FARADAY`S LAW OF ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION In 1831
advertisement

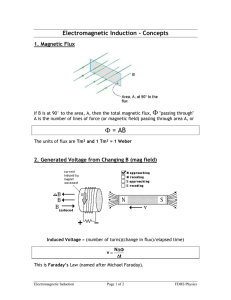
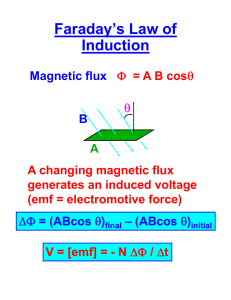
Université Kasdi Merbah Ouargla 3ème année LMD : Contrôle et Automatique, télécommunication Module : Anglais FARADAY’S LAW OF ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION In 1831, where pursuing his experiment, Joseph faraday made one of the most important discoveries in electromagnetism, know is known as faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, It revealed a fundamental relationship between the voltage and flux in a circuit. Faraday’s law states that: 1-If the flux linking a loop (or turn) varies as function of time; a voltage is induced between its terminals. 2-The value of the induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux. By definition, and according to the system of units, when the flux inside a loop varies at rate of 1 Weber per second, a voltage of 1V is induced between its terminals, consequently, if a flux varies inside a coil of N turns, the voltage induced is given by: faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction opens the door to a host of practical applications and establishes the basis of operation of transformers, generators and alternating current motors. In many motors and generators, the coils move with respect to a constant flux. The relative motion produces a change in the flux linking the coils and consequently, a voltage is induced, according to faraday’s 1aw. However, in this special case, it is easier to calculate the induced voltage with reference to a conductor, rather than with reference the coil itself. In effect, whenever a conductor “cuts” a magnetic field voltage is induced across its terminals. The value the induced voltage is given by: VOLTAGE INDUCED IN A RECTANGULAR CONDUCTOR Following the discovery of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction’ scientists and technicians of the 19th century did not wait long to invent and build all kinds of mechanical machines to generate electricity. The operating principal of these machines is always based upon the relative motion of a rectangular coil with respect to a magnetic. Consider a permanent magnet SN revolving at constant speed inside a stationary iron ring. The ring reduces the reluctance of the magnetic circuit; consequently, the flux density in the air gap is greater than if the ring were absent. A rectangular conductor ABCD is mounted inside the ring, but insulated from it. Année universitaire 2014/2015