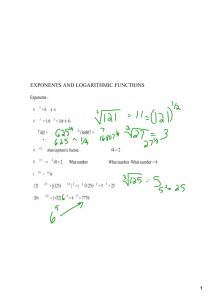PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
advertisement

PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS An exponential function is a function of the form f ( x ) = b x , where b > 0 and x is any real number. (Note that f ( x ) = x 2 is NOT an exponential function.) LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS log b x = y means that x = b y where x > 0, b > 0, b ≠ 1 Think: Raise b to the power of y to obtain x. y is the exponent. The key thing to remember about logarithms is that the logarithm is an exponent! The rules of exponents apply to these and make simplifying logarithms easier. Example: log 10 100 = 2 , since 100 = 10 2 . log 10 x is often written as just log x , and is called the COMMON logarithm. log e x is often written as ln x , and is called the NATURAL logarithm (note: e ≈ 2.718281828459... ). PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMS EXAMPLES 1. log b MN = log b M + log b N log 50 + log 2 = log 100 = 2 Think: Multiply two numbers with the same base, add the exponents. M 56 = log b M − log b N log 8 56 − log 8 7 = log 8 = log 8 8 = 1 N 7 Think: Divide two numbers with the same base, subtract the exponents. 2. log b 3. log b M P = P log b M log 100 3 = 3 ⋅ log 100 = 3 ⋅ 2 = 6 Think: Raise an exponential expression to a power and multiply the exponents together. log b b x = x log b 1 = 0 (in exponential form, b 0 = 1 ) log b b = 1 log 10 10 = 1 ln e = 1 log b b = x log 10 10 = x ln e x = x b logb x = x Notice that we could substitute y = log b x into the expression on the left x x ln 1 = 0 to form b y . Simply re-write the equation y = log b x in exponential form as x = b y . Therefore, b logb x = b y = x . Ex: e ln 26 = 26 CHANGE OF BASE FORMULA log b N = log a N , for any positive base a. log a b log 12 5 = log 5 0.698970 ≈ ≈ 0.6476854 log 12 1.079181 This means you can use a regular scientific calculator to evaluate logs for any base. 1. 2. 3. 4. Practice Problems contributed by Sarah Leyden, typed solutions by Scott Fallstrom Solve for x (do not use a calculator). 2 log 9 (x − 10 ) = 1 6. log 3 27 x = 4.5 10. log 2 x 2 − log 2 (3x + 8) = 1 3 log 3 3 2 x +1 = 15 7. log x 8 = − 11. ( 1 2 ) log 3 x − ( 13 ) log 3 x 2 = 1 2 log x 8 = 3 8. log 6 x + log 6 ( x − 1) = 1 log 5 x = 2 1 9. log 2 x 2 + log 2 ( 1x ) = 3 log (x 2 − 7 x + 7 ) = 0 5. 5 Solve for x, use your calculator (if needed) for an approximation of x in decimal form. 12. 7 x = 54 15. 10 x = e 18. 8 x = 9 x 13. log 10 x = 17 16. e − x = 1.7 19. 10 x +1 = e 4 17. ln (ln x ) = 1.013 20. log x 10 = −1.54 14. 5 x = 9 ⋅ 4 x Solutions to the Practice Problems on Logarithms: 1. log 9 (x 2 − 10) = 1 ⇒ 91 = x 2 − 10 ⇒ x 2 = 19 ⇒ x = ± 19 2. log 3 3 2 x +1 = 15 ⇒ 315 = 3 2 x +1 ⇒ 2 x + 1 = 15 ⇒ 2 x = 14 ⇒ x = 7 3. log x 8 = 3 ⇒ x 3 = 8 ⇒ x = 2 4. log 5 x = 2 ⇒ 5 2 = x ⇒ x = 25 5. log 5 (x 2 − 7 x + 7 ) = 0 ⇒ 5 0 = x 2 − 7 x + 7 ⇒ 0 = x 2 − 7 x + 6 ⇒ 0 = ( x − 6)( x − 1) ⇒ x = 6 or x = 1 ( ) 6. log 3 27 x = 4.5 ⇒ log 3 33 x = 4.5 ⇒ log 3 33 x = 4.5 ⇒ 3 x = 4.5 ⇒ x = 1.5 7. log x 8 = − 32 ⇒ x − 2 = 8 ⇒ x = 8 − 3 ⇒ x = 3 2 1 4 log 6 x + log 6 ( x − 1) = 1 ⇒ log 6 (x 2 − x ) = 1 ⇒ x 2 − x = 6 ⇒ x 2 − x − 6 = 0 ⇒ 8. (x − 3)(x + 2) = 0 ⇒ x = 3 or x = −2. Note : x = −2 is an extraneous solution, which solves only the new equation. x = 3 is the only solution t o the original equation. x 2 1 9. log 2 x + log 2 = 3 ⇒ log 2 x x 1 1 = 3 ⇒ log 2 x − 2 = 3 ⇒ 2 3 = x − 2 ⇒ x = 2 3 2 2 x2 log 2 x − log 2 (3 x + 8) = 1 ⇒ log 2 3 x +8 = 1 ⇒ 3 xx+8 = 2 ⇒ x 2 = 6 x + 16 ⇒ ( ) 1 1 10. 11. 2 −2 ( ) x 2 − 6 x − 16 = 0 ⇒ ( x − 8)( x + 2 ) = 0 ⇒ x = 8 or x = −2 ( x 2 1 2 = 1 ⇒ log 3 2 3 = 1 ⇒ x 2 − 3 = 3 ⇒ 2 ) log 3 x − ( 3 ) log 3 x = 1 ⇒ log 3 x − log 3 x x 1 1 1 2 1 x − 6 = 3 ⇒ x = 3−6 = 1 5x 4x 3 1 729 log 54 ≈ 2.0499 13. log 10 x = 17 ⇒ x = 1017 log 7 12. 7 x = 54 ⇒ x = log 7 54 ⇒ x = 14. 5 x = 9 ⋅ 4 x ⇒ 2 2 = 9 ⇒ ( 54 ) = 9 ⇒ x = log 5 9 ⇒ x ≈ 9.8467 x 4 15. 10 = e ⇒ x = log 10 e ⇒ x = log e ≈ 0.4343 x 16. e − x = 1.7 ⇒ − x = ln 1.7 ⇒ x = − ln 1.7 ≈ −0.5306 1.013 17. ln (ln x ) = 1.013 ⇒ ln x = e1.013 ⇒ x = e e ≈ 15.7030 18. 8 x = 9 x ⇒ 1 = ( 98 ) ⇒ x = log 9 1 ⇒ x = 0 x 8 19. 10 x +1 = e ⇒ x + 1 = log e ⇒ x = log e 4 − 1 = log e 4 − log 10 ⇒ x = log 4 4 20. log x 10 = −1.54 ⇒ x −1.54 = 10 ⇒ x = 10 − 1.54 ≈ 0.2242 1 ( ) ≈ 0.7372 e4 10 = 1 64