Transmission Line Security System Based on RFID and
advertisement

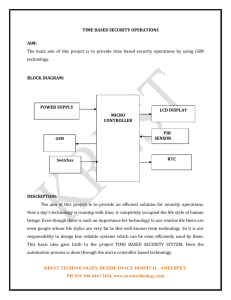
Transmission Line Security System Based on RFID and GSM Technology Swati Chandrakar Completed B.E in “Electrical and Electronics” from CSIT in 2014. Right Now She is Working as a Teacher at Yugantar Institute of Management and Technology Rajnandga on Chhattisgarh. 1. Introduction: In this present age, safety has become an essential issue for most of the power stations in the rural and urban areas. To overcome the security threat, most of the power stations create different type of security system. There are many types of security systems available in the market which utilized different type of sensors. In this project we will implement the security system of the power stations and their sub-stations by using RFID and GSM technology which will be more secure than other systems. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) based access-control system allows only authorizes persons to do any modifications at the power stations. Basically RFID systems consist of an antenna or coil a transceiver and a transponder electronically programmed with unique information. There are many types of RFID systems in the market. These are categorized on the basis of their frequency ranges. Some of the most commonly used RFID kits are low-frequency (30-500 kHz), mid- frequency (900 kHz-1500 kHz) and high-frequency (2.4-2.5GHz). The passive tags are lighter and less expensive than the active tags. Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM ia a common European mobile telephone standard for s mobile cellular radio system operating at 900 MHz. in the current work, SIM900 GSM module is used. The SIM900 module is a Triband, GSM/GPRS solution in a compact plug in module is a featuring an industry-standard interface. It delivers voice, data and fax in a small from factor with low power consumption. 2. Abstract: The main goal of this project is to implement a power station security system based on RFID and GSM technology. In this system only authentic person will be able to perform the action in the related power stations. We will implement a security system based on RFID and GSM technology containing a scanning system using RFID and GSM which can activate, authenticate and validate the user and unlock the stations. The main advantage of using RFID and GSM is more secure than other systems. This system consists of microcontroller, RFID reader, GSM modem, keyboard, and LCD, in this system. The RFID reader reads the id number of the user. The users scan the id-card and choose the sub-station to at the main power stations. The RFID reader reads the id number and sends to the micro-controller in the sub-stations selected by user at main station. Now the user again scans the id-card at that particular sub-station. Then the RFID reader at the sub-station scans the idnumber and matches from the id-number received from main station. If the both ids will match then the user will be valid and authenticated to be worked at those sub-stations otherwise the sub-station remains closed. The process of security and authentication will remain same for the other sub-stations. This system is more secure because the same id-numbers are required at the main power station and its sub-stations. Page 709 3. PROPOSED WORKING: In this proposed work, the RFID reader read the data from the tag and send to the microcontroller, if the card is valid then microcontroller display the user authentication message and the id number. If the id number is valid then the user will be validated for modification work. The user id number is send by the main station to the microcontroller at sub-station. The microcontroller compares the id scanned and id received through main station. If these ids are same the microcontroller provides necessary control and authentication to the user. The working is simple and more secure than others systems. 4. RFID Fundamentals: RFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identification. The acronym refers to small electronic devices that consist of a small chip and an antenna. The chip typically is capable of carrying 2,000 bytes of data or less. The RFID device serves the same purpose as a bar code or a magnetic strip on the back of a credit card or ATM card; it provides a unique identifier for that object. And, just as a bar code or magnetic strip must be scanned to get the information, the RFID device must be scanned to retrieve the identifying information. 4.1 How RFID Works: A Radio-Frequency Identification system has three parts: A scanning antenna A transceiver with a decoder to interpret the data A transponder - the RFID tag - that has been programmed with information. It provides a means of communicating with the transponder (the RFID tag) AND It provides the RFID tag with the energy to communicate (in the case of passive RFID tags). This is an absolutely key part of the technology; RFID tags do not need to contain batteries, and can therefore remain usable for very long periods of time (maybe decades). The scanning antennas can be permanently affixed to a surface; handheld antennas are also available. They can take whatever shape you need; for example, you could build them into a door frame to accept data from persons or objects passing through. When an RFID tag passes through the field of the scanning antenna, it detects the activation signal from the antenna. That "wakes up" the RFID chip, and it transmits the information on its microchip to be picked up by the scanning antenna. In addition, the RFID tag may be of one of two types. Active RFID tags have their own power source; the