HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms
advertisement

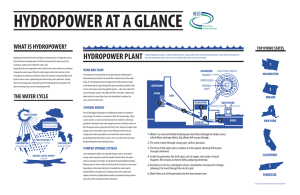
HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Alternating current (AC) Electric current that reverses direction many times per second. Ampere A measure of electric current (similar to describing water volume in cubic feet per second). Ancillary services Operations provided by hydroelectric plants that ensure stable electricity delivery and optimize transmission system efficiency. Cavitation Noise or vibration causing damage to the turbine blades as a result of bubbles that form in the water as it goes through the turbine. Cavitation causes capacity loss, head loss, efficiency loss. Conductor Material, such as wire or cable, used to carry electricity. This term can also be used in reference to a pipeline that carries water. Consumption End use of energy and energy sources, such as electricity, and is typically measured in kilowatt-hours. Current The flow of electrons in an electrical conductor - measured in amperes. Dam A barrier constructed to store or divert water for different purposes, including electricity production. Typically made of earth, rock, or concrete. Direct current (DC) Electric current that flows in one direction. Distribution A process of moving power at lower voltages from substations to customers. Draft tube A water conduit that maintains a column of water from the turbine outlet to the downstream water level, which can be straight or curved depending upon the turbine installation. Efficiency A percentage obtained by dividing the actual power or energy by the theoretical maximum power or energy available. It represents how well the hydropower plant converts the potential energy of the water into electrical energy. Electric energy Power delivered over a period of time; commonly measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) or megawatt-hours (MWh). HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Electric power Rate of electric energy delivery; also a measure of a power plant’s generating capacity or installed capacity; the basic measures are the kilowatt (kW) and megawatt (MW). Environmental assessments Planning and decision-making tool used by industry and regulators to identify the environmental impacts and costs of proposed energy projects, and potential solutions. Fish ladder A series of pools arranged like steps that allow fish to pass upstream over a dam. Flow Volume of water, expressed as cubic feet (or cubic meters) per second. Flow management Management of hydroelectricity operations to control downstream water flows and their effects. Generating capacity A power plant’s ability to produce a specific amount of electricity at a specific moment in time; measured in kilowatts or megawatts - also known as “installed capacity” or “nameplate capacity”. Generation The process of converting different forms of energy — thermal, mechanical, chemical, or nuclear, into electricity. Gigawatt (GW) A measure of electric power; the equivalent of 1,000 megawatts or 1 million kilowatts. Gigawatt-hours (GWh) A measure of electric energy; the equivalent of 1,000 megawatt-hours or 1 million kilowatt-hours. Grid A regional or nation-wide network of high-voltage transmission lines. Head The vertical change in elevation expressed in either feet or meters, between the reservoir (“head water”) level and the downstream river (“tailwater”) level. Headwater The water level above the powerhouse or at the upstream face of a dam. HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Hydropower (“Hydro”) The process of generating electricity by capturing the potential energy of falling water through the use of a water wheel (turbine) to mechanically spin rotating magnets which create electrical current that can be distributed to users by transmission lines. Large Hydropower: Although definitions vary, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) defines large hydropower as facilities that have a capacity of more than 30 megawatts. Small Hydropower: The DOE defines small hydropower as facilities that have a capacity of 100 kilowatts to 30 megawatts. Micro Hydropower: A micro hydropower plant has a capacity of up to 100 kilowatts. A small or micro-hydroelectric power system can produce enough electricity for a home, farm, ranch, or village. Hydrologic Cycle The natural process by which water evaporates, primarily from the oceans as energy from the sun and wind is absorbed. Water vapor in the form of clouds is transported by winds to higher atmospheric levels and over land where water condenses and falls as precipitation (rain & snow). The cycle continues when water then runs off the land into rivers, and back to the oceans where the cycle repeats. Installed capacity The amount of power that can be generated at a given moment by a power plant. Usually measured in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW) – NOTE: actual generation is measured in kilowatt-hours or megawatt-hours. Intake The entrance to a turbine unit at a hydroelectric dam. Kilowatt A measure of electric power; the equivalent of 1000 watts. Kilowatt-hour (kWh) A measure of electric energy; the equivalent of 1,000 watt-hours (e.g. if you burn ten 100-watt light bulbs for one hour, they will use one kilowatt-hour of electricity) – NOTE: residential