CO2 Cycle: Sources, Sinks, and Feedbacks Answer Key
advertisement

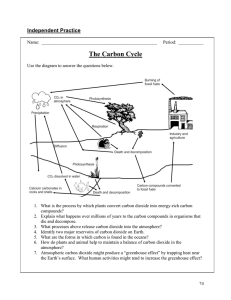
Sources, Sinks, and Feedbacks Answer Key 1. Which statement is true about the CO2 cycle? Carbon dioxide is constantly moving throughout the environment. 2. Is there a reservoir that serves only to take in carbon dioxide? Explain your reasoning. There is no reservoir that serves only to take in carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide may spend a lot of time in one reservoir, but it continually cycles through Earth’s surface and atmosphere. 3. Use the picture of the model to make a prediction about the effect that temperature will have on the ability of CO2 to dissolve in the ocean. Will higher temperatures increase or decrease CO2 solubility? decrease (less carbon dioxide will dissolve) 4. Explain your prediction. Answers will vary. Students should back up their prediction with evidence. Students may not know how to answer these questions as they are predictions, but you should encourage them to back up their claims with evidence. 5. How does the water temperature affect the amount of carbon dioxide that can dissolve in the ocean? Increased water temperature leads to less carbon dioxide dissolved in the ocean. 6. Which statement best describes the relationship between temperature and solubility of carbon dioxide in the ocean? When Earth’s ocean temperature is higher, less carbon dioxide can be dissolved in the ocean. 8. Explain your answer. When atmospheric carbon dioxide is high, the temperature is high. When the temperature is high, less carbon dioxide can be dissolved in the water. Therefore, high atmospheric carbon dioxide levels lead to higher carbon dioxide levels as carbon dioxide comes out of the oceans. 9. How certain are you about your claim based on your explanation? Answers will vary. NatGeoEd.org 1 © 2014 National Geographic Society 7. Of course, in the real world, we can’t just magically change the temperature of the Earth with a slider. What is the relationship between atmospheric CO2 levels and its absorption by the ocean? High CO2 leads to less absorption by the ocean. Sources, Sinks, and Feedbacks Answer Key, continued 10. Explain what influenced your certainty rating. Answers will vary. Scientific evidence includes: carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, increased heat leads to lower solubility of carbon dioxide in the ocean, lower solubility in the ocean leads to more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere (less in the ocean means it has to go somewhere, and the somewhere is the air), and more carbon dioxide in the air leads to further warming. 11. What is the relationship between water vapor and temperature? When the temperature is high, there is more water vapor in the atmosphere. 12. Water vapor is a greenhouse gas. What do you think will happen to the temperature when the amount of water vapor increases? Temperature will increase. 13. Explain your answer. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere as they absorb and re-emit infrared radiation. Water vapor is a greenhouse gas. More water vapor (more greenhouse gases) would increase the temperature. 14. How certain are you about your claim based on your explanation? Answers will vary. 15. Explain what influenced your certainty rating. Answers will vary. Scientific evidence includes: greenhouse gases increase temperature, water vapor is a greenhouse gas, and increased water vapor (greenhouse gas) leads to increased temperature. 17. Explain your answer. Increased levels of carbon dioxide will increase the levels of water vapor. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to higher temperatures. Higher temperatures lead to more water vapor as water evaporates into the atmosphere. 18. What happens to the temperature when the CO2 level increases in this model? The temperature increases. NatGeoEd.org 2 © 2014 National Geographic Society 16. How does the level of carbon dioxide affect the level of water vapor in the atmosphere? Increased levels of carbon dioxide ________ levels of atmospheric water vapor. increase Sources, Sinks, and Feedbacks Answer Key, continued 19. Explain your answer. When I increased the CO2 in the model, the temperature increased. This is because increased levels of carbon dioxide increase the levels of water vapor. Carbon dioxide and water vapor are greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to higher temperatures. Higher temperatures lead to more water vapor as water evaporates into the atmosphere. This cycle continues on and on, continually increasing the temperature. 20. How certain are you about your claim based on your explanation? Answers will vary. 22. Describe a positive feedback system that affects Earth’s temperature. A positive feedback system that affects Earth’s temperature is the feedback loop between carbon dioxide and water vapor. Increased carbon dioxide leads to higher temperatures, which leads to more water vapor as water evaporates, which leads to higher temperatures, which leads to more carbon dioxide coming out of the ocean, which leads to higher carbon dioxide levels, which leads to more water vapor, and on and on as the temperature increases. 23. So far, the models have only shown increasing temperatures. But, obviously, since Earth has had ice ages in the past, temperatures don’t only increase. What kinds of things could decrease Earth’s temperature? Clouds and ice could decrease Earth’s temperature. NatGeoEd.org 3 © 2014 National Geographic Society 21. Explain what influenced your certainty rating. Answers will vary. Scientific evidence includes: greenhouse gases increase temperature, water vapor is a greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, increased carbon dioxide leads to increased temperature, increased temperature leads to increased evaporation of water (and increased levels of water vapor), and increased water vapor (greenhouse gas) leads to increased temperature.