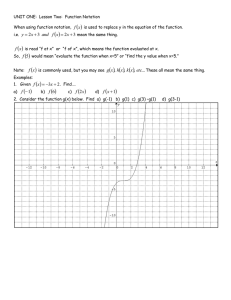
SAMPLE Terminology: Variable: usually denoted by x, usually the
advertisement

SAMPLE Terminology: Variable: usually denoted by x, usually the number you are trying to find Coefficient: the number before the variable that you times the variable by. E.g. the 4 in “4x” Exponent: the power. E.g. the 6 in 26 SAMPLE Derivatives Derivate is synonymous for differentiation. Derivatives are used to find the instantaneous rate of change, or how the rates change as the variable does, or to find the tangent line of a slope (tangent lines explained later on) Differentiation allows us to find rates of change. For example, it allows us to find the rate of change of velocity with respect to time (which is acceleration). It also allows us to find the rate of change of x with respect to y, which on a graph of y against x is the gradient of the curve. There are a number of simple rules which can be used to allow us to differentiate many functions easily Notation: Sometimes the notation is f'(x)= pronounced "f prime of x" Or sometimes the notation is dx/dy= as in it is derived in respect to x, the variable. The latter is more useful when using the chain rule for deriving more complicated equations (explained later)