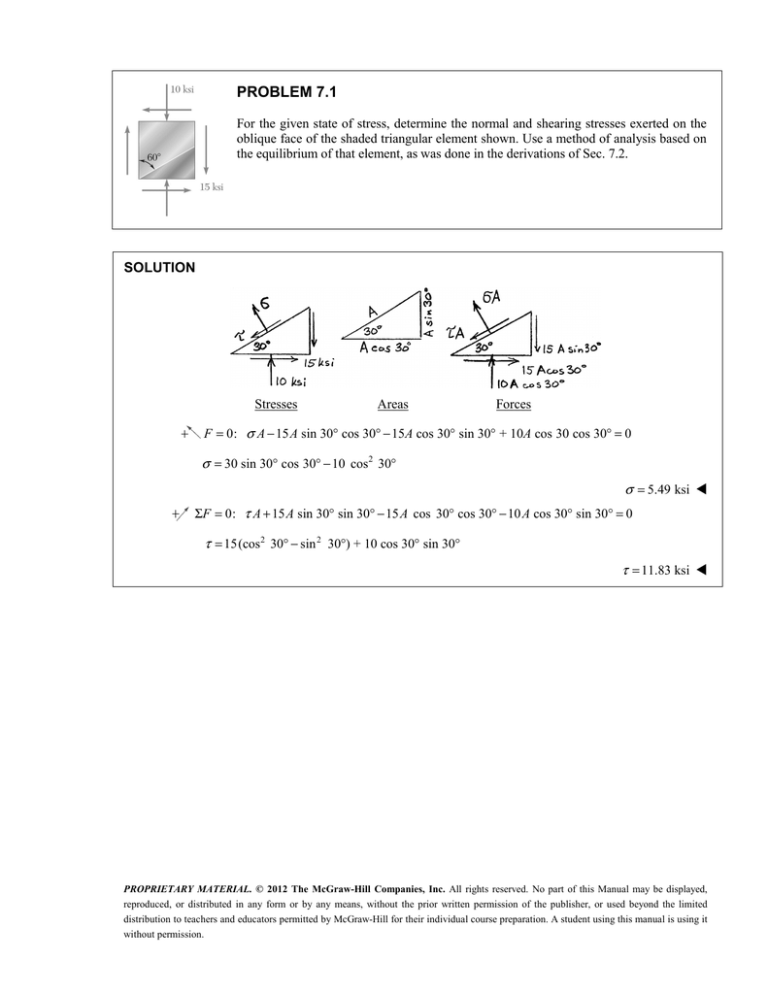
PROBLEM 7.1
For the given state of stress, determine the normal and shearing stresses exerted on the
oblique face of the shaded triangular element shown. Use a method of analysis based on
the equilibrium of that element, as was done in the derivations of Sec. 7.2.
SOLUTION
Stresses
Areas
Forces
F = 0: σ A − 15 A sin 30° cos 30° − 15A cos 30° sin 30° + 10A cos 30 cos 30° = 0
σ = 30 sin 30° cos 30° − 10 cos 2 30°
σ = 5.49 ksi
ΣF = 0: τ A + 15 A sin 30° sin 30° − 15 A cos 30° cos 30° − 10 A cos 30° sin 30° = 0
τ = 15(cos 2 30° − sin 2 30°) + 10 cos 30° sin 30°
τ = 11.83 ksi
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed,
reproduced, or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited
distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
PROBLEM 7.4
For the given state of stress, determine the normal and shearing stresses
exerted on the oblique face of the shaded triangular element shown. Use a
method of analysis based on the equilibrium of that element, as was done in the
derivations of Sec. 7.2.
SOLUTION
Stresses
Areas
Forces
ΣF = 0: σ A + 18 A cos 15° sin 15°
+ 45 A cos 15° cos 15° − 27 A sin 15° sin 15°
+ 18A sin 15° cos 15° = 0
σ = −18 cos 15° sin 15° − 45 cos 2 15°
+ 27sin 2 15° − 18 sin 15° cos 15°
σ = −49.2 MPa
ΣF = 0: τ A + 18 A cos 15° cos 15°
− 45 A cos 15° sin 15°
− 27 A sin 15° cos 15°
− 18 A sin 15° sin 15° = 0
τ = −18(cos 2 15° − sin 2 15°) + (45 + 27) cos 15° sin 15°
τ = 2.41 MPa
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed,
reproduced, or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited
distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
PROBLEM 7.5
For the given state of stress, determine (a) the principal planes, (b) the principal
stresses.
