Analysis of Very Fast Transient over Voltages (VFTOs) of
advertisement

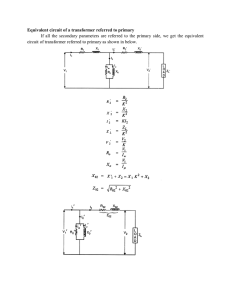
3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 Analysis of Very Fast Transient over Voltages (VFTOs) of Transformer in Gas Insulated Substations (GIS) using Wavelet Techniques (WT) Prakasam.K, Surya Kalavathi.M, Prabhavathi.D *PhD schalor, JNTUCEA, Anantapur India, prabhavathi10@gmail.com, 9966783293,Prof, JNTUHCEH, Hyderabad, India,munagala12@yahoo.co.in,PhD schalor, JNTUCEAAnantapur, India, gvitgem@gmail.com,9966783293 Keywords: Analysis; Damping; mitigation; surge; transients, wavelet Abstract Switching operating generates very fast transient over voltages(VFTOs) in gas insulated substations (GIS) and it is very dangerous to transformers and causes the damage to insulation because of its short rise time, in some cases its magnitude may be very close the basic insulation level (BIL),Mitigation and analysis of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) of power transformer is very important in gas insulated substations (GIS) as very fast transient over voltages causes’ damage to the insulation of the power devices like transformer. In this research work power transformer is considered as it plays major role in the electrical substation. Initially a power transformer rating of 500MVA in 765kV/400kV gas insulated substation with the load of 3 X 500MW capacity has been considered and the simulation model is developed using Mat Lab platform on the basis of very fast transient (VFT). The very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) generated due to circuit breaker (CB) operation has been evaluated at transformer, open end and circuit breaker (CB) and in the next sate of this research work, mitigation methods like RC filter and Ferrite ring have been employed and then the effect the proposed damping methods on peak magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) [5, 4, 11] has been evaluated. In the further stage, the effect of terminal components on peak of VFTOs has been estimated for two time constants 1ns. The outcome of the proposed techniques again is explored to wavelet transform (Db4) for extraction of high frequency signals. As wavelet transform is a powerful tool for analysis very fast transient signals. The results shows that peak value of VFTOs can be reduced to considerable level by employing the proposed damping methods and it has proved that the terminal components of gas Insulated substation (GIS) also influences the peak magnitudes of VFTOs. 1 Introduction The power system is large and interconnected one in which the transformer plays an important role and thereby it is very essential to protect it against the internal and external faults as well as from the over voltages due to any reason particularly when it is used in gas insulated substation since there is always possibility continuously the likelihood of reason for fast transient over voltages. Gas insulation substations (GIS) have been utilized as a part of force frameworks in the course of the most recent three decades on account of their high unwavering quality, simple support, and small ground space necessity and so on. In India likewise, a couple GIS units are under different phases of establishment. The basic insulation level (BIL)[7] required for a gas insulated substation (GIS) is different from that of the conventional substation because of certain unique properties of the former. Switching operations generate very fast transient over voltages (VFTOS) [1, 2, 7, 9] VFTOS may cause secondary breakdowns inside a GIS and Transient Enclosure Voltages (TEV) outside the GIS, Prolonged arcing may produce corrosive / toxic byproducts, Support spacers can be weak points when arc by products and metallic particles are present, From the reliability point of view, partial discharge detection is important. The methods of detection are of electric systems etc. These methods lack quality control. For these reasons, VFTOs generated in a GIS should be considered as an important factor in the insulation design. The major Problems Associated with the Very Fast Transient over Voltages (VFTOs) generated in GIS causes , Flash over to ground at the disconnecting switch (DS) switch contacts, Failure of electronic control circuits connected to GIS due to electromagnetic interference of VFTOs, Dielectric strength is reduced under VFTOs, if non-uniform electric field is formed by the particles (primarily metallic), effect on equipments such as bushing, power transformer and instrument transformers, Transient Enclosure Voltage (TEV) on external surface of the sheath. This may cause flashovers to nearby grounded objects 2 Modelling of GIS Components Many authors have discussed about generation, computation, mitigation suppression [2, 12], measurement and analysis of very fast transient over voltages in different ways and many of the researchers presented their articles about mitigation and analysis of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) [9, 10, 5] in gas Insulated substations (GIS) however most of them considered low voltage low rating transformer and comparison given between the existing and proposed damping methods. This paper presents a robust 749 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 wavelet technique based analysis of peak magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) at