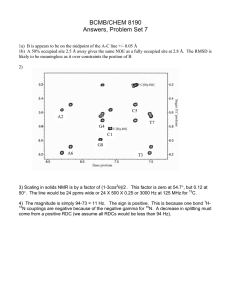
NMR of large proteins
advertisement

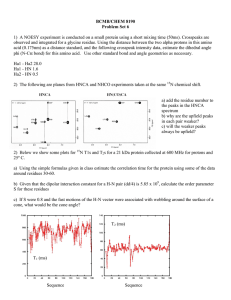
NMR of large proteins • • • • TROSY (up to 100 kDa) CRINEPT (> 100 kDa) H/D exchange (up to X MDa) Membrane Proteins Chemical shift monitoring • • • • • • • Acquisition (Ernst) CW Chemical shift evolution (Ernst, Jener) GFT (Szyperski) Hadamard Spectroscopy (Kupce) Off-resonance decoupling Spin state selective off-resonance decoupling (SITAR) • Coded Spectroscopy 1 1D 1H NMR Jr(H,C) 1 Jr(H,C) Jr(H,C) cw IZ IX R2 1 1 ω IX(t) = IX(0) Cos(ω t) Exp[- R2 t] Multi-dimensional NMR Spectroscopy: The problem of chemical shift monitoring in the indirect dimension H N 2 Chemical shift evolution 1H 15N Ix t2 t1= 1 in0 --> IzSx cos[ωS in0] --> Ix cos[ωI t2] cos[ωS in0] Chemical shift evolution 1H 15N Ix t2 t1= 2 in0 --> IzSx cos[ωS 2 in0] --> Ix cos[ωI t2] cos[ωS 2 in0] 3 Chemical shift evolution 1H t2 t1= 3 in0 15N Ix Ix --> --> IzSx cos[ωS 3 in0] IzSx cos[ωS 2 in0] --> --> Ix cos[ωI t2] cos[ωS 3 in0] Ix cos[ωI t2] cos[ωS 2 in0] Ix --> IzSx cos[ωS 1 in0] --> Ix cos[ωI t2] cos[ωS 1 in0] Polarization transfer Acquisition Polarization transfer Chemical shift evolution ( n increments) Chemical shift evolution 1H 15N t1 t2 Polarization transfer: - relaxation (T1, T2) - incomplete transfer - other active couplings (pathways) - many pulses (rf inhomogenity) 4 Chemical shift evolution 1H 15N t1 t2 Polarization transfer: - relaxation (T1, T2) - incomplete transfer - other active couplings (pathways) - many pulses (rf inhomogenity) Chemical shift evolution: - relaxation (T1, T2) - active couplings (unwanted pathways) - 1.41 signal loss due to complex acquisition - resolution limitation in 3D and 4D exp ( n increments per indirect dimensions) TROSY: Transverse Relaxationoptimized Spectroscopy 5 CSA AND DD contribution to relaxation 6 [15N,1H]-TROSY 7 [15N,1H]-TROSY of DHNA (110 kDa) 8 Magnetic field dependent effect of TROSY Magnetic field-dependent effect of [15N,1H]-TROSY 100 kDa 30 kDa 9 TROSY is a building block • 15N-resolved [1H,1H]-NOESY • Triple resonance experiments • Relaxation measurements TROSY-Triple resonance experiments 10 TROSY-HNCA (110 kDa DHNA; Salzmann et al) ZQ TROSY and 13Carom/methyl TROSY • TROSY can be expanded to transverse relaxation optimization due to CSA/CSA cross correlation: ZQ TROSY • TROSY can be expanded to 13Cmethyl/arom due to DD/DD(CSA) cross correlation • TROSY can be applied to DNA/RNA for the sugar 13C and base 15N 11 NMR of large proteins • • • • TROSY (up to 100 kDa) CRINEPT (> 100 kDa) H/D exchange (up to X MDa) Membrane Proteins 2H,15N-labeled GroEL (880 kDa) [15N,1H]-TROSY [15N,1H]-CRIPTTROSY 10 9 8 12 High resolution solution NMR of macromolecules with a molecular weight up to 1 MDa • Introduction • Technique – Polarization transfer – T1(1H): inter-scan delay and water-protein interaction – [15N,1H]-correlation experiments • Application – 2H,15N-labeled GroES in complex with GroEL – 2H,15N-labeled GroEL in complex with GroES [15N,1H]-TROSY 1H 15N t1 t2 PFG Transverse relaxation-optimization during polarization transfers 13 Polarization transfer: INEPT y x 1H 15N Ix 2IySz 2IzSx Polarization Transfer efficiencies 14 Polarization transfer: CRIPT (Cross-correlated relaxation-induced polarization transfer) y y 1H 15N Ix 2IxSz 2IzSx = + CRIPT Transfer Time T 0.02 250 200 SR1 I rel 0.015 100 T[s] 50 GroEL 0.01 DHNA 20C 0.005 2 8 T[ms] 46 GroES + GroEL DHNA 4C SR1 50 100 150 GroES + SR1 200 250 GroEL 300 τc[ns] 15 Polarization Transfer efficiencies Polarization transfer: CRINEPT (Cross-correlated relaxation-enhanced polarization transfer) y φ 1H 15N Ix 2IySz 2IzSx + evolution 16 Improvement of CRINEPT by Glaser/Pervushin φ y 1H 15N Ix 2IySz 2IzSx Selective inversion Polychromatic inversion [15N,1H]-TROSY 1H 15N t2 t1 PFG [15N,1H]-correlation experiments TROSY CRINEPT-TROSY P t1 t2 N. of T PT - + + 3 PT type peak selectio n 3J HN CRINEPT-HMQC CRIPT-TROSY 17 [15N,1H]-CRINEPT-TROSY T 1H T T t1 15N t2 PFG [15N,1H]-correlation experiments TROSY CRINEPT-TROSY P t1 t2 N. of T PT + + + 3 + + 2 PT type peak selectio n 3J HN 3J HN+R C CRINEPT-HMQC CRIPT-TROSY [15N,1H]-CRINEPT-HMQC-1H-TROSY 1H 15N t2 t1 PFG [15N,1H]-correlation experiments P t1 t2 N. of T PT PT type TROSY CRINEPT-TROSY + + + 3 + + 2 3J CRINEPTHMQC/TR CRIPT-TROSY + - 3J + 2 peak selectio n HN 3J HN+R C HN+R C 18 [15N,1H]-CRIPT-TROSY 1H t2 t1 15N PFG [15N,1H]-correlation experiments P t1 t2 T N. of PT PT type TROSY CRINEPT-TROSY + + + 3 + + 2.5 3J HN 3J +R HN C CRINEPTHMQC/TR CRIPT-TROSY + - 3J +R HN C + + + 1 + 2 peak selectio n RC [15N,1H]-CRINEPT-TROSY of 2H,15N-labeled GroES in complex with SR1 (0.5 MDa) 19 [15N,1H]-CRIPT-TROSY of 2H,15N-labeled GroES in complex with SR1 (0.5 MDa) ω1(15N) [ppm] ω2(1H) [ppm] [15N,1H]-CRINEPT-HMQC-1H-TROSY of 2H,15Nlabeled GroES in complex with SR1 (0.5 MDa) 20 2H,15N-labeled GroEL (880 kDa) [15N,1H]-TROSY [15N,1H]-CRIPTTROSY 10 9 8 High resolution solution NMR of macromolecules with a molecular weight up to 1 MDa • Introduction • Technique – Polarization transfer – [15N,1H]-correlation experiments – T1(1H): inter-scan delay and water-protein interaction • Application – 2H,15N-labeled GroES in complex with GroEL – 2H,15N-labeled GroEL in complex with GroES 21 Water-Protein Interaction T1(1H) [s] 10000 100 SR1 in D2O 1 BPTI 0.01 10-12 τc [s] 10-9 T1H2O 10-8 T1H2O = T1D2O + ρHOH+ σHOH 10-7 10-6 Fast exchange 22 High resolution solution NMR of macromolecules with a molecular weight up to 1 MDa • Introduction • Technique – Polarization transfer – [15N,1H]-correlation experiments – T1(1H): inter-scan delay and water-protein interaction • Application – 2H,15N-labeled GroES in complex with GroEL – 2H,15N-labeled GroEL in complex with GroES GroES-GroEL interaction Sequential backbone assignment of 2H, 13C,15N-labeled GroES with TROSY-based triple resonance exp. Homo heptamer 70 kDa [15N,1H]-CRIPT-TROSY Of 2H,15N-labeled GroES In complex with 2H-labeled SR1 or 2H-labeled GroEL Homo heptamer 500 kDa or 950 kDa 23 2H, 15N-labeled free GroES in complex with SR1 114.0 116.0 ppm ppm 118.0 9.5 9.0 9.5 9.0 ppm 9.8 9.8 ppm [15N,1H]-CRIPT-TROSY CRIPT Transfer Time T -> τc 0.02 250 200 SR1 I rel 0.015 100 T[s] 50 GroES + SR1 DHNA 20C 0.005 GroES + GroEL GroEL 0.01 2 8 T[ms] 46 GroES + GroEL DHNA 4C SR1 50 100 150 GroES + SR1 200 250 GroEL 300 τc[ns] 24 GroES GroES GroES + SR1 GroES + SR1 GroES GroES GroES + SR1 GroES + SR1 GroES+GroEL GroES+GroEL GroES+GroEL GroES+GroEL 25 Assignment 26 318 256 310 213 214 ω1(15N) [ppm] 326 361 ω2(1H) [ppm] GroES-GroEL complex 27 Glu 310 Conclusion Identification of protein-protein interfaces is possible with molecular complexes of 1 MDa Prerequisites: • 2H,15N-labeling • Multimeric proteins or highly soluble proteins • Partial sequential assignment 28 NMR of large proteins • • • • TROSY (up to 100 kDa) CRINEPT (> 100 kDa) H/D exchange (up to X MDa) Membrane Proteins Inclusion Bodies of E. Coli 29 Structural Studies of inclusion bodies of BMP2 and ESAT6 Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2) is a member of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) superfamily, and it plays an important role during early stages of embryonic development. 6-kDa early secretory antigenic target (ESAT6) is an immunogenic antigen recognized during the Tuberculosis disease. Thio-T binding indicates inclusion bodies are amyloidlike ThT binding 20 15 10 5 0 BMP2 ESAT6 MOG _-Synuclein 30 Quenched H/D exchange by NMR D2O H2O N-H N-H N-H DMSO N-H N-D N-D Hoshino, Goto et al., 2002 31 H/D exchange of BMP2 Inclusion Body Study Lei Wang 4.24.2007 H/D exchange of BMP2 inclusion bodies 1 V67 Irel I62 V21 F41 0 0 100 H/D exchange Time [hours] 32 H/D exchange of BMP2 inclusion bodies Amyloid Fibrils • • • • • • Disease-associated Infectious proteins (prions) Native functions of fibrils Protein structure dogma Inherent to all proteins (Dobson) Nanotechnology (storage container, in vivo mini-column) 33 NMR investigations on KcsA potassium channel 20 pA 500 ms 1s 7 -> 4 pH Roland Riek The Salk Institute KcsA x-ray structure (MacKinnon et al, 1998) 34 KcsA x-ray structure (MacKinnon et al, 1998) KcsA x-ray structure (MacKinnon et al, 1998) 35 KcsA x-ray structure (MacKinnon et al, 1998) KcsA x-ray structure (MacKinnon et al, 1998) 36 KcsA x-ray structure (MacKinnon et al, 1998) Goooooooooal !!! KcsA (4*160 aa, 130 kDa) 17 Gly 17 Gly peaks (plus 3 sharp little peaks) 17 Arg 17 Arg peaks 5 Trp 5 Trp peaks (plus 2 