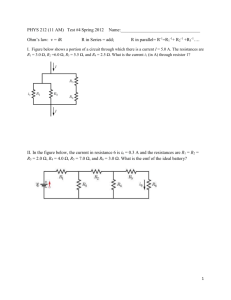
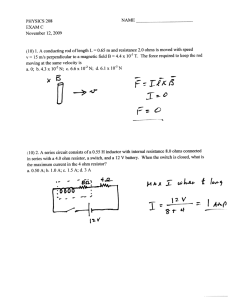
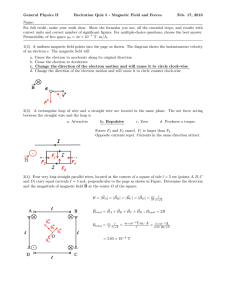
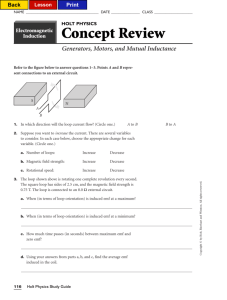
EMF = Blv = 5 x 10 T* 70 m * 280 m/s = 1 volt Clockwise
advertisement

Induction S432 Physics Name: Period: 1) An airplane travels at 280 m/s in a region where the earth’s B field is 5 x 10 –5 T and is nearly vertical. What is the potential difference induced between the wing tips that are 70 m apart? (1 V) EMF = Blv = 5 x 10 –5 T* 70 m * 280 m/s = 1 volt 2) A rectangular loop of wire is being pulled to the left out of a B field that points into the page. In what direction is the induced current? Clockwise x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 3) x x x x x x B= 0.5 T x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x X 5ž 3 m/s 2m Y 4m A wire loop that is 2m x 4m is in the plane of the page as shown. The field is contained to the region shown and the loop is being pulled to the right with a speed of 3 m/s. Make all determinations for the time that the left end of the loop is still in the field and points X and Y are not in the field. a) Determine the potential difference induced between points X and Y. EMF = Blv = 0.5 T * 2m * 3m/s = 3 volts b) On the figure above, show the direction of the conventional current induced in the resistor. Clockwise c) Determine the force required to keep the loop moving at 3 m/s. F = Bil = 0.5 T*(3 volts/5 ohms) * 2 m = 0.6 N to the right d) Determine the rate at which work must be done to keep the loop moving at 3 m/s. P = W/t = VI = 3 volts* .6 a = 1.8 Watts 4) The figure above shows a cross section of a cathode ray tube. An electron initially moves horizontally in the plane of the cross section at a speed of 2 x 107 m/s. The electron is deflected upward by a magnetic field that has a field strength of 6 x 10-4 T. a. What is the direction of the magnetic field? Out of the page b. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic force acting on the electron. -4 –19 7 F = Bqv = 6 x 10 T * 1.6 x 10 1.92 x 10 –15 N coul * 2 x 10 m/s = - c. Determine the radius of curvature of the path followed by the electron in the B field. An electric field is later established in the same region as the magnetic field such that the electron no passes through the magnetic and electric fields without deflection. d. Determine the magnitude of the electric field. e. What is the direction of the electric field? F=qE E = F/q = 1.92 x 10 –15 N/ 1.6 x 10 –19 coul = 12000 N/c 5) A straight wire , 0.5 m long, is moved straight up through a 0.4 T magnetic field directed to the east at a speed of 20 m/s. What EMF is induced in the wire? EMF = Blv = 0.4 T * 0.5m * 20m/s = 4 volts The wire is part of a circuit of total resistance of 6.0 ohms. What is the current in the circuit? V = IR I = V/R = 4 v/6 = .66 a into the page 6) A horseshoe magnet is mounted so that the B field lines are vertical. If a student passes a straight wire between the poles and pulls the wire toward herself, the current flow is from right to left. Which is the north pole of the magnet? the lower part of the magnet S N