1st year

Sanju 9681634157 1
Transistor Biasing
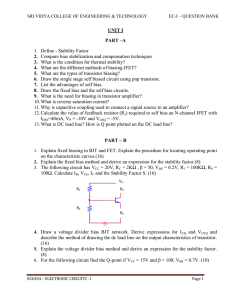
A transistor is used as an amplifier. For faithful amplification, the following three conditions must be satisfied. i)The emitter base junction should be forward bias. ii)The collector base junction should be reverse bias. iii)There should be proper zero signal collector current.(Proper operating point)
The proper flow of zero signal collector current and maintenance of proper collector emitter voltage during the passage of signal is known as transistor biasing.
The biasing is achieved with a bias battery or associating a biasing circuit with a transistor, with a biasing circuit.
Requirement of a biasing ckt:- Following are the requirements of proper biasing a circuit. i.
Proper selection of Q point, such that on the application of the input signal, the Q point should not move either to the saturation region or to the cut-off region. ii.
To stabilize the collector current against the temperature variation. iii.
To make the operating point independent of transistor parameters (i.e. The transistor is replaced by another transistor of same kind, the operating point should not change.
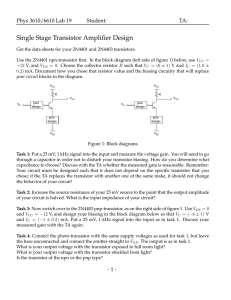
For the following circuit of S i
transistor find (1) Maximum collector current that can be allowed during the application of signal for faithful amplification. (2) Minimum zero signal collector current.(given knee voltage=1V)
Knee voltage for silicon transistor = 1V.
.
voltage drop at R
.
c
should be less than 6-1=5V.
. Maximum allowed I
C
=
5
2.5
= 2mA
The minimum collector current with signal should not be less than zero.
As –ve and +ve half cycles of the signals are equal,
Minimum zero signal collector current =
2𝑚𝐴
2
= 1𝑚𝐴
Sanju 9681634157 2
Stability of Biasing :- After selecting the d.c. operating point at the desired location, one must consider its stability.
I
The operating point can change due to the instability of collector current I
C
. Since I
C
= 𝛽
B
(=
𝑉
𝐵𝐵
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
𝑅𝐵
) + (1+𝛽) I
CO
, there are three sources of instability of I
C
.
i) Reverse saturation current I
CO
ii) Current amplification actor 𝛽
iii) Base emitter voltage V
BE
.
The stability factors S, S,’ S” measures the change of the collector current I
C
with respect to I
CO
, V
BE
respectively as follow,
S =
𝜕𝐼
𝐶
𝜕𝐼
𝐶𝑂 V
BE ,𝛽
S’ =
𝜕𝐼
𝐶
𝜕V
BE , I co
S” =
𝜕𝐼
𝜕β
𝐶
I co
,β
,V
BE ,
Here we only discuss about S , i.e. stability against I co .
Thermal Runway:- The collector current for a CE configuration is given by I
C
= 𝛽I
B
+
(1+ 𝛽) I
CO
. An increase of temperature enhances I
CO
. Hence collector current I
C
also increases. The increment of I
C
heats more the collector junction which is term increases
I
CO
further. This process is cumulative in nature, causing the junction temperature to exceed its rated value. The transistor thus can be damaged. This known as Thermal runway.
Methods of transistor biasing :- The following are the most commonly used methods of obtaining transistor biasing. i) Base resistor method or fixed bias. ii) Biasing with feedback resistor or collector base bias. iii)Self bias or voltage- divider Bias method.
Sanju 9681634157 3
Fixed – Bias:- The fig shows the fixed – bias arrangement for an n-p-n transistor operating in CE mode.
Circuit analysis:- It is required to find out I
C
.
In terms of circuit parameters,
I
B
=
𝑉
𝐶𝐶
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
𝑅𝐵
.
.
. I
C
= 𝛽 I
B
+ (1+𝛽) I
CO
= 𝛽
𝑉
𝐶𝐶
−𝑉
𝑅𝐵
𝐵𝐸 + (1+𝛽) I
CO
Now stability factors,
S =
S’ =
𝜕𝐼
𝐶
𝜕𝐼
𝐶𝑂
𝜕𝐼
𝐶
𝜕𝛽
1+ 𝛽
= +
𝑉
𝐶𝐶
𝑅𝐵
S” =
𝜕𝐼𝑐
𝜕𝑉
𝐵𝐸
= − 𝛽
𝑅
𝐵
+ I
CO
Advantages:- i.
Biasing circuit is very simple . ii.
Biasing condition can easily be set.
Disadvantages:-
Stability against I
CO
is very poor since (1+𝛽) is a very high quantity.
Collector to base bias:- A resistance is connected between the base and the collector of the transistor.
Analysis:-Applying KVL to the circuit,
V
CC
= (I
C
+ I
B
)𝑅
𝐿
+ I
B
𝑅
𝐵
+ 𝑉
𝐵𝐸
.
.
. I
B
=
𝑉
𝐶𝐶
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
− 𝐼
𝐶
𝑅
𝐿
𝑅
𝐵
+𝑅
𝐿
Now I
C
= 𝛽 I
B
+ (1+𝛽) I
CO
.
