AC Potentiometers
advertisement

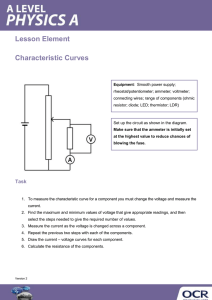
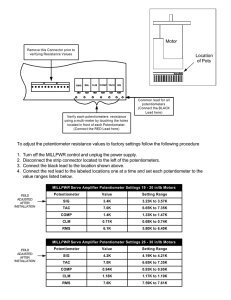
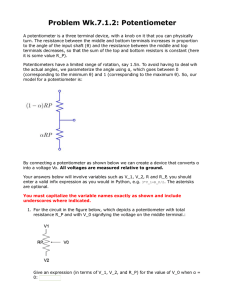
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & MEASURING INSTRUMENTS Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Droncacharya College of Engineering, Gr. Noida UNIT 4 Part (i) AC Potentiometers Polar type & Co-ordinate type AC potentiometers Potentiometers is an instrument used to measure voltage by using differentiates method with one of standard value. The measurement has made with adjusting of contactor until the zero reading has been recorded. This condition we called as balance condition due to depletion voltage is same as standard voltage that provided on slide wire. SLIDE WIRE POTENTIOMETER It uses the depletion voltage concept on conductor wire which is proportional directly with long of conductor wire that used. The maximum depletion voltage on entire of conductor wire is equal to supply voltage that used. PRINCIPLE It must be calibrated with one of standard value. In the calibration process, when the switch is closed circuit, the working current will flow through a slide wire potentiometer (namely as conductor wire) and rheostat. The value of this current can be modifying by adjusting the rheostat. ADVANTAGES OF POTENTIOMETER To measure the voltages by differentiate with standard value. To measure resistance by differentiate with standard resistor. To measure the current by measuring voltage to the unknown resistor value. To calibrate volt meter. To calibrate ampere meter. A.C. POTENTIOMETER Its principle is same as a d.c. potentiometer. One very important difference between the two. In d.c. potentiometer, only the magnitudes of the unknown e.m.f. and slide-wire voltage drop are made equal for obtaining balance. But in an a.c. potentiometer, not only the magnitudes but phases as well have to be equal for obtaining balance. To avoid frequency and waveform errors, the a.c. supply for slide-wire must be taken from same source as the voltage or current to be measured. Types Two Types Polar potentiometers in which the unknown voltage is measured in polar form i.e. in terms of magnitude and relative phase. Co-ordinate potentiometers which measure the rectangular co-ordinates of the voltage under test. DRYSDALE POLAR TYPE AC POTENTIOMETER It is basic d.c. potentiometers along with some auxillary components such as, drysdale phase shifter and electrodynamometer type ammeter. When the current flows through stator winding, a rotating field is produced inducing e.m.f in the rotor. The phase of rotor current can be changed through any angle relative to stator supply voltage by rotating rotor. Thus the change in the phase of secondary e.m.f. is equal to the angle through which rotor is moved from its original zero position. Circuit Diagram Standardization of Polar AC Potentiometer Both d.c. as well as a.c. standardization is done. The d.c. standardization is done first by replacing vibration galvanometer by D’arsonval galvanometer. A standard cell such as Weston cell is used for d.c standardization. Then by adjusting sliding contacts null deflection in galvanometer is achieved. The reading of a precision ammeter included in battery supply is noted. During a.c. standardization again vibration galvanometer is used. Measurement of Unknown E.M.F. An emf to be measured connected across terminals A-A’. Sliding contacts P1 and P2 and the position of rotor in phase shifter are adjusted simultaneously till the balance is obtained as indicated by the null deflection of vibration galvanometer. At balance, the magnitude of the unknown emf is obtained from P1 and P2 and the phase angle is measured from the scale reading which is mounted on the top of the instrument. Thus the unknown emf can be expressed in polar form as E∟Ө°. Circuit Diagram GALL TINSLEY CO-ORDINATE TYPE AC POTENTIOMETER The in-phase and quadrature potentiometer consist of sliding contacts BB’ and CC’ respectively. Rheostats r and R’ are also provided in the respective potentiometers for the adjustment of current. By using different arrangement, the supply for the potentiometer are obtained. A vibration galvanometer VG is tuned to the supply freq and it is connected in series with a switch K and electrodynamometer type ammeter. Circuit Diagram Measurement of Unknown EMF The emf to be measured is connected across the terminals A-A’ using selector switch S3. Sliding contacts of both the potentiometers are adjusted till the contacts of both the potentiometers are adjusted till the null deflection is obatained Under the balance condition, the in-phase component of the unknown emf is obtained from inphase potentiometer while the quadrature component of the unknown emf is obtained from quadrature potentiometer. If needed the polarity of the test voltage may be reversed by using sign changing switches S1 and S2 to balance the potentiometer. APPLICATION OF AC POTENTIOMETER Voltmeter Calibration Ammeter Calibration Wattmeter and Energy meter Testing Measurement of self-Reactance of a coil