advantage of these tags is that the reader can be much farther away and still get the signal. Even though some of these devices are built to have up to a 10 year life span, they have limited life spans. Passive RFID tags, however, do not require batteries, and can be much smaller and have a virtually unlimited life span. RFID tags can be read in a wide variety of circumstances, where barcodes or other optically read technologies are useless. The tag need not be on the surface of the object (and is therefore not subject to wear) The read time is typically less than 100 milliseconds Large numbers of tags can be read at once rather than item by item. The scanning antenna puts out radio-frequency signals in a relatively short range. The RF radiation does two things: Page 710 General Features: 1 Quad-Band 850/ 900/ 1800/ 1900 MHz 2 GPRS multi-slot class 10/8 3 GPRS mobile station class B 4 Compliant to GSM phase 2/2+ 5 Weight: 3.4g 6 Control via AT commands (GSM07.07, 07.05 and SIMCOM enhanced AT Commands) 7 SIM application toolkit 8 Supply voltage range 3.4 ... 4.5 V 9 Low power consumption. FIG:- RFID READER 5. SIM 900: The SIM900 is a complete Quad-band GSM/GPRS solution in a SMT module which can be embedded in the customer applications. Featuring an industrystandard interface, the SIM900 delivers GSM/GPRS 850/900/1800/1900MHz performance for voice, SMS, Data, and Fax in a small form factor and with low power consumption. With a tiny configuration of 24mm x 24mm x 3 mm, SIM900 can fit almost all the space requirements in your M2M Application, especially for slim and compact demand of design. 1. SIM900 is designed with a very powerful single-chip processor integrating 2. AMR926EJ-S core 3. Quad - band GSM/GPRS module with a size of 24mmx24mmx3mm 4. SMT type suit for customer application 5. An embedded Powerful TCP/IP protocol stack 6. Based upon mature and field-proven platform, backed up by our support 7. service, from definition to design and production FIG:- SIM 900 FIG .SIM 900 6.AT89C51: The AT89C51 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit microcomputer with 4K Bytes of Flash programmable and erasable read only memory (PEROM). The device is manufactured using Atmel’s high-density non-volatile memory technology and is compatible with the industry-standard MCS-51 instruction set and pin out. The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional. Page 711 Non-volatile memory programmer. By combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel AT89C51 is a powerful microcomputer which provides a highly-flexible and cost-effective solution to many embedded control applications. The AT89C51 is shipped with either the high-voltage or low-voltage programming mode enabled. The respective top-side marking and device signature codes are listed in the following table. The AT89C51 code memory array is programmed byte-by-byte in either programming mode. 6.1 Features: 1. Compatible with MCS-51™ Products 2. 4K Bytes of In-System Reprogrammable Flash Memory 3. Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles 4. Fully Static Operation: 0 Hz to 24 MHz 5. Three-level Program Memory Lock 6. 128 x 8-bit Internal RAM 7. 32 Programmable I/O Lines 8. Two 16-bit Timer/Counters 9. Six Interrupt Sources 10. Programmable Serial Channel 11. Low-power Idle and Power-down Modes. The AT89C51 provides the following standard features: 4Kbytes of Flash, 128 bytes of RAM, 32 I/O lines, two 16-bit timer/counters, a five vector two-level interrupt architecture, a full duplex serial port, on-chip oscillator and clock circuitry. In addition, the AT89C51 is designed with static logicfor operation down to zero frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes. The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down Mode saves the RAM contents but freezes the oscillator disabling all other chip functions until the next hardware reset. FIG:- AT89C51 The AT89C51 is normally shipped with the on-chip Flash memory array in the erased state (that is, contents = FFH) and ready to be programmed. The programming interface accepts either a high-voltage (12-volt) or a low-voltage (VCC) program enable signal. The low-voltage programming mode provides a convenient way to program the AT89C51 inside the user’s system, while the high-voltage programming mode is compatible with conventional third party Flash or EPROM programmers. FIG . AT89C51 7. GLOBAL SYSTEM COMMUNICATIO (GSM): FOR MOBILE A GSM modem is one of the wireless modem that is devised to work with a GSM wireless network. It works with the same frequency of GSM wireless network. it is an important part of the GSM network Page 712 .Now a day’s GSM based cell phones are more preferred than CDMA phones, Hence let us see its operation and its features. The GSM wireless modem works in the way like a dial –up modem. The main difference between the GSM modem and dial – up modem is that a dial-up modem sends and receives data through a fixed telephone line while a GSM wireless modem sends and receives data through radio wave propagation.A GSM modem can be external device, A pc card or a PCMCIA card. A GSM modem can be connected to a computer using a serial cable or USB cable.it works similar to a GSM mobile phone, and also a GSM modem requires SIM card for operation .It can be used for internet purpose also depending on various subscriptions to the service provider. There are so many features and operations that can be perform using GSM modem. The GSM modem is specialized type of modem which accept a SIM card operate on a subscriber’s mobile number over a network, just like a cellular phone. Basically, it is a cell phone without display. Modem SIM900 is a triband GSM/GPRS engine that work on EGSM 900 MHz, DCS 1800 MHz and PCS 1900 MHz frequencies. GSM is RS232 logic level compatible. i.e. it takes -3 volt to -15 volt as logic high and +3 volt to +15 volt as logic low. MAX 232 is used to convert TTL into RS232 logic level converter used between the microcontroller and GSM board. The signal at pin 11 of the microcontroller is send to the GSM modem thorough pin 11 of MAX232. This signal is received at pin 2 (RX) of the GSM modem. The GSM modem transmit the signal from pin 3 (TX) to the microcontroller through MAX232, which is received at pin 10 of IC1. 