Chapter 28
advertisement
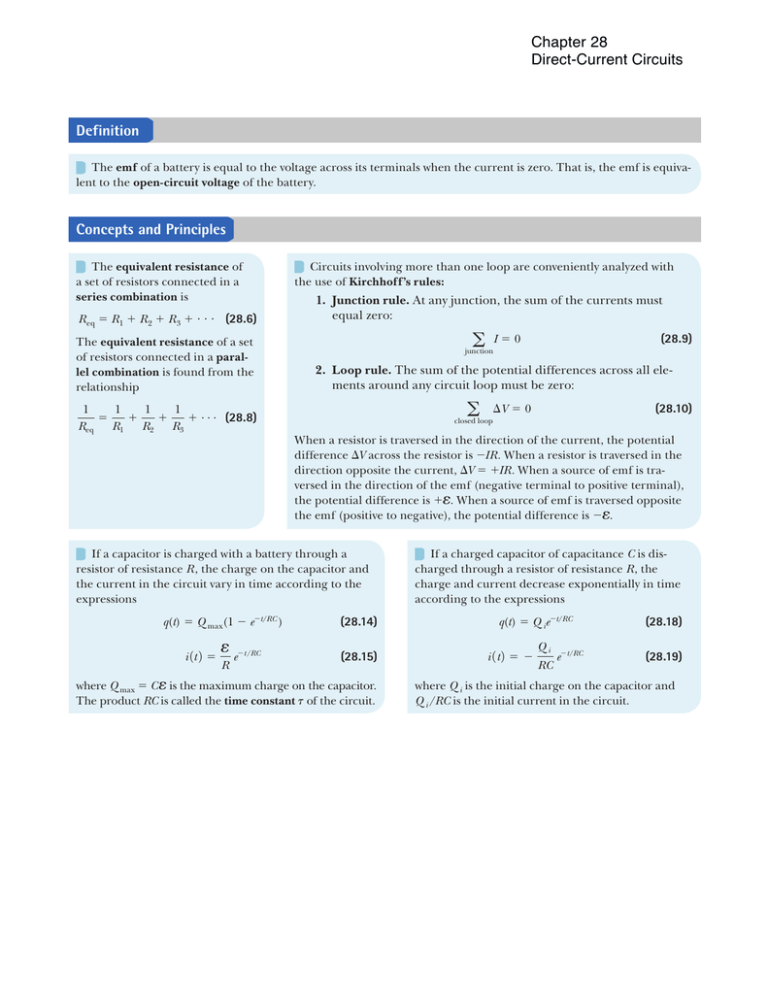
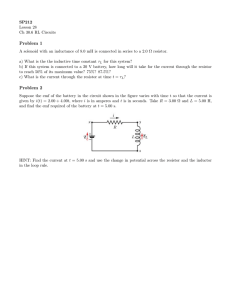
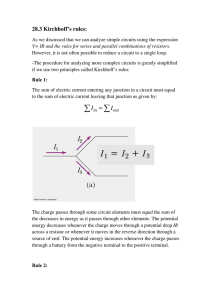
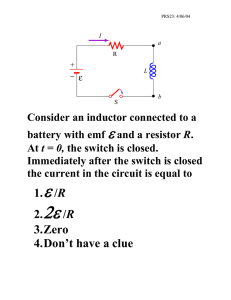
is described in Chapter 31.) When an excessive leakage current is detected, the current is shut off in less than 1 ms. Chapter 28 Direct-Current Circuits Summary Definition The emf of a battery is equal to the voltage across its terminals when the current is zero. That is, the emf is equivalent to the open-circuit voltage of the battery. Concepts and Principles The equivalent resistance of a set of resistors connected in a series combination is R eq 5 R 1 1 R 2 1 R 3 1 ? ? ? (28.6) The equivalent resistance of a set of resistors connected in a parallel combination is found from the relationship 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 c (28.8) Req R1 R2 R3 Circuits involving more than one loop are conveniently analyzed with the use of Kirchhoff’s rules: 1. Junction rule. At any junction, the sum of the currents must equal zero: a I50 2. Loop rule. The sum of the potential differences across all elements around any circuit loop must be zero: a i 1t 2 5 e e2t/RC R When a resistor is traversed in the direction of the current, the potential difference DV across the resistor is 2IR. When a resistor is traversed in the direction opposite the current, DV 5 1IR. When a source of emf is traversed in the direction of the emf (negative terminal to positive terminal), the potential difference is 1e. When a source of emf is traversed opposite the emf (positive to negative), the potential difference is 2e. (28.14) (28.15) where Q max 5 C e is the maximum charge on the capacitor. The product RC is called the time constant t of the circuit. Objective Questions (28.10) DV 5 0 closed loop If a capacitor is charged with a battery through a resistor of resistance R , the charge on the capacitor and the current in the circuit vary in time according to the expressions q(t) 5 Q max(1 2 e2t/RC ) (28.9) junction If a charged capacitor of capacitance C is discharged through a resistor of resistance R, the charge and current decrease exponentially in time according to the expressions q(t) 5 Q ie2t/RC i 1t 2 5 2 Qi RC e2t/RC (28.18) (28.19) where Q i is the initial charge on the capacitor and Q i /RC is the initial current in the circuit. 1. denotes answer available in Student Solutions Manual/Study Guide 1. Is a circuit breaker wired (a) in series with the device it is protecting, (b) in parallel, or (c) neither in series or in parallel, or (d) is it impossible to tell? 2. A battery has some internal resistance. (i) Can the potential difference across the terminals of the battery be equal to its emf? (a) no (b) yes, if the battery is absorbing energy by electrical transmission (c) yes, if more than one wire is connected to each terminal (d) yes, if the current in the battery is zero (e) yes, with no special condition required. (ii) Can the terminal voltage exceed the emf? Choose your answer from the same possibilities as in part (i).