sharp satelite peaks) 37 Technical comments KcsA binds agitoxin 2 and is a tetramer 38 Selective Labeling and Alaselective 2D HNCA 15N-Asp 15N-Xxx 15N-Phe sequential to Ala 115.00 116.00 118.00 118.00 120.00 120.00 120.00 122.00 122.00 125.00 124.00 8.50 8.00 124.00 8.50 7.50 8.00 7.50 9.00 8.50 8.00 7.50 Leu, Phe, Tyr, Asp, Ile Specific Assignment Tyr78 Tyr82 Tyr62 Tyr137 ω 1(15N) [ppm] 120 Tyr45 120 9 8.5 8 ω 2(1H) [ppm] 125 9 8 7.5 KcsA(F78Y) 39 9 1 0 9 1 1 3 1 1 7 1 2 1 1 2 5 1 2 9 1 3 3 1 3 7 1 4 1 1 4 5 1 4 9 1 5 3 1 5 7 5 1 7 3 9 9 9 8 8 5 8 7 7 3 7 6 5 1 7 6 6 5 3 9 5 4 5 1 7 4 4 3 0 1 1 9 3 3 2 9 9 13 3 13 7 14 1 14 5 14 9 15 3 15 7 12 12 5 11 3 11 7 12 1 10 1 10 5 10 9 97 93 89 85 81 77 73 69 65 61 57 53 49 45 41 37 33 29 25 21 17 13 6 0 1 7 5 1 1 2 2 9 deltaRC 6 1 1 6 12 1 12 6 13 1 13 6 14 1 14 6 15 1 15 6 11 11 1 10 6 10 96 91 86 81 76 71 66 61 56 51 46 41 36 31 26 21 16 11 -1 3 1 1 5 deltaRC pH 7.0 closed 5 pH 4.0 open 1 deltaCA[ppm] KcsA assignment 6 Ca Chemical Shifts 5 4 3 2 1 0 -2 5 Residue 4 3 2 1 -1 0 -2 0.6 0.8 1 Residue -0.4 -0.2 -0.6 0.4 -0.8 0.2 -1 0 Residue 40 Detergent-KcsA interactions Hydrogen exchange of KcsA 41 9 5 7 1 3 0 0 1 9 7 3 9 2 1 1 2 5 1 2 9 1 3 3 1 3 7 1 4 1 1 4 5 1 4 9 1 5 3 1 5 7 1 1 1 5 9 8 8 8 7 7 7 3 6 9 5 1 6 6 7 3 5 5 9 4 1 1 1 4 5 4 7 3 3 3 9 5 2 1 0 1 7 2 2 1 1 9 10 3 7 12 1 12 5 12 9 13 3 13 7 14 1 14 5 14 9 15 3 15 7 11 5 9 10 11 1 10 97 93 89 85 81 77 73 69 65 61 57 53 49 45 41 37 33 29 25 21 17 13 6 1 9 deltaRC 6 1 96 10 1 10 6 11 1 11 6 12 1 12 6 13 1 13 6 14 1 14 6 15 1 15 6 91 86 81 76 71 66 61 56 51 46 41 36 31 26 21 16 11 -1 3 1 1 5 deltaRC pH 7.0 closed 5 pH 4.0 open 1 deltaCA[ppm] Ca Chemical Shifts 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 -2 5 Residue 4 3 2 1 -1 0 -2 0.6 0.8 1 Residue -0.4 -0.2 -0.8 -0.6 0.2 0.4 -1 0 Residue pH-Titration of 15N-Tyr KcsA 42 Population in open state 75% 15N 50% 25% Tyr78 0% pH 43 CT-ZQ-TROSY for the measurement of 3J(N,HA) couplings 44 More Dynamics? - Fast exchange between open and closed state -> inactivated state -19F-Tyr good probe to measure dynamics for large proteins (high sensitivity, CSA dominates) - Dynamical change: pH 7 (closed): slow dynamics present pH 4 (open): slow dynamics absent 3000 pH 7: T2(19F-Y78) & T1ρ(19F-Y78) 2500 2500 2000 pH 4: T2(19F-Y78) & T1ρ(19F-Y78) 2000 1500 Irel 1500 1000 1000 500 500 0 0 0.002 0.004 - 0.006 0.008 0.01 0.012 0.014 0 0 0.002 T [s] 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.01 T [s] NMR of large proteins • • • • TROSY (up to 100 kDa) CRINEPT (> 100 kDa) H/D exchange (up to X MDa) Membrane Proteins 45 NMR of large proteins • TROSY: Konstantin Pervushin, Gerhard Wider, Kurt Wuthrich, Jocelyne Fiaux • H/D exchange: Thorsten Luhrs, Marcial Vilar, Lei Wang • Membrane Proteins: Kent Baker, Christos Tzitzilonis, Senyon Choe 46