On Inductance, Lenz`s Law, and Faraday`s Law. Homework: pg 700
advertisement

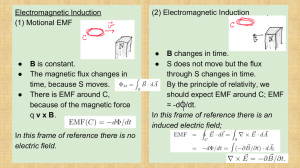
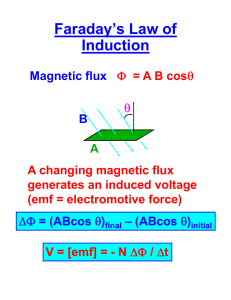
3/28/2016 On Inductance, Lenz’s Law, and Faraday’s Law. Homework: pg 700: 1 & 3 The magnetic flux depends upon the number of field lines through a given area. If you increase the area the flux will increase. ◦ What happens for the opposite? If you increase the magnetic field strength you will increase the flux. ◦ What happens for the opposite? The magnetic flux is the product of the area perpendicular to the magnetic field. ◦ F = BA cos(q) 1 3/28/2016 F = BA F = magnetic flux, unit is Weber, Wb = Tm2 B = magnetic field strength, unit is Tesla, T A = area, unit is m2 Inductance is a measure of the amount of magnetic flux produced for a given electric current. L = F/I L = inductance, unit is Henry, H F = magnetic flux, unit is Weber, Wb I = current, unit is Ampere, A L = NF/I N = Number of coils, no unit 2 3/28/2016 The effect of inductance can be understood using a single loop of wire as an example. Of a voltage is suddenly applied between the ends of the loop of wire, the current must change from zero to non-zero. A non-zero current induces a magnetic field by Ampere’s law. This change is the magnetic field induces an emf that is in the opposite direction of the change in current. The strength of this emf is proportional to the change in current and the inductance. When these opposing forces are in balance, the result is a current that increases linearly with time where the rate of this change is determined by the applied voltage and the inductance. Faraday’s law states an electromotive force, Emf or E or EMF, produced along a closed path is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through any surface bound by the path. An electrical current will flow in any closed conductor when the magnetic flux through a surface bounded by the conductor changes. This applies whether the field itself is changes in strength of the conductor is moved through it. EMF = Emf = E = - F/t = - (DBA)/t = - B(l w)/t = - Blv E = electromotive force, unit is voltage, V F = magnetic flux, unit is Weber, Wb t = time, unit is second, s l = length of wire, unit is meter, m v =velocity (speed), unit is meter/second, m/s 3 3/28/2016 EMF = Emf = - NF/t N = Number of coils, no unit An Emf is an induced voltage due to the changing magnetic flux. Lenz’s law will give the direction of the induced Emf. Lenz’s law states the induced Emf will oppose the changing magnetic flux. Since the direction of the Emf is opposing the change in magnetic flux, the equation has a negative sign. 4