Review 5 - Department of Physics
advertisement
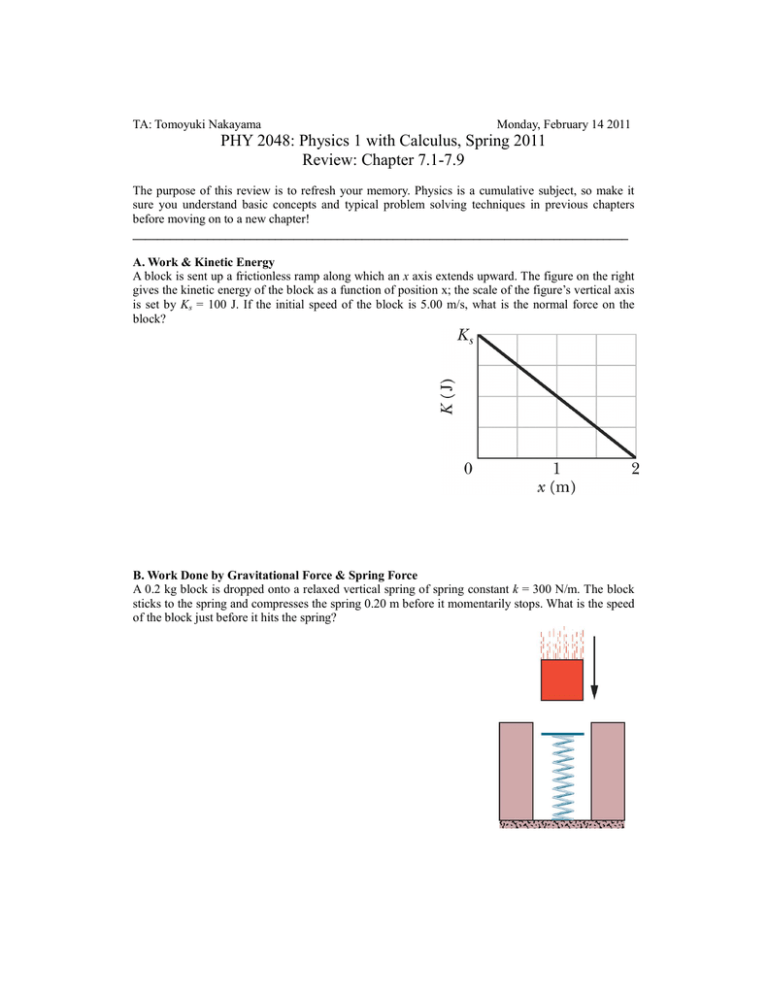
TA: Tomoyuki Nakayama Monday, February 14 2011 PHY 2048: Physics 1 with Calculus, Spring 2011 Review: Chapter 7.1-7.9 The purpose of this review is to refresh your memory. Physics is a cumulative subject, so make it sure you understand basic concepts and typical problem solving techniques in previous chapters before moving on to a new chapter! ________________________________________________________________________________ A. Work & Kinetic Energy A block is sent up a frictionless ramp along which an x axis extends upward. The figure on the right gives the kinetic energy of the block as a function of position x; the scale of the figure’s vertical axis is set by Ks = 100 J. If the initial speed of the block is 5.00 m/s, what is the normal force on the block? B. Work Done by Gravitational Force & Spring Force A 0.2 kg block is dropped onto a relaxed vertical spring of spring constant k = 300 N/m. The block sticks to the spring and compresses the spring 0.20 m before it momentarily stops. What is the speed of the block just before it hits the spring? TA: Tomoyuki Nakayama Monday, February 14, 2011 PHY 2048: Physics 1 with Calculus, Spring 2011 Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 7.1-7.9) Working on this problem set is optional, but it is strongly recommended. It is quite possible that some of these problems will appear in the exams. Do it on a weekly basis. Cramming is tiring and sometimes it ends up in a disaster. ________________________________________________________________________________ 1. A man pushes an 80-N crate a distance of 5.0 m upward along a frictionless slope that makes an angle of 30º with the horizontal. His force is parallel to the slope. If the speed of the crate decreases at a rate 1.5 m/s2, then the work done by the man is (Work) a. -200 J b. 61 J c. 140 J d. 200 J e. 260 J 2. A 8000-N car is traveling at 12 m/s along a horizontal road when the brakes are applied. The car skids to a stop in 4.0 s. How much kinetic energy does the car lose in this time? (Kinetic Energy) a. b. 5.9×104 J c. 1.2×105 J d. 5.8×105 J e. 4.8×105 J 4.8×104 J 3. An ideal spring, with a pointer attached to its end, hangs next to a scale. With a 100-N weight attached, the pointer indicates “40” on the scale as shown. Using a 200-N weight instead results in “60” on the scale. Using an unknown weight X instead results in “30” on the scale. The weight of X is: (Hooke’s Law) a. 10 N b. 20 N c. 30 N d. 40 N e. 50 N 4. An ideal spring is hung vertically form the ceiling. When a 2.0-kg mass hangs at rest from it, the spring is extended 6.0 cm from its relaxed length. A upward external force is now applied to the block to move it upward a distance of 16 cm. While the block is moving upward the work done by the spring is: (Work done by spring) a. -1.0 J b. -.52 J c. -0.26 J d. 0.52 J e. 1.0 J 5. A woman lifts a barbell 2.0 m in 5.0 s. If she lifts it the same distance in 10s, the work done by her is: (Work done by gravitational force) a. four times as great b. two times as great c. the same d. half as great e. one fourth as great 6. A particle moving along the x-axis is acted upon by a single force F = F0e-kx, where F0 and k are constants. The particle is released from rest at x = 0. It will attain a maximum kinetic energy of: (Work Done by Variable Forces) a. F0/ k b. F0/ ek c. F0 k d. (1/2)( F0 k) 2 e. kF0ek 7. An escalator is used to move 20 People (60 kg each) per minute from the first floor of a department store the second floor, 5m above. Neglecting friction, the power required is approximately: (Power) a. 100 W b. 200 W c. 1000 W c. 2000 W e. 60 000 W Answers: 1-c 2-b 3-e 4-a 5-c 6-a 7-c



