Power Factor Correction (PFC) Parts Selection Guide
Infineon Controllers, CoolMOS™ & SiC thinQ!™ Diodes
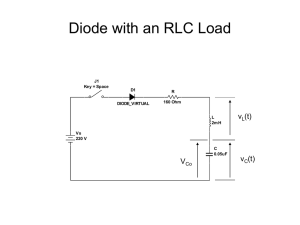
Power factor correction BASICS
What is PFC?
Difference between DCM and CCM mode PFC
Power Factor Correction is a technique of shaping the input current so that it will in-phase with the input
DCM
voltage in an AC circuit. The purpose of it is to minimize the unwanted effects (harmonic distortion)
1) Highest efficiency (not ON through full cycle limits conduction losses)
introduced by electronic equipments in the power system and utilizing the usable power in the mains.
2) Triangular waveform causes EMI due to di/dt changes. (also high ripple)
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
2)
1)
2)
Choke Current
Vin
Iin
Choke Current
3) Normally below 300W. (EMI is costly to get rid of above 300W topologies).
Passive and active PFC explained
time
AC input current is lagging with respect to AC
input voltage hence both current and voltage
are not purely in-phase.
AC input current is almost perfectly in-phase with
AC input voltage.
MOSFET VDS
Active PFC
MOSFET VDS
Passive PFC
time
PFC Simulation*
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin
Iin
Vin V
in
Iin Iin
Vin
Iin
CCM
1) Fast turn on needed, requires fast PFC diode. Good fit for SiC Diode.
2) Trapezoidal current waveform with low ripple (lower di/dt so EMI easier to get rid of)
Passive PFC
Typical input current with
Typical input current without
passive
harmonic line current
1)
Harmonic line current reduction
2)
reduction
Pros:
–– Simple and rugged circuitry
–– Cheaper than active PFC
Cons:
–– Not able to effectively
eliminate line current
harmonics
–– Bulky and heavy magnetics
required
* Source: EPSMA, Harmonic Current
–
–
Not possible for universal
Emissions. Guideluines to the
input range
standard EN 61000-3-2, Nov. 2010
MOSFET VDS
Choke Current
Active PFC
Typical input current with
active harmonic
line current reduction
Pros:
time
–– Extensive suppression
of
line current harmonics
–– Can comply with regulatory
requirements such as
IEC 61000-3-2 (Limits for
harmonic current emissions)
–– Able to operate in universal
time
input range
Cons:
–– Complex and costly circuitry
2)
time
MOSFET VDS
No PFC
Choke Current
3) Normally 300W and above
time
Power Factor Correction (PFC) Selection Guide
Active Power Factor Correction
Discontinous Conduction Mode (DCM) or Continous Conduction Mode (CCM)
DCM
CCM
PFC Topologies
Standard
Interleaved
Standard
Interleaved
Dual Boost (bridgeless)
CoolMOS™, SiC thinQ!™ Diodes & Controllers
CoolMOS™ P6 series
CoolMOS™ C7 or P6 series
SiC thinQ!™ Generation 5 Diodes
CCM PFC Controller
ICExPCxx
DCM PFC Controller
TDA48xx
