VJ DAY - The National WWII Museum
advertisement

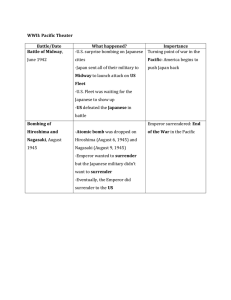
Remembering V-J DAY The Allied celebrations on Victory in Europe Day (V-E Day), on May 8, 1945, were subdued by the knowledge that war raged on in the Pacific. As the fighting ended in Europe, US troops were drawing a noose around the Japanese home islands. But there were ominous signs that Japan’s fierce resistance would continue. The battles for Iwo Jima and Okinawa during the first half of 1945 were marked by spectacular carnage, and Americans were chastened by the knowledge that Japan had never surrendered to a foreign power and that no Japanese military unit had surrendered during World War II. After Okinawa fell to US forces on June 22, 1945, an invasion of the Japanese home islands was set to begin. But instead, the most destructive war in history came to a shattering and rapid end. On August 6, the US dropped the first atomic bomb over Hiroshima, killing as many as 140,000 people. Two days later, the Soviet Union declared war on Japan. Then, on August 9, the US dropped a second atomic bomb over Nagasaki, killing approximately 70,000. Overcoming internal debates, the Japanese government accepted Allied surrender terms without qualifications on August 14, 1945. That same day, President Harry Truman announced from the White House that the Japanese acceptance met the terms laid down at the Potsdam Conference for unconditional surrender. Victory over Japan Day (V-J Day) would officially be celebrated on the day formal surrender documents were signed aboard the USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay: September 2, 1945. But as soon as the news of Japan’s surrender was announced, celebrations erupted across the United States. The United Kingdom announced that its official V-J Day would be the next day, August 15, 1945, and Americans exuberantly joined in that day’s merriment. In New York City’s Times Square, sailors climbed lampposts to unfurl American flags as ticker tape rained down upon the throngs gathered to celebrate the war’s end. In thousands of small towns like North Platte, Nebraska, similar scenes included fireworks, confetti, and impromptu parades down Main Street. In San Francisco, parades celebrated that troops would soon return home through that city. In Honolulu, marching bands, parades, ticker tape, and blowing papers filled the streets. In backyard celebrations, shirtless veterans drank celebratory toasts in the warm sunlight. Veterans and their girlfriends also crowded into and on top of trucks and cars (some even riding on fenders), waved flags, and excitedly drove through the city, relishing the moment Americans had hoped for since the attack on Pearl Harbor. But as welcome as victory over Japan was, the day was bittersweet in light of the war’s destructiveness. More than 400,000 Americans – and an estimated 60 million people worldwide – had died in the conflict. As historian Donald L. Miller, PhD, wrote in his book The Story of WWII, “It was too much death to contemplate, too much savagery and suffering; and in August 1945 no one was counting. For those who had seen the face of battle and been in the camps and under the bombs – and had lived – there was a sense of immense relief.” The war was over. The National WWII Museum remembers V-J Day: September 2, 1945. The National WWII Museum 945 Magazine Street New Orleans, LA 70130 www.nationalww2museum.org