Resistance and Ohm`s Law
advertisement

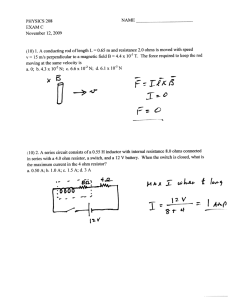
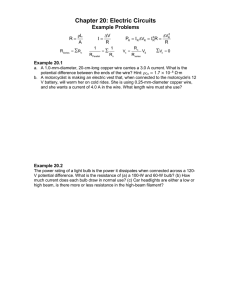
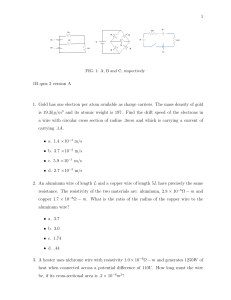
Resistance and Ohm's Law 1. The ratio of the potential difference across a conductor to the current in the conductor is called (1) conductivity (3) charge (2) resistance (4) power 2. A manufacturer recommends that the longer the extension cord used with an electric drill, the thicker (heavier gauge) the extension cord should be. This recommendation is made because the resistance of a wire varies (1) directly with length and inversely with cross-sectional area (2) inversely with length and directly with cross-sectional area (3) directly with both length and cross-sectional area (4) inversely with both length and cross-sectional area 3. If the length of a copper wire is reduced by half, then the resistance of the wire will be (1) halved (3) quartered (2) doubled (4) quadrupled 4. A piece of wire has a resistance of 8 ohms. A second piece of wire of the same composition, diameter, and temperature, but one-half as long as the first wire, has a resistance of (1) 8 Ω (3) 16 Ω (2) 2 Ω (4) 4 Ω 9. The current through a 10.-ohm resistor is 1.2 amperes. What is the potential difference across the resistor? (1) 8.3 V (3) 14 V (2) 12 V (4) 120 V 10. A 330.-ohm resistor is connected to a 5.00-volt battery. The current through the resistor is (1) 0.152 mA (3) 335 mA (2) 15.2 mA (4) 1650 mA 11. The graph at the right shows how the voltage and current are related in a simple electric circuit. For any point on the line, what does the ratio of V to I represent? (1) work in joules (2) power in watts (3) resistance in ohms (4) charge in coulombs 12. The graph below shows the relationship between current and potential difference for four resistors A, B, C, and D. 5. A complete circuit is left on for several minutes, causing the connecting copper wire to become hot. As the temperature of the wire increases, the electrical resistance of the wire (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 6. An incandescent light bulb is supplied with a constant potential difference of 120 volts. As the filament of the bulb heats up, its resistance (1) increases and the current through it decreases (2) increases and the current through it increases (3) decreases and the current through it decreases (4) decreases and the current through it increases 7. The resistance of a copper wire is measured to be 4 ohms at 20ºC. If the wire is heated to 30ºC, the resistance of the wire will be (1) zero ohms (3) more than 4 ohms (2) less than 4 ohms (4) 4 ohms 8. If the diameter of a wire were decreased, its electrical resistance would (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase Which resistor has the greatest resistance? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D 13. Which voltage would cause a current of 0.5 ampere in a circuit that has a resistance of 24 ohms? (1) 6.0 V (3) 24 V (2) 12 V (4) 48 V 14. A 0.686-meter-long wire has a cross-sectional area of 8.23 ×10–6 meter2 and a resistance of 0.125 ohm at 20° Celsius. This wire could be made of (1) aluminum (3) nichrome (2) copper (4) tungsten Resistance and Ohm's Law Answer Key [New Exam] 1. 2 2. 1 3. 1 4. 4 5. 2 6. 1 7. 3 8. 2 9. 2 10. 2 11. 3 12. 1 13. 2 14. 3