transformer, open end and at the disconnecting switch (DS) along with the terminal components effects on peak values of VFTOs. An exact peak value of VFTOs must be measure for proper insulation design and to protect the transformer or other important electrical equipments in GIS and this can be achieved by the proposed technique. The wavelet transforms gives the accurate measurement [6] since the outcomes of wavelet transform is based on the time and frequency analysis, unlike individual time domain and frequency domain. The proposed 765kV/400kV, 500MVA GIS system has been designed on the basis of very fast transient (VFT) as very fast transients are travelling wave nature. The components of the proposed system are designed taking surge impedance, propagation velocity, formative time length and into account. 2.2 Circuit Breaker In the proposed work 1.5 model of circuit breaker (CB) [4, 11] fig.2 has been employed for switching transients and it can be designed as per open and closed conditions. During the closing operation of circuit breaker (CB) the electric field increases still sparking occur and the sparking occurs at power frequency first. 2.1Powet Transformer The power transform can be designed either by multi conductor model or by detailed model in general. However in gas insulated substation the very fast transit over voltages generated due to switching operations is of high frequency in Thank you for your cooperation in the range of MHz and non stationary with very short rise time. The windings transformer at very high frequency behaves like capacitive network [7,8, 10] there by it should be treated as coactive nature, the series capacitance and shunt capacitance should be considered to evaluate an exact value of VFTOs. In the proposed system the parameters of transformer are calculated on the basis of VFT. Since the transformer coil at high frequencies behaves as capacitive network the modelling of transformer[7] has been designed based on very fast transients(VFT)[7, 8, 9] i.e. The parameters of transformer are estimated for accurate simulation results and are given by R1 = 22.8 Ω , R2=22.8 Ω,R3=300 Ω and inductance of the coils L1= 5.µH, L2 = 47.5 µH , L3 = 9.42 µH and the capacitance C1 = 0.84pF, C2 = 1.74pf, C3 = 35.4pF, C4 = 120pF the surge impedance, velocity of propagation, formative time and length are considered as well as the series capacitance between the turn and coil and the shunt capacitance between the turn[6], coil and grounded core and transformer tank are considered for accurate results of the peak magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs).The parameters of power transformer is estimated as per the very fast transient nature for accurate measurement of VFTOs [1, 5, 8]. Fig1 shows the equivalent circuit of power transformer in the proposed system. Fig.2.Equivalent circuit of circuit breaker (CB) During the closing operation of the circuit breaker (CB) the charging current flows and charge the load to the source voltage and voltage collapses and extinguish [5, 7]. The sparking charge depend on the speed of the circuit breaker (CB)The circuit breaker (CB)4, 11] is represented to by a PI section contains two travelling wave models [ 7], which is shown in figure 2, with the parameters as Z1=58 Ω, L1= 560mm L2=390mm, Z2 16 Ω, L3 = 400mm, C1=20µand C2=25µF. The sparkle utilized as a part of circuit breaker (CB) re-strike cases is displayed as an exponentially rotting resistance Ro e(-t/τ) in arrangement with a little resistance, r of 0.5 Ω to deal with the lingering flash resistance. Value of fixed resistance rs has been selected on the basis of the practical consideration as discussed. Where, R0 = 1012 Ω, Fixed Resistance =0.5Ω. T (spark time constant) = 1 ns, Open end section of GIS - The open ended section of GIS has been presented in the following figure where a lumped shunt capacitance has been considered. Assuming the same as a coaxial hemisphere, its capacitance has been estimated using following equation. Figure.1.Equivalent circuit of power transformer The surge impedance, propagation velocity and formative time can be evaluated from the equations (1), (2) and (3). Where, R= internal radius of enclosure, r=external radius of enclosure 750 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 3 Methods of Mitigation 4 Simulation Results and Conclusions In this section, the different possible and efficient methods of damping like, RC filter; Ferrite ring and also terminal components like OHTL, XLPE Cable and GIL have been presented in different sections as follows. The proposed system has been designed using mat lab plat form and simulated with different methods as mentioned earlier for the estimation of Very Fast Transient Over Voltages at transformer (Vtr), open end (Voc) and at circuit breaker (Vcb) and the outcomes of the proposed techniques are shown as follows 3.1 RC – Filter Method RC filters have been widely used in vacuum circuit breakers to suppress the over voltages. RC filter is parallel next to circuit breaker. In the proposed work, the comparable circuit of 765kV GIS is considered with likeness RC channel. The main reason of which is that capacitor absorbs the high frequency component and finally energy is consumed by the resistor because of this character of capacitor it has been executed as one of the strategy for mitigation and analysis The parameters of R and C are picked as per the literature survey as R can be chosen from 50 to 400 Ω and C can be from 0.01 to 0.2µF ,R = 100 Ω and C = 0.2µF and recreations are completed. Fig. 6.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Fig.7.Magnitude of VFTO at Open end (Voc) Fig. 4.Equivalent circuit of RC-Filter 3.2 Ferrite ring Method As per the literature survey it has been observed that, the VFTOs can damp to a great considerable level of peak using ferrite rings. The most of the authors tested the ferrite ring under low voltage and low frequency and conventional comparison given between the shunt resistor and ferrite ring, In this research work, we introduced a new method of analysis of very fast transient over voltages VFTOs which is known as ferrite ring in association with wavelet transform as the VFTOs are concern to high frequency transients R = 100 Ω, L = 2H and S at t = 10ms. Fig. 8.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit breaker (CB) Fig.9.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Db4 Fig.5.Ferrite ring Method 3.3 Terminal Components (OHTL, GIL & XLPE Cable) In the next stage of this research work, the gas insulated substation (GIS) has been terminated with over head transmission line, gas insulated line (GIL) and XLPE cable, the OHTL and cable parameters are estimated based on surge impedance (Z0) and propagation velocity (𝝊) with the equations (1) and (2).The parameters used shown below. For GIS Bus- Bar, Z0 = 270Ω, 𝝊= 270m/µs, OHTL, Z0 = 350, 𝝊 =300m/µs , XLPE Cable, Z0 = 30Ω, 𝝊= 1.9557X105 km/s The very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) at transformer, open end and at disconnecting switch has been estimated. Fig. 10.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Db4 Fig. 11.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit breaker (CB) Db4 751 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 Fig. 12.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Fig. 13..Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Fig. 14.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit breaker (CB) Fig. 15.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Db4 Fig. 16.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Fig. 19.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Fig. 20.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit breaker (CB) Fig. 21.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Db4 Fig. 22.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Fig. 23.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit breaker (CB) Fig. 17.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit breaker (CB) Fig. 24.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Fig. 18.Magnitude of VFTO at transformer (Vtr) Fig. 25.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) 752 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 Fig. 26.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit Breaker (VCB) Fig. 27.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Db4 Fig. 28.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Db4 Fig. 29.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit Breaker (VCB) Fig. 30.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Fig. 31.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Voc) Fig. 32.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit Breaker (VCB) Fig. 33.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Db4 Fig. 34.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Db4 Fig. 35.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit Breaker (VCB) Fig. 36.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Fig. 37.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Fig. 38.Magnitude of VFTO at circuit Breaker (VCB) Fig. 39.Magnitude of VFTO at Transformer (Vtr) Db4 753 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 Fig. 40.Magnitude of VFTO at open end (Voc) Db4 Fig. 41.Magnitude of VFTO at Circuit Breaker (VCB) Db4 Table 1: Peak Magnitudes of VFTOs with different methods in p.u PEAK VALUES OF VFTOS IN P.U No Damp OHTL CABLE GIL RC Filter Ferrite ring Method Vtr(p.u) Vds(p.u) 3.28 Voc(p. u) 2.28 Direct Db4 2.79 1.88 1.65 Direct 2.43 1.72 2.21 Db4 1.79 1.69 2.18 Direct 1.49 1.48 1.16 Db4 1.52 1.47 1.21 Direct 1.64 1.51 1.86 Db4 1.6 1.51 1.98 Direct 1.18 1.14 1.124 Db4 1.08 1.09 1.047 Direct 1.08 1.12 1.15 Db4 1.08 1.097 1.095 2.12 The magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) without any damping is found 2.89 p.u at transformer (Vtr), 1.98p.u at open end (Voc) and 1.87p.u at circuit breaker (VCB).With the application of RC filter the magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) has been considerably reduced 1.18p.u, 1.14p.u and 1.1234p.u respectively and steepness of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) is also considerably reduced and which can be observed from figure 43 to figure 48, particularly at circuit breaker it has been considerably reduced to low level. However the impact of RC filter is very good at transformer and it has no much effect at open end and the same can be observed from the same figures. (Very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) is 1.01p.u with RC filter at open end) .Which can be understood that, RC filter can protect the transformer only, though it reduces the very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) to very low level. To overcome this problem the proposed system is employed with a new technique named as ferrite ring, with the ferrite ring method the magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) has been reduced to very considerable level 1.08p.u, 1.12 and 1.15p.u at transformer, open end and circuit breaker respectively. Comparing with the above methods the ferrite ring has very good impact on very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) and can reduce the very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) to almost unity and fatherly the steepness of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) is also considerably reduced. However no of ferrite ring to be connected is depends on the operating voltage, pressure, surge impedance, formative time constant and length also. In the present research work, the influences of terminal components OHTL, GIL and XLPE cable on magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) also studied and it has been observed that the magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) is high (2.43p.u at transformer, 1.72p.u at open end and 2.21p.u at circuit breaker respectively) when GIS is terminated with over head transmission line (OHTL) and is low when terminated with cable (1.52p.u at transformer, 1.47p.u at open end and 1.21p.u at circuit breaker respectively) and the magnitude of very fast transient over voltages (VFTOs) is in between OHTL and XLPE cable (1.64p.u at transformer, 1.51p.u at open end and 1.51 at circuit breaker respectively). From the study of influence of terminal components on magnitude of VFTOs it has come to conclude that, the magnitude of VFTOs can be somewhat reduced by terminating with the XLPE cable. Finally, by this research work it has come to conclude that by employing the above mitigation methods the magnitude of very fast transient over voltages at transformer, open end and at circuit breaker can be reduced to very considerable level with RC filter and ferrite ring compared to other methods. By this study it has been concluded that the terminal components also influences the magnitude of VFTOs. In the present research work the formative time constant τ is considered as 1ns. Last but not the least, by employing wavelet transform (WT) an exact, crisp and accurate measurement has been done in this analysis since the wavelet transform (WT) is a power full tool for extraction of high frequency transient signals and is tabulated in table 1. Acknowledgements Affirmations I might want to express my gratitude to Prof. Prof M Surya Kalavathi who has taught me to seek after this 754 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Engineering Trends, Communication, Optimization and Sciences (EEECOS)-2016 work and taught me the "Mitigation methods and Analysis of very fast transient over voltages of transformer in gas insulated substation and 'Applications of wavelet transform (WT) in Electrical Engineering' is my pleasure to recognize part of my co creator D.Prabhavathi in fulfillment of this research work. References [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] Bi.Tiechen,Lu.,Zhang,“Calculation of Very Fast Transient Overvoltage in GIS”, IEEE/PES Conference on Transmission and Distribution, Vol.4, 2005. Kamakshaiah.,“Simulation and measurement of very fast transient over voltages in a 245kv gis and research on suppressing method using ferrite rings” ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, vol. 5, No. 5, 88- 95, 2010. V.Vinod Kumar, Joy .M.Thomas and M.S. Naidu, “VFTO Computation in a 420kV GIS”, Eleventh International Symposium on High Voltage Engineering, (Conf. Publ. No. 467), pp. 319-32,199. S.A. Boggs, F.Y.Chu and N. Fujimoto“Disconnect Switch Induced Transients and Trapped charge in GIS’, IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, Vol. PAS-101, pp. 3593-3596,1998. Y. Shibuya, S. Fuji, and N. Hosokawa, “Analysis of very fast transient over voltage in transformer winding”, IEE Proc. Generation transmission and distribution, Vol.144, No.5, pp461-46, 1997. H. Nobuhiro Shimoda,I.,Murase, and H.Oshima ,Aoyagi, I. ,Miwa, "Measurement of transient voltages induced by disconnect switch operation", IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, PAS-104NO. 1, 1985. J.A.P. MartinezmR.Iravani,A. Keri and D. Povh(1998)1” Modeling guidelines for very fast transients in Gas Insulated substations”, IEEE working group modeling and analysis of system transients,Vol.11,no.4, pp, 20282047 N.Hosokawa, ‘Very fast Transient Phenomena associated with Gas Insulated Substations’, CIGRE, pp. 33-13, 1996. S.Cariimavoid and R.Mahmutdehajid,“More accurate modeling of Gas insulated components in digital simulations of very fast transients”, IEEE Transactions on Power delivery, Vol.7, NO.1, pp. 434-441, 1963. R. Witzman ‘Fast Transients in Gas Insulated substations – Modeling of Different GIS components’, Fifth ISH, Braunschweig,. WorkingGroup33. Pp.13-09, ‘Very Fast Transient Phenomenon Associated With GIS, CIGRE, 1998. U. Riechert, Krüsi and D. Sologuren-Sanchez, “Very Fast Transient Overvoltage’s during Switching of BusCharging Currents by 1100 kV Disconnector”, CIGRÉ Report A3-107, 43rd CIGRÉ Session, pp.22-27,2010 S. Burow,U.Riechert, W.Köhler and S.Tenbohlen, “New mitigation methods for transient overvoltages in gas insulated substations”2013. 755