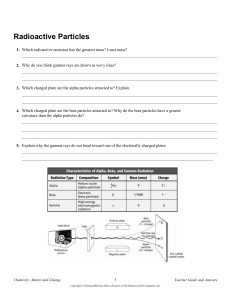
Sir Joseph John Thomson, (JJ Thomson) was a British Physicist who
advertisement

Student 5: Low Achieved Beta Particle Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons emitted by some types of radioactive nuclei. They are a form of ionizing radiation also known as beta rays. The production of beta particles is termed beat decay. Low ionising ability. Particles have a longer range than alphas, but ionise much less strongly, with the result that they do around 1/20th of the damage done by the same dose of alpha particles. However, they do have more penetrating power, which means that they can get through your skin and affect cells inside you. Gamma Particle This is electromagnetic radiation with a very short wavelength and high frequency. It occurs as a result of a nucleus being left in a very excited state immediately following other types of radioactive decay. The nucleus emits the energy in the form of Gamma rays. Being electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays travel at the speed of light. Gamma rays can penetrate through several centimetres of lead, Very low ionising ability an travel at the speed of light. Gamma rays hardly ionise atoms at all, so they do not cause damage directly in this way. However, gamma rays are very difficult to stop, you require lead or concrete shielding to keep you safe from them. When they are absorbed by an atom, that atom gains quite a bit of energy, and may then emit other particles. If that atom is in one of your cells, this is not good! Alpha Particle A positively charged particle ejected spontaneously from the nuclei of some radioactive elements. It is identical to a helium nucleus that has a mass number of 4 and an electrostatic charge of +2. It has low penetrating power and short range (a few centimetres in air). The most energetic alpha particle will generally fail to penetrate the dead layers of cells covering the skin, and can be easily stopped by a sheet of paper. Alpha particles are hazardous when an alpha-emitted isotope is inside the body. Particles are slow, have a short range in air, and can be stopped by a sheet of paper. You might therefore assume that alpha particles are the least dangerous of the 3 types of radiation. Chernobyl Disaster The Chernobyl disaster occurred on 26 April 1986 in Ukraine. It is considered the worst power plant accident in history. The accident raised concerns about the safety of the nuclear power industry as well as nuclear power in general. Four hundred times more radioactive material was released than had been by the atomic bombing of Hiroshima. The fallout was detected over all of Europe. In the aftermath of the accident, 237 people suffered from acute radiation sickness, of whom 31 died within the first three months. Most of these were fire and rescue workers trying to bring the accident under control, who were not fully aware of how dangerous exposure to the radiation in the smoke was. Immediately after the disaster, the main health concern involved radioactive iodine. Today, there is concern about contamination of the soil with strontium-90 and caesium-137. The highest levels of caesium137 are found in the surface layers of the soil where they are absorbed by plants, insects and mushrooms, entering the local food supply. Some scientists fear that radioactivity will affect the local population for the next several generations. The majority of premature deaths caused by Chernobyl are expected to be the result of cancers and diseases induced by radiation in the decades after the event.