SOLUTION
σ x = −60 MPa σ y = −40 MPa τ xy = 35 MPa
(a)
tan 2θ p =
2τ xy
σx −σ y
=
(2) (35)
= −3.50
−60 + 40
2θ p = −74.05°
(b)
σ max, min =
=
σx +σy
2
θ p = −37.0°, 53.0°
±
−60 − 40
±
2
σx −σ y
2
2
−60 + 40
2
2
+ τ xy
2
+ (35) 2
= −50 ± 36.4 MPa
σ max = −13.60 MPa
σ min = −86.4 MPa
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed,
reproduced, or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited
distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
PROBLEM 7.8
For the given state of stress, determine (a) the principal planes, (b) the principal
stresses.
SOLUTION
σ x = −8 ksi σ y = 12 ksi τ xy = 5 ksi
(a)
tan 2θ p =
2τ xy
σx − σy
2(5)
= −0.5
−8 − 12
=
2θ p = −26.5651°
(b)
σ max, min =
=
σx + σy
2
±
−8 + 12
±
2
= 2 ± 11.1803
θ p = −13.3°, 76.7°
2
σx − σy
2
+τ xy
2
−8 − 12
2
2
+ (5)2
σ max = 13.18 ksi
σ min = −9.18 ksi
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed,
reproduced, or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited
distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
PROBLEM 7.19
A steel pipe of 12-in. outer diameter is fabricated from 14 -in. -thick plate by
welding along a helix that forms an angle of 22.5° with a plane perpendicular
to the axis of the pipe. Knowing that a 40-kip axial force P and an 80-kip ⋅ in.
torque T, each directed as shown, are applied to the pipe, determine σ and τ
in directions, respectively, normal and tangential to the weld.
SOLUTION
1
d 2 = 6 in., t = 0.25 in.
2
c1 = c2 − t = 5.75 in.
d 2 = 12 in., c2 =
(
π
J = (c
2
)
π
− c ) = (6
2
A = π c22 − c12 = π (62 − 5.752 ) = 9.2284 in 2
4
2
4
1
4
− 5.754 ) = 318.67 in 4
Stresses:
σ =−
P
A
40
= −4.3344 ksi
9.2284
Tc
τ= 2
J
(80)(6)
=
= 1.5063 ksi
318.67
σ x = 0, σ y = −4.3344 ksi, τ xy = 1.5063 ksi
=−
Choose the x′ and y ′ axes, respectively, tangential and normal to the weld.
Then
σ w = σ y′ and τ w = τ x′y′ θ = 22.5°
σ y′ =
σx +σy
σx −σ y
cos 2θ − τ xy sin 2θ
2
2
(−4.3344) [ −(−4.3344)]
=
−
cos 45° − 1.5063 sin 45°
2
2
= −4.76 ksi
τ x′y′ = −
−
σ w = −4.76 ksi
σx −σy
sin 2θ + τ xy cos 2θ
2
[ −(−4.3344)]
=−
sin 45° + 1.5063 cos 45°
2
= −0.467 ksi
τ w = −0.467 ksi
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed,
reproduced, or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited
distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.
PROBLEM 7.22
Two steel plates of uniform cross section 10 × 80 mm are welded
together as shown. Knowing that centric 100-kN forces are applied to
the welded plates and that the in-plane shearing stress parallel to the
weld is 30 MPa, determine (a) the angle β, (b) the corresponding normal
stress perpendicular to the weld.
SOLUTION
Area of weld:
Aw =
=
(a)
Fs = 0: Fs − 100sin β = 0
τw =
Fs
Aw
sin β cos β =
(b)
30 × 106 =
(10 × 10−3 )(80 × 10−3 )
cos β
800 × 10−6 2
m
cos β
Fs = 100sin β kN = 100 × 103 sin β N
100 × 103 sin β
= 125 × 106 sin β cos β
−6
800 × 10 / cos β
1
30 × 106
sin 2β =
= 0.240
2
125 × 106
Fn = 0: Fn − 100cos β = 0
β = 14.34°
Fn = 100cos14.34° = 96.88 kN
Aw =
800 × 10−6
= 825.74 × 10−6 m 2
cos14.34
σ =
Fn
96.88 × 103
=
= 117.3 × 106 Pa
Aw
825.74 × 10−6
σ = 117.3 MPa
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2012 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed,
reproduced, or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited
distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. A student using this manual is using it
without permission.