customers are usually charged for electricity based on a rate of cents per kilowatt-hour. HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Load The total amount of electricity on a specific power system required to meet customer demand at any moment. Base Load Plant – Plant operates at maximum output at all times to provide maximum energy into the grid used to meet some or all of a given region's continuous energy demand. Load Following Plant (“Intermediate Peaking”) – A plant that operates at variable power output setting to meeting the changing energy demand of customers, usually slow moving changes such as from night periods to day periods. Dispatchable Power (“Fast Peaking”) – Dispatchable generation refers to sources of electricity that can be dispatched at the request of power grid operators; that is, generating plants that can be quickly turned on or off, or can adjust their power output on demand. HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Megawatt (MW) A measure of bulk power; the equivalent of 1,000 kilowatts or 1 million watts; the unit is generally used to describe the output of a generator. Megawatt-hour (MWh) A measure of electric energy; the equivalent of 1,000 kilowatt-hours or 1 million watthours – NOTE: Megawatt-hours are determined by a hydropower plant’s capacity and how long the plant is running (e.g. a 1,000-megawatt power plant running at full power for one hour produces 1,000 megawatt-hours (MWhs) of electricity; and if that plant runs all day, it produces 24,000 MWhs). Penstock A closed conduit or pipe for conducting water to the powerhouse. Power In electricity transmission, current delivered at a given voltage is measured in watts or kilowatts. Powerhouse The physical structure of an electric generating facility. Runner The rotating part of the turbine that converts the energy of falling water into mechanical energy. Scroll case A spiral-shaped steel intake guiding the flow into the wicket gates located just prior to the turbine. Spill The release of water from a dam or hydropower project without passing it through the powerhouse – NOTE: Typically a situation to be avoided as water “spilled” is lost powergeneration revenue. Spillway The structure or portion of a larger structure that is used to release excess water over or around a dam. HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Stratification A variation in temperature and quality of deep water as surficial water is warmed by the sun fostering biologic growth while colder, oxygen-depleted water sinks to lower levels. Substation An electrical facility where the voltage of incoming and outgoing circuits is changed and controlled. Supersaturation Change in water quality that occurs when turbulent water passing over a spillway absorbs and entrains free air. This process increases nitrogen levels in the water – NOTE: fish exposed to supersaturated water can be injured or killed when the nitrogen gas produces bubbles in their bloodstream. This effect is called “gas bubble disease” and is similar to “the bends” that can occur in human divers. Sustainable Ecosystem condition in which biodiversity, renewability and resource productivity are maintained over time. Sustainable development Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs (as defined by United Nations World Commission on Environment and Development). Tailrace The downstream channel that carries water away from a dam or powerhouse. Tailwater The water level downstream of the powerhouse or dam. Terawatt A measure of electric power, the equivalent of 1,000 gigawatts or 1 billion kilowatts; the unit is generally used to describe generating capacity at national or international levels. Terawatt-hour A measure of electric energy; the equivalent of 1,000 gigawatt-hour or 1 billion kilowatthours. Transformer An electromagnetic device for changing alternating current (AC) electricity to higher or lower voltages. Transmission The process of moving electric power at high voltages from the generation facility to local communities. Turbidity Muddy or unclear water quality caused by suspended sediments. HYDROPOWER Basics Glossary of Terms Turbine A rotary engine that converts the energy of a moving stream of water, steam or gas into mechanical energy. TURBINE TERMS: Generator An arrangement of magnets spinning inside a coil of wire to produce electricity. Rotor The moving part of an electric generator – NOTE: the rotor's outer surface is covered with electromagnets and as the rotor turns inside the stator, the electrons in the copper windings "vibrate" such that their movement generates an electric current. Stator The stator is the stationary part of an electric generator – NOTE: the stator is comprised of a series of vertically oriented copper coils nestled in the slots of an iron core so that as the rotor spins its magnetic field induces a current in the stator's windings thereby generating electricity. Wicket gates Adjustable elements that control the flow of water from the scroll case into the turbine passage. Voltage A measure of the electric pressure that pushes electric current through a circuit (just as pressure causes water to flow in a pipe); measured in volts or kilovolts. Watershed Area draining into a stream or river. Watt A measure of electric power; standard light bulbs are rated at 25, 40, 60 or 100 watts.