.
. I
C
= 𝛽(𝑉
𝐶𝐶
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
− 𝐼
𝐶
𝑅
𝐿
𝑅
𝐵
+𝑅
𝐿
)
+ (1+𝛽) I
CO
Or, I
C
(1 + 𝛽𝑅𝐿
𝑅
𝐵
+𝑅
𝐿
) = 𝛽
𝑉
𝐶𝐶
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
𝑅
𝐵
+𝑅
𝐿
+ (1 + 𝛽)𝐼
𝐶𝑂
Or, AI
C
= 𝐵𝛽 + (1 + 𝛽)𝐼
𝐶𝑂
.
.
. I
C
=
𝐵
𝐴
𝛽 +
1+𝛽
𝐴
I
CO
Stability factor,
S =
𝜕𝐼
𝐶
𝜕𝐼
𝐶𝑂
=
1+𝛽
𝐴
=
1+𝛽
1 + 𝛽𝑅𝐿
𝑅𝐵+𝑅𝐿
Advantages:-
Sanju 9681634157 4 i.
Till a simple method and only once resistor to choose. ii.
This circuit provides some stability as discussed below,
When I
C
tends to increase by any mean, the voltage V
CE
decreases due greater drop across R
C
(as V
CC
= I
C
R
C
+ V
CE
). Hence lesser voltage available at collctor .
Consequently base current I
B
decreases which in term tends to decrease the collector current to its original value.
Disadvantages:- i.
The circuit does not provide good stabilization, as stability factor is still very high operating point may shift. ii.
Here the resistance provides a dc feedback as well as a.c. signal as the feedback from output (collector) terminal to input (base) signal. This reduces the voltage gain of the amplifier.
Voltage Divider Bias or Self Bias:- The self-bias or voltage-divider bias ckt is shown in the fig. Forward bias of the emitter-base junction and reverse bias of the collector-base junction are provided by the supply voltage V
CC
through the resistances
R
1
,R
2
,R
E
, and R
L
.
Analysis:- Applying Thevenin’s theorem to the left of the circuit we have,
𝑉
𝑇ℎ
𝑅
𝑇ℎ
=
=
𝑅
1
𝑅
1
+𝑅
2
𝑅
2
𝑅
1
𝑅
2
+𝑅
2
v cc
Sanju 9681634157 5
As R
1
,R
2
serve as a voltage divider, the arrangement is referred as voltage divider bias.
The resulting simplified fig is shown below.
According to this fig,
𝐼
𝐵
𝑅
𝑇𝐻
+ 𝑉
𝐵𝐸
+ (𝐼
𝐵
+ 𝐼 𝑐
) 𝑅
𝐸
𝐼
𝐵
(𝑅
𝑇𝐻
+ 𝑅
.
.
. I
B
=
𝑉
𝑇ℎ
𝐸
) = 𝑉
−𝑉
𝑅
𝑇ℎ
𝐵𝐸
−𝐼
𝐶
+𝑅
𝐸
𝑇𝐻
𝑅
𝐸
– 𝑉
𝐵𝐸
Now 𝐼
𝐶
= 𝛽I
B
+ (1+𝛽) 𝐼
𝐶𝑂
= 𝑉
𝑇𝐻
− 𝐼 𝑐
𝑅
𝐸
.
.
. 𝐼
𝐶
= 𝛽
𝑉
𝑇ℎ
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
𝑅
𝑇ℎ
−𝐼
𝐶
+𝑅
𝐸
𝑅
𝐸 + (1+𝛽) 𝐼
𝐶𝑂
Or, 𝐼
𝐶
(1 +
𝑅
𝑇 𝛽𝑅
𝐸
+𝑅
𝐸
(1+𝛽) 𝐼
𝐶𝑂
) = 𝛽
𝑉
𝑇ℎ
𝑅
𝑇ℎ
−𝑉
𝐵𝐸
+𝑅
𝐸
+
Or, AI
C
= 𝐵𝛽 + (1+𝛽) 𝐼
𝐶𝑂
Or, I
C
=
𝐵
𝐴
𝛽 +
1+𝛽
A
𝐼
𝐶𝑂
Stability factors, S =
𝜕𝐼
𝐶
𝜕𝐼
𝐶𝑂
=
1+𝛽
A
=
1+𝛽
1 + 𝛽𝑅 𝐸
𝑅Th +𝑅𝐸
Advantages:-
I.
For 𝑅
Th
<< R
E against I
CO
, 𝑅
Th
, the stability factor S tends to unity i.e. for stability
must be less than R
E
.
The physical reason for improvement in the stability of the operating point in the circuit is as follows
Sanju 9681634157 6
If the collector current I
C
tends to increase because I
CO
has increased due to rise in temperature, the current in the resistance R
E
increased. The consequent rise of the voltage drops across R
E
decreases the forward bias of the emitter junction. As a result I
B is lowered and hence I
C reduces back to the initial value.
Further when self bias circuit is used to amplify ac signals, ac voltage drop appears across R
E
. This gives a –ve feedback and reduces gain. Hence a capacitor C
E having a small resistance at the signal frequency is connected parallel with
R
E
. The ac signal is thus effectively by pass through C
E
; which is known as by pass capacitor.