small business management-challenges and road of
advertisement

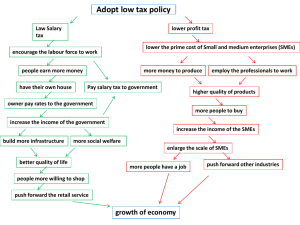
International Journal of Science Technology & Management Volume No.04, Special Issue No.02, February 2015 www.ijstm.com ISSN (Print) 2394-1529, (Online) 2394-1537 SMALL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT-CHALLENGES AND ROAD OF OPPORTUNITIES: AN INDIAN PROSPECTIVE Dr. Hotam Singh1, Mr. Rohit Kumar Singh2, Mrs. Tejasvita Singh3 1 BBA, Bareilly College, Bareilly, (India) 2 Management, Future Institute of Management Studies, (India) 3 BBA, Bareilly College, Bareilly/ Rohilkhand University (India) ABSTRACT Small Enterprises play a pivotal role in the economic and social development of the country. It alsoplays a key role in the development of the economy with its effective, efficient, flexible and innovative entrepreneurial spirit. Small Enterprises contribute nearly 8 percent of the country’s GDP, 45 percent of the manufacturing output and 40 percent of the exports. They provide the largest share of employment after agriculture. It employees 60 million people, create 1.3 million jobs every year. It produces more than 8,000 quality products for the Indian and international markets. Keywords: Economic Growth, GDP, Small business, Enterprises, performance I. INTRODUCTION Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) play a pivotal role in the economic and social development of India. The SME sector contributes in the manufacturing output, employment and exports. It plays a key role in the development of the economy with their effective, efficient, flexible and innovative entrepreneurial spirit. SME sector has emerged as a dynamic and vibrant sector of the economy. It is expected that Indian economy will grow by over 8% per annum until 2020. [2] Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) sector has emerged as a highly vibrant and dynamic sector of the Indian economy over the last five decades. SMEs not only play crucial role in providing large employment opportunities at comparatively lower capital cost than large industries but also help in industrialization of rural & backward areas, thereby, reducing regional imbalances, assuring more equitable distribution of national income and wealth. SMEs are complementary to large industries as ancillary units and this sector contributes enormously to the socio-economic development of the country.[1] The major advantage of this sector is its generating employment at low cost. The MSME sector is highly heterogeneous. There are different size of the enterprises, variety of products and services and level of technology.[9] It helps in the industrialization of rural and backward areas. It reduces regional imbalances. It provides equitable distribution of national income and wealth. Therefore there importance cannot be ignored by Thenation. [3] 11 | P a g e International Journal of Science Technology & Management Volume No.04, Special Issue No.02, February 2015 www.ijstm.com ISSN (Print) 2394-1529, (Online) 2394-1537 II. DEFINITION OF SMALL BUSINESS Micro, small and medium enterprises (MSME) are the engines of growth of any country’s economy. In accordance with the provision of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development Act 2006 the micro, smalland medium enterprises are classified into two classes.[1] [10] 2.1 Manufacturing Enterprises The Enterprises engaged in the manufacturing or production of goods pertaining to any industry specified in the first schedule to the industries (Development and Regulation Act 1951) the manufacturing enterprises are defined in the terms of investment in plant and machinery.[6] 2.2 Service Enterprises a. The enterprises engaged in providing or rendering of services and are defined in the terms of investment inequipment. b. The limit of investment in plant and machinery/equipment for manufacturing/ Service Enterprises as notified.[6][8] 12 | P a g e International Journal of Science Technology & Management Volume No.04, Special Issue No.02, February 2015 www.ijstm.com ISSN (Print) 2394-1529, (Online) 2394-1537 III. CONTRIBUTION TOWARDS ECONOMY In a country like India, the positionof SSI is quite worth mentioning. Thenumber of small scale units has beenincreasing in a comprehensive manner inrecent years, more particularly after theintroduction of economic reforms. Following tableshows the performance of Micro and SSIunits in India.The performance of the small scaleindustry sector based on final results of theThird All India Census of SSIs, 2004 isgiven in Table. It is observed from thetable that total number of SSI units hasincreased from 79.6 lakhs in 1994-95 to133.68 lakhs in 2007-08, indicating anannual average growth rate of 5.22 percent,but their production (at 1993-94 prices)increased from Rs. 1,09,116 crores in 1994-95 to Rs.5,32,979 crores in 2007-08 i.e. anannual average growth of 29.88 percent.