Week 10
advertisement

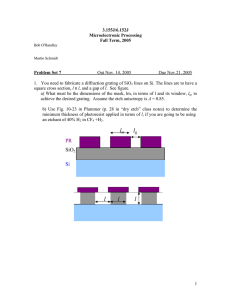
Testing and Application of various Capacitor Circuits Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Capacitive reactance Capacitive Reactance XC – Measured in ohms, it is the ability of a capacitor to oppose current flow without the dissipation of energy. XC = 1/(2πfC) f = frequency in hertz C = Capacitance in farads Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Purely resistive circuit In a purely resistive circuit, there is a 0° phase shift between current and voltage. Current is in phase with voltage. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Purely capacitive circuit In a purely capacitive circuit, there is a 90° phase shift between current and voltage. Current leads voltage by 90°. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen RC series circuit Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Vector diagram An arrangement of vectors showing the phase relationships between two or more ac quantities of the same frequency. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Voltage in an RC series circuit VS = V + V 2 R Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen 2 C Impedance in an RC series circuit Impedance (Z) – Measured in ohms, it is the total opposition a circuit offers to current flow (resistive and reactive). Z= R +X 2 Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen 2 C V I= Z V Z= I V = I×R Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Phase angle or phase shift XC θ = arctan R VC θ = arctan VR Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Power in a purely resistive circuit P =V ×I 2 V P= R 2 P = I ×R Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Power in a purely resistive circuit Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Power in a purely capacitive circuit Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Power in an RC Circuit Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Power factor Resistive Power or True Power (PR) – The average power consumed by a circuit during a complete cycle of alternating current. PR = I × R 2 Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Reactive power or imaginary power Also called wattless power, it is the power value obtained by multiplying the effective value of current by the effective value of voltage and the sine of the angular phase difference between current and voltage. PX = V × I sin θ PX = I × X C 2 Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Apparent Power The power value obtained in an ac circuit by multiplying the effective values of voltage and current, which reach their peaks at different times. PA = P + P 2 R Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen 2 X Power Factor The ratio of actual power to apparent power. A pure resistor has a power factor of 1 or 100% while a capacitor has a power factor of 0 or 0%. PF = True Apparent PF = cosθ (PR ) Power (PA ) Power R PF = Z Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Voltage in a parallel RC circuit VR = VC = VS Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Current in a parallel RC circuit VS IR = R VS IC = XC Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen IT = I + I 2 R 2 C Phase angle in a parallel RC circuit IC θ = arctan IR R θ = arctan XC Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Impedance in a parallel RC circuit VS Z= IT Z= R× XC R +X 2 Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen 2 C Power in a parallel RC circuit PR = I × R PX = I × X C 2 R 2 C PA = P + P 2 R 2 x PR PF = PX Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Testing a capacitor using an ohmmeter Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Capacitance meter An instrument used to measure the capacitance of a capacitor or a circuit. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Combining ac and dc Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Capacitive voltage divider Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen RC filters Filter – A network composed of resistors, capacitors, and inductors used to pass certain frequencies yet block others through heavy attenuation. Low-Pass Filter – A network or circuit designed to pass any frequencies below a critical or cutoff frequency and reject or heavily attenuate all frequencies above. Attenuate – To reduce in amplitude an action or a signal. High-Pass Filter – A network or circuit designed to pass any frequencies above a critical or cutoff frequency and reject or heavily attenuate all frequencies below. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Frequency response curve A graph indicating how effective a circuit or device responds to the frequency spectrum. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Low-pass filter Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen High-pass filter Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen RC Integrator Integrator – A device that approximates, and whose output is proportional to, an integral of the input signal. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen RC Differentiator Differentiator – A circuit whose output voltage is proportional to the rate of change of the input voltage. The output waveform is then the time derivative of the input waveform, and the phase of the output waveform leads that of the input by 90°. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen End of Testing and Application of various Capacitor Circuits Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen