Troubleshooting Guide PVC Extrusion of rigid PVC pipes
advertisement
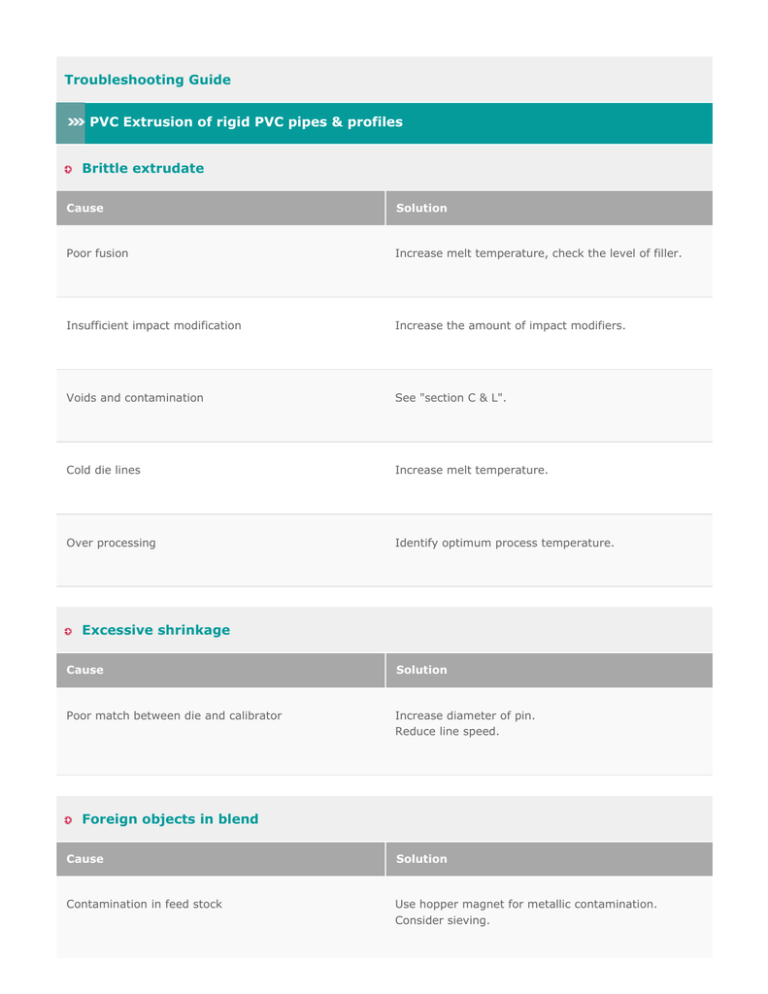
Troubleshooting Guide PVC Extrusion of rigid PVC pipes & profiles Brittle extrudate Cause Solution Poor fusion Increase melt temperature, check the level of filler. Insufficient impact modification Increase the amount of impact modifiers. Voids and contamination See "section C & L". Cold die lines Increase melt temperature. Over processing Identify optimum process temperature. Excessive shrinkage Cause Solution Poor match between die and calibrator Increase diameter of pin. Reduce line speed. Foreign objects in blend Cause Solution Contamination in feed stock Use hopper magnet for metallic contamination. Consider sieving. Poor acetone or methylene chloride test Cause Solution Material too cold and not fully fused Barrel and screw temperatures too low. Increase melt temperature. Formulation may be over-lubricated Decrease external lubricant. Add or increase process aid to promote fusion. Wavy or lumpy internal surface Cause Solution Wavy or lumpy internal surface is indicative of different thermal or shearing histories in the melt The screw and barrel in the metering zone should be about the same temperature. A little higher heat in both will help smooth out the internal surface. Low gloss Cause Solution Over lubrication Reduce internal lubrication. Melt too cold Increase process temperature. Poor gelation Increase process aid level. Not fully sized Increase vacuum or increase air pressure on plug to insure fully contact with sizing sleeve. Possible inaccuracy in the mix blend Check the mix room scales for accuracy. Rough (orange peel) internal surface or outer surface leading to burn Cause Solution Over heating Reduce spider and cone heat zones. Lower melt temperature. Formulations may be under lubricated Check formulation. Increase lubrication. Uniform yellowing or discoloration of material Cause Solution Level of stabilizer too low Check level and adjust formulation if required. Melt temperature excessive Lower overall melt temperature. Incorrect lubrication Increase lubrication. Rear barrel too hot Reduce rear barrel temperature. Visible spider lines on internal diameter Cause Solution Spider and die heating zone may be too cold Check operating temperatures. Material may be over lubricated Adjust lubrication. Non-uniform outer diameter Cause Solution Sizing sleeve may have build-up / plate out of pigments, lubricants etc Mineral spirits added drop-wise on hot melt just as it enters vacuum sizing sleeve usually will remove most of the plateout. Otherwise line should be stopped and cleaned up. On large pipe, die and head may not be uniformly heated at the start of the run or heaters may be hunting for set temperatures, controllers It will take several hours to heat soak the large mass of metal. Allow adequate time to heat up properly. Also check heater bands and thermocouple and PID controllers. Pipe not round Cause Solution Insufficient sizing Check for full sizing for pressure or sufficient vacuum. Cooling water not cold enough Use a chiller for increase cooling. The haul off may be applying excessive pressure Lower the haul off pressure. Inefficient cooling On large pipes cascade or spray cooling is more efficient than flooded tank. Worn out plug If this problem continues after a long run, replace plug to insure no loss of air pressure for sizing. Bubbles/voids Cause Solution Degradation Check barrel, screw, and die temperature control. Use screw cooling. Reduce melt temperature. Moisture or trapped air Check material is not gelled at vent, check vacuum pump if not blocked. Internal diameter exhibits occasional tearing Cause Solution Plug too close to die pulling material apart before it is cooled sufficiently Use longer chain – at last 75% of the cooling tank length. Bridging in the throat section / non-uniform powder flow to the screw Cause Solution Poor flow at the hopper throat Turn the cooling water on at the throat section. Use a crammer in the hopper. Install a vibrator to encourage powder flow. High amps / overloading Cause Solution Material too cold Increase barrel temperature. Check barrel thermocouples for accuracy. Under lubrication Increase external lubricant. Over feeding Increase main screw speed or reduce feeder speed. Check die is appropriate for the extruder. Thin wall pipe in vacuum sizing collapsing, or jamming up, or drawing down too thin Cause Solution Extrudate unstable entering into vacuum tank Decrease the distance. Two to three inches between the die and the tank should be sufficient. Melt too hot Reduce die temperature. Pulling friction too high. Lower the vacuum. Non-uniform wall thickness around the pipe circumference Cause Solution Thick thin wall opposite each other Bushing is not centered. Adjust die bolts for even flow out of die. Thick thin opposite each other Use segmented die heaters to adjust flow. Increasing or decreasing wall thickness Cause Solution Feed stock inconsistencies between batches or mixes Adjust puller speed. Monitor feedstock consistency. Bridging at the hopper See section "high amps / overloading". Surging Cause Solution Partial plugging of screw channel with solids du to excessive fillers i.e. not enough polymer to allow fluxing Raise process temperatures, adjust formulation. Inconsistent feed rate Check the feeding system.