Applications
Telecom
Server
All in One PC (AIO)
PC Silverbox/AIO
LCD TV/Adapter
Notebook/Adapter
C5 C8 Compact Lamp
HID
Order Number: B152-H9804-X-X-7600-DB2012-0013
Date: 04/2013
Lighting HID
All rights reserved. © 2013 Infineon Technologies AG
Topologies
TDA486xx
TDA486xx
TDA486xx
ICE3PCSxx
TDA486xx
CoolMOS™
AC
CoolMOS™
AC
AC
CoolMOS™
AC
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
AC
CoolMOS™
AC
AC
CoolMOS™
CoolMOS™
AC
CoolMOS™
CoolMOS™
SiC Diode
ICE3PCSxx
ICE3PCSxx
ICE3PCSxx
Standard DCM PFC
Standard CCM PFC
Used in cost performance applications up to 300W,Controller, CoolMOS™ but no SiC thinQ!™ Diode
Used in applications above 300W Controller, CoolMOS™ & SiC thinQ!™ Diode used
SiC Diode
SiCDiode
Diode
SiC
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
400V400V
400V
L1 L1
L1
L2 L2
CoolMOS™
L2
L2
CoolMOS™
400V
L1
CoolMOS™
ACAC
CoolMOS™
400V
400V
CoolMOS™
AC
AC
CoolMOS™
400V
400V
SiC Diode
SiCDiode
Diode
SiC
CoolMOS™
SiC Diode
CoolMOS™
CoolMOS™
AC
AC
L2
L2
SiC Diode
CoolMOS™
CoolMOS™
AC
AC
CoolMOS™
CoolMOS™
L2
SiC Diode
L1
L1
CoolMOS™
CoolMOS™
L1
L1
L2
SiC Diode
SiC Diode
Interleaved CCM PFC
Dual boost (Bridgeless)
Higher power applications 2 CoolMOS™ and 2 SiC thinQ!™ Diode used
Used in critical efficiency applications. Removes losses from input bridge rectifier diodes
Can save around 1.5% efficiency
Infineon Parts (CoolMOS™ & thinQ!™)
CoolMOS™ P6 600V
RDS(on)
[mΩ]
600
380
280
230/255
190/210
160/180
125
99
70
41
ThinPAK
8x8
TO-252
DPAK
IPD60R600P61)
IPD60R380P62)
225/230
190/195
125/130
95/99
65/70
45
19
TO-220
FullPAK
TO-247
IPA60R600P61)
IPA60R380P62)
IPA60R280P62)
IPA60R230P62)
IPA60R190P61)
IPA60R160P62)
IPA60R125P62)
IPA60R099P62)
IPW60R280P62)
IPW60R230P62)
IPW60R190P61)
IPW60R160P62)
IPW60R125P62)
IPW60R099P62)
IPW60R070P62)
IPW60R041P62)
New!
ThinPAK
8x8
IPL65R230C7
IPL65R195C72)
IPL65R130C7
IPL65R099C72)
IPL65R070C72)
TO-220
IPP60R600P61)
IPP60R380P62)
IPP60R280P62)
IPP60R230P62)
IPP60R190P61)
IPP60R160P62)
IPP60R125P62)
IPP60R099P62)
IPL60R255P62)
IPL60R210P62)
IPL60R180P62)
CoolMOS™ C7 650V
RDS(on)
[mΩ]
New!
TO-252
DPAK
IPD65R225C7
IPD65R190C72)
TO-263
D2PAK
IPB65R225C7
IPB65R190C72)
IPB65R125C72)
IPB65R095C72)
IPB65R065C72)
IPB65R045C7
TO-220
TO-220
FullPAK
IPP65R225C7
IPP65R190C72)
IPP65R125C72)
IPP65R095C72)
IPP65R065C72)
IPP65R045C7
TO-247
IPW65R190C72)
IPW65R125C72)
IPW65R095C72)
2)
IPW65R065C7
1.3
IPW65R045C7
1.2
1.1
IPW65R019C7
IPA65R125C7 3)
IPA65R095C7 3)
IPA65R065C7 3)
IPA65R045C7 3)
Samples available by Q2/2013
2)
Samples available by Q3/2013
3)
Samples available by Q4/2013
Difference [%]
1)
900W CCM PFC PSU
Silicon Carbide Diode (SiC) thinQ!™ Gen 5
650V
TO-220 R2L
TO-247 New!
D2PAK R2L New!
ThinPAK 8x8 New!