[10] Asa consequence of the increase in SSI units,more especially in the unregistered sector,employment increased from 191.4 lakhs in1994-95 to 322.28 lakhs in 2007-08,recording an average growth rate of 5.26percent per annum. So far as exports by SSIsector are concerned, they increased fromRs. 29,068 crores in 1994-95 to Rs. 1,77,600crores in 2006-07, recording a growth rate of42.58 percent per annum. On the whole, itcan be stated that during 1994-95 to 2007-08, the SSI sector recorded an annual average growth rate of production by 29.88 percent (at constant prices), of employment by 5.26 percent and of exports by 42.58 percent.[8]This is a creditable achievement. IV. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY a) To study the need of importance of SME b) To review the challenges to be faced by SMEs in India c) To evaluate the opportunities in India V. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY a) The descriptive methodology has been used to collect data. b) Secondary data has been collected from various published sources and websites. c) The explanation of the data is more qualitative than on quantitative terms. 13 | P a g e International Journal of Science Technology & Management Volume No.04, Special Issue No.02, February 2015 www.ijstm.com ISSN (Print) 2394-1529, (Online) 2394-1537 VI. CHALLENGES FACED BY SME SMEs are very important in the economic growth of Indiabut this sector is not getting sufficient support from theconcerned government Departments, banks, financialinstitutions and corporate. This proves hurdle in the growth path of the SMEs. SMEs faces a number of problems. a) Absence of adequate and timely banking finance. b) Limited capital and knowledge, non-availability ofsuitable technology. c) Low production capacity. d) High cost of credit. e) Ineffective marketing strategy. f) Lack of skilled man power for manufacturing, services,marketing etc. g) Lack of access to global markets. h) Constraints on modernization of expansion. i) Problems of storage, designing, packing and productdisplay. j) In adequate infrastructure facilities, including power,water, roads. VII. OPPORTUNITIES IN SME 1. Less capital intensive 2. Most important employment generating sector. It provides 50% of private sector employment 3. Effective tool for promotion of balanced regional development 4. It is extensively promoted and supported by the Government 5. Finance and subsidies are provided by the government. 6. Produced goods are purchased by the Government. 7. 40% exports in India are through MSME channel. 8. Procurement of machinery and raw material. 9. Globalization has offered new opportunities for the SMEs. 10. Trade fares and exhibitions played a vital role in the economic growth of the countries. VIII. CONCLUSION The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprise SMEs are an important sector and play’s a critical role in the Indian economy. SMEs will continue to play a very important and vital role in our economy where the twin problems of unemployment and poverty constitute a major development challenge. There are several challenges in the sector of SMEs. If the Government, Bank and Financial Institutions will take proper initiatives in the sector of SME and they will take pride while servicing the SMEs, these challenges can be solved and the economic growth rate of India will be 8-10% for the next decades. REFERENCES [1]. http://msme.gov.in/Web/Portal/About-ministry.aspx#bottom [2]. K. Hallberg – Small and Medium scale enterprises [3]. Dr. Mukund Chandra MehtaChallenges and Opportunities in Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises in India 14 | P a g e International Journal of Science Technology & Management Volume No.04, Special Issue No.02, February 2015 www.ijstm.com ISSN (Print) 2394-1529, (Online) 2394-1537 [4]. http://www.deloitte.com/assets/DcomIndia/Local%20Assets/Documents/SME%20Report(1).pdf [5]. Source: Ministry of Small Scale Industries and Economic Survey, 2007-08, p. 198 [6]. Rudra Dutta and Sundaram , K.P.M.(2010), [7]. Indian Economy, SChand & Company, New Delhi [8]. Mishra S.K. and Puri, V.K.(2010),Indian Economy, Himalaya PublishingHouse, Mumbai [9]. Dhar P.K.(2011), Indian Economy,Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi. 15 | P a g e