5. Supported SIM card: 1.8v, 3v. 6. Support wide range of frequencies (from 850 MHz to 1900 MHz for different classifications of GSM networks). 7. Supports integration with RS232 cable. 8. Can be interface to system using USB cables. 9. Very less weight in few grams. 10. Provided with SIM holder and SMA antenna connecter. 11. Programmable with AT commands. 7.2 Operation that can be perform using GSM modem: 1. We can read, write and delete messages. 2. We can start sending SMS messages. 3. We can reply to SMS messages. 4. We can monitor signal strength in particular locality. 5. We can monitor the charging status and also the charge level in the battery. 6. We can read, write and search phone-book entries. 7. We can use it in various projects for different purpose. FIG GSM MODEM 7.1 Features of GSM: 1. Single supply voltage 3.2 volt-4.5 volt. 2. Typical power consumption in sleep mode 2.5mA. 3. SIM900 tri-band. 4. MT, MO, CB, text and PDU mode, SMS storage: SIM card. FIG . GSM NETWORK Page 713 8. CIRCUIT DISCRIPTION: The power supply section is the important for any electronic circuit. To derive the power supply, the 230v, 50Hz AC mains is stepped down by transformer X1 to deliver a secondary output of 12v, 500mA. The transformer output is rectified by a full wave rectifier comprising diodes D1 through D4, filter by capacitor C1 and regulated by ICs 7812 (IC2) and 7805 (IC3). Capacitor C2 by passes the ripples present in the regulated supply. LED1 act as a power indicator and R1 limit the current through LED1. The circuit diagram shows the circuit of transmission line circuitry system based on RFID and GSM technology. The compact circuitry is built around Atmel AT89C51 microcontroller. The AT89C51 is a low power, high performance CMOS 8-bit microcontroller with 8 Kb of flash programmable and erasable read only memory. It has 256 bytes of RAM, 32 input/output lines 316 bit timer/counters, a 6 vectors two level interrupt architecture, a full duplex serial port , a on chip oscillator and clock circuitry. The system clock also plays a significant role in operation of the microcontroller. An 11.0592MHz quartz crystal connected to pin 18 and 19 provides basic clock to the micro controller. Power on reset is provided by the combination of electrolytic capacitor C3 and register R1 port P2.0 through P2.7 of the microcontroller are connected to the data port pins D0 through D7 of the LCD, respectively. Port P3.7 and P3.6 of the microcontroller are connected to registers select (RS) an enabled (E) pins of the LCD, respectively. Read/write pin of the LCD is grounded to enable for write operation. All the data is send to the LCD is ASCII format for display. Only the commands are send in HEX form. Register select signal is used to distinguish between data and command. Pre-set RV1 is used to control the contrast of the LCD register 10k limit the current through backlight of the LCD. Ports pins P3.0 (RXD) and P3.1 (TXD) of the microcontroller are used to interface with the RFID reader through Max232(1) and GSM modem are used to interface through Max232(2). When a allowed person having the tag enters the RF field generated by the transmit energy to the tag and retrieve data from the tag. Then the RFID reader communicates through RXD and TXD pins of the microcontroller for further processing. Thus on identifying the authorised person, the authorised person enters the id card and sends to the microcontroller. If the id number is correct then the microcontroller displays a validation message. If the id is correct, the microcontroller provides high signal to port pin P3.2 transistor. Q2 drives into saturation and relay RL1 energize to open the substations. Simultaneously, the LCD sows the authentication. If the id number does not match or valid, the LCD shows “access denied”. FIG .Block Diagram of Transmission Line Security system 9.CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: 9.1 MAIN POWER STATION: Page 714 FIG 4.2.1 MAIN POWER STATION DIAGRAM 9.2 SUB STATION 1: FIG ZONE 2 STATION DIAGRAM Further Scope: 1. The system can be enhanced for long distance power supply. 2. The time will be reduced by updating the software of microcontroller at the power stations. 3. More sub-stations can be secured at a main power station. 4. In further the system will be used for improving the tariff structure by different consumer. FIG ZONE 1 STATION 9.3 SUB-STATION 2: References: Islam N.S. Wasi-ur-Rahman, M, 12th international conference on computers and information technology 2009. Mohd helmy Abd Wahab integrated billing system through GSM network in proceeding of 3rd international conference on robotics, vision, information and signal processing 2007. Page 715 Www.ijaiem.org Email: editor@ijaiem.org Deepak Gupta, "RFID Interface to 8051", www.electronicsmaker.com Al-Ali, A.R. Rousan, M.A. Mohandes, M. “GSM-Based Wireless Home Appliances Monitoring & Control System”, Proceedings of International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies: From Theory to Applications, pp 237-238, 2004. Page 716