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
0
100
TO-247-4
IPZ65R095C72)
IPZ65R065C72)
IPZ65R045C7
IPZ65R019C7
Efficiency Difference High Line
200
300
Efficiency difference shown between CP/G2 SiC Diode & C7/G5 SiC Diode
IDW10G65C5
IDW12G65C5
IDW16G65C5
IDW20G65C5
IDW30G65C5
IDW40G65C5
IDL04G65C5
IDL06G65C5
IDL08G65C5
IDL10G65C5
IDL12G65C5
1.3
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
CP/Gen2
C7/Gen5
Difference [%]
IDL02G65C5
Difference [%]
IDK02G65C5
IDK03G65C5
IDK04G65C5
IDK05G65C5
IDK06G65C5
IDK08G65C5
IDK09G65C5
IDK10G65C5
IDK12G65C5
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
Efficiency Difference Low Line
1.6
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1000
1.6
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
600
700
800
900
1000
CP/Gen2
C7/Gen5
0
100
200
300
400
500
Pout [W]
Pout [W]
]
IDH02G65C5
IDH03G65C5
IDH04G65C5
IDH05G65C5
IDH06G65C5
IDH08G65C5
IDH09G65C5
IDH10G65C5
IDH12G65C5
IDH16G65C5
IDH20G65C5
500
Pout [W]
Efficiency Difference Low Line
Efficiency Difference High Line
2A
3A
4A
5A
6A
8A
9A
10A
12A
16A
20A
30A
40A
400
CP/Gen2
C7/Gen5
CP/Gen2
C7/Gen5
600
700
800
900
1000
Infineon Parts (Controllers)
2nd Generation Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
Power Factor Correction IC Features
TDA4862
Power Factor Controller (PFC) IC for high-power factor and active harmonic filter
IC for sinusoidal line-current consumption
Power factor approaching 1
Controls boost converter as an active harmonics filter
Internal start-up with low current consumption
Zero current detector for discontinuous operation mode
High current totem pole gate driver
Trimmed ±1.4% internal reference
Undervoltage lock out with hysteresis
Very low start-up current consumption
Pin compatible with world standard
Output overvoltage protection
Current sense input with internal low pass filter
Totem pole output with active shutdown during UVLO
Junction temperature range -40 to +150°C
Available in DIP-8 and SO-8 packages
TDA4863 / TDA4863-2
Power Factor Controller IC for high-power factor and low THD additional features to TDA4862
Reduced tolerance of signal levels
Improved light load behavior
Open loop protection
Current sense input with leading edge blanking LEB
Undervoltage protection
Discontinuous Continuous Conduction Mode (DCM) Power Factor Correction IC Portfolio
Product
TDA4862
TDA4863 / TDA4863-2
Package
DIP-8 and SO-8
DIP-8 and SO-8
Fulfills Class D Requirements of IEC 61000-3-2
Lowest count of external components
Adjustable and fixed sw frequencies
Frequency range from 20kHz to 285kHZ
Versions with brown-out protection
available
Wide input range supported
Enanched Dynamic Response during
load jump
Cycle by Cycle Peak Current Limiting
Integrated protections OVP, OCP
DIP8 and DSO8
Leadfree, RoHS compliant
2nd Generation Continous Conduction Mode (CCM) Power Factor Correction IC Portfolio
Product
ICE2PCS01
ICE2PCS02
ICE2PCS03
ICE2PCS04
ICE2PCS05
ICE2PCS01G
ICE2PCS02G
ICE2PCS03G
ICE2PCS04G
ICE2PCS05G
Frequency (SW)
50kHZ - 285kHZ
65 kHZ
100 kHz
133 kHz
20 kHz - 250 kHz
50kHZ - 285kHZ
65 kHZ
100 kHz
133 kHz
20 kHz - 250 kHz
Current Drives
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
2.0 A
Package
DIP-8
DS0-8
3rd Generation Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
Power Factor Correction IC Features
Fulfills Class D Requirements of
IEC 61000-3-2
Integrated digital voltage loop compensation
Boost follower function
Bulk voltage monitoring signals, brown-out
Multi protections such as Double OVP
Fast output dynamic response during
load jump
External synchronization
Extra low peak current limitation threshold
SO8 and SO14
Leadfree, RoHS compliant
3rd Generation Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) Power Factor Correction IC Portfolio
Product
ICE3PCS01G
ICE3PCS02G
ICE3PCS03G
Frequency
Adjustable
Current Drives
0.75A
0.75A
0.75A
Features
OVP+Brown-out
OVP
Brown-out
Package
DSO-14
DSO-8
DSO-8