note: The Distance Learning version of this course (if available) may have a different grading scheme than the classroom version. Check the information page of the Distance Learning version for details. Students must pass the proctored final exam for any other test and lab assignments to count towards their final mark. V REQUIRED TEXTS AND OTHER LEARNING MATERIALS Introductory DC/AC Electronics, 5th Edition, by Nigel P. Cook: Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13031085-9 Complete Electronic Technician's parts kit, and one Floppy disk. VI DELIVERY FORMAT Lecture and Lab sessions. VII SUPPLEMENTARY ASSIGNMENTS/TESTS/EXAMINATIONS Supplementals are not available in this course, unless extraordinary, documentable circumstances have prevented a student from participating in scheduled course activities. All applications for supplementals are made to the course instructor. VIII ACADEMIC CONCERNS/APPEALS Any student having an academic concern or questioning an academic decision should first discuss the matter directly with their professor; then with the program coordinator if the issue cannot be resolved; then with the Dean (or designate) if the prior two steps were unsuccessful. Complete details regarding academic appeals are found in the College’s Academic Complaint and Appeal Policy. IX POLICIES AND PROCEDURE It is the student's responsibility to be aware of the COLLEGE’S ACADEMIC REGULATIONS and the SCHOOL OF APPLIED TECHNOLOGY POLICIES AND PROCEDURES. (See School of Applied Technology's Academic Handbook). The College’s Academic Regulations can be found at http://registrar.humberc.on.ca/acregs.html X PRIOR LEARNING ASSESSMENT AND RECOGNITION (PLAR) Course credits may be granted in recognition of prior learning. Application for consideration is made through the Office of the Registrar. The method(s) of assessment are: Challenge Exam √ XI Portfolio Skills Test Interview Other (please specify) Not Available for PLAR √ DISCLAIMER While every effort is made by the professor to cover all content material listed in this outline, the order, content and/or evaluation may change as a result of special circumstances (e.g. time constraints due to inclement weather, College closure, technology/equipment problems and/or changes, etc.) In any such case, every effort will be made to make appropriate adjustments to the course delivery.