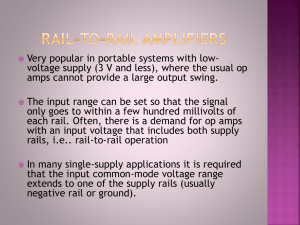
Wire Chart: Cable Size, Voltage Drop, & Ampacity
advertisement

Wire Wire WIRE CHART 12 Vol t acceptable cable size (mm²) Amps 0.5 1 1.5 2 3 4 5 7.5 10 15 20 25 30 40 60 80 100 125 1 0.4 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 25.7 32.2 49.2 2 0.4 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 25.7 32.2 49.2 Cabl e Length (metres) 5 10 15 20 25 0.4 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 1.84 2.9 4.6 7.9 7.9 1.84 4.6 4.6 7.9 7.9 2.9 4.6 7.9 13.6 13.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 13.6 13.6 4.6 13.6 25.7 25.7 25.7 7.9 13.6 25.7 25.7 32.2 7.9 25.7 25.7 32.2 49.2 13.6 25.7 32.2 49.2 49.2 13.6 25.7 49.2 49.2 25.7 49.2 25.7 49.2 32.2 49.2 30 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 7.9 7.9 13.6 25.7 25.7 32.2 49.2 49.2 1 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 25.7 32.2 49.2 2 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 25.7 32.2 49.2 All the methods ofdeterminingvoltage drop on this page are for DC only. AC electricitybehaves quite differently. M etriccables are specifiedbythe copper area (in square millimetres),the number ofstrands ofwire and the number ofconductors or cores in each sheath. The voltage drop is the same regardless ofvoltage,assuming that amps,distance and cross sectional areas are the same. Ifthe wattage remains the same for different voltages,the amps can be calculatedbydividingwatts byvolts. TheFormul a Ifyou needto calculate the voltage drop under a given set ofcircumstances,there is a formula bywhich it can be determined. Let: A = cross sectional area ofcable in (mm² ) L = route length in metres I= current measuredin amps R = resistance ofcable ( ) aluminium = 0.028 resistance ofcopper = 0.017 steel = 0.18 Example: You have a power point connectedto a power source. The route length is 8 metres. Ifthe wire is 4.6 mm² multi-strandedcopper cable andthe expectedcurrent is expectedto be 10amps,we have: acceptable cable size (mm²) Amps 1 2 3 4 5 7.5 10 15 20 25 30 40 60 80 100 125 Copper Conductor Voltage Drop = 2x L x Ix R ÷A 24 Vol t Cabl e Length (metres) 5 10 15 20 25 0.4 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 1.84 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 7.9 1.84 4.6 4.6 7.9 7.9 2.9 4.6 7.9 13.6 13.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 13.6 25.7 4.6 7.9 13.6 25.7 25.7 4.6 13.6 25.7 25.7 25.7 7.9 13.6 25.7 25.7 32.3 13.6 25.7 32.2 49.2 49.2 25.7 25.7 49.2 49.2 32.2 32.2 49.2 49.2 49.2 Pl asti c Insul ati on Wh at: Low voltage power systems often operate at rather high current levels. Ifthe interconnectingcables are too small, a large proportion ofthe power available will be wastedin the cable itself. This loss can be reducedbyusinga larger cable,but this increases costs. The acceptable maximum voltage drop for DC loads is 5% of nominal battery voltage. The chart and the formula on this page are providedto help you in selectingthe best cost /power loss compromise. A =5 30 1.84 1.84 2.9 4.6 4.6 7.9 13.6 25.7 25.7 25.7 32.2 49.2 NOTE: The Cable Length in the above tables are route length which is halfthe total conductor length. Ifthe positive and negative leads are different lengths an average must be taken. L =9 I= 10 R = 0.017 Voltage drop can then be calculatedto be 0.58volts. If this figure is consideredto be acceptable it wouldavoid spendingmore moneyon larger wire. mm² per metre 30 m rol l ampaci ty 1.84 twi n sheathed W IR-M02 W IR-302 15 amps 2.9 twi n sheathed W IR-M03 W IR-303 20 amps 4.6 twi n sheathed W IR-M05 W IR-305 25 amps 7.9 si ngl e (bl ackor red) W IR-M08 W IR-308 45 amps 13.6 si ngl e (bl ackor red) W IR-M14 W IR-314 70 amps 25.7 si ngl e (bl ackor red) W IR-M25 W IR-325 90 amps 32. si ngl e (bl ackor red) W IR-M32 W IR-332 110 amps 49 si ngl e (bl ackor red) W IR-M49 W IR-349 150 amps or extra low voltage NOTE: The above cables are ratedf 133