Summary of CFV Exemptions
advertisement

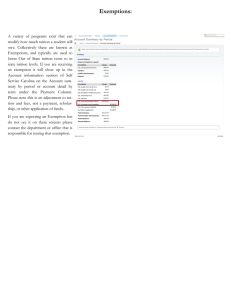
ON THE ROAD CFV EXEMPTIONS For Illinois Farmers In 2012, the US Congress passed a major transportation bill titled “Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century” — otherwise known as “MAP-21”. That Act included two substantial regulatory exemptions for agriculture— one dealing with Hours of Service and the other covering a broad range of farm exemptions from Federal Motor Carrier Safety Regulations for the Covered Farm Vehicle (CFV.) This document provides a general introduction to those exemptions. To date, Illinois has implemented exemptions for all but the CDL—expected by 2015. There are now two levels of exemptions. The agricultural exemptions for the CFV are in addition to the agricultural exemptions from Federal Motor Carrier Safety Regulations (FMCSRs) that had previously existed. This creates a two-tier exemption system allowing farmers to select the set of exemptions that best fits their purpose for any individual trip. Exemptions included for CFVs cover five major areas: Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) [49 CFR 383] Previously available to most farmers. MAP-21 exemption not yet available in Illinois. Controlled Substances and Alcohol Use and Testing [49 CFR 382] Previously available to most farmers. While the CFV exemptions are generous, they are more difficult to qualify for than those previous. CFV qualifiers generally include the previous requirements that the driver be a farmer or employee and hauling for the farm and not for hire, but then adds two additional hurdles to qualifying. First, the truck has to be identifiable as a farm vehicle. In Illinois, that means it will have to be “farm” plated. And, if it’s a truck and trailer combination, Illinois will require that both the truck and the trailer have “farm” plates. Because farmers are each allow to register only a limited number of vehicles with a “farm” plate, those with more vehicles will not be able to take advantage of this CFV exemption in non-”farm”-plated trucks. [Under the previous exemption, the vehicle had only to be used for farming, not be registered as such.] Hours of Service [49 CFR 395] Previously available to virtually all farmers. Secondly, the MAP-21 exemption for covered farm vehicles does not apply if the vehicle is required to be placarded due to a cargo of hazardous material. The most likely problem spots here will be anhydrous nurse tanks and larger quantities of diesel fuel. [Under the previous exemptions, placarding was not a factor.] Inspection, Repair and Maintenance [49 CFR 396] Not previously available to farmers. Start-up problems are anticipated. Physical Qualifications and Examinations [49 CFR 391, Subpart E] Previously available only to some farmers. The CDL exemption is not yet effective in Illinois. Though all other CFV agricultural exemptions have been enacted in Illinois, the CDL exemptions will require a legislative change by the Illinois General Assembly. That action is expected to be completed in the spring of 2014, with an effective date likely in 2015. So, for now, only the CDL exemptions that preceded MAP-21 are available to Illinois farmers. Both farmers and the law enforcement community will be confused for a while; if for no other reason than the change is new. But that’s compounded by the fact that there are now two layers of exemptions, each with different sets of qualifiers. And to top if off, the CDL provisions have yet to be implemented—awaiting legislation—while the rest of the CFV exemption is in place in Illinois. And finally, exemptions in other states can be at differing stages of implementation, adding to the confusion. A Summary of Agricultural Exemptions for the CFV QUESTION HOS EXEMPTION COVERED FARM VEHICLE (CFV) Who can use the exemption? Anyone Farmer, their employees or family members What commodities are covered? Agricultural commodities, farm supplies, livestock, inputs Agricultural commodities, farm supplies, livestock, machinery Are special plates or other vehicle identification required? No Yes [The following apply in the State of Illinois] Truck must be registered as a “farm” vehicle Where truck and trailer are combined, both vehicles must display the “farm” plate On semis, the tractor must be “farm” plated; the semi-trailer may have an “ST” or “Apportioned” plate Does the size of the vehicle affect the exemption? No Yes If ≤ 26,001 pounds GVW or GVWR, then exemption is available anywhere in the USA. If > 26,001 pounds GVW or GVWR, then exemption is available anywhere in the state of registration OR (if outside the state) within 150 air-miles of the farm. Are crop share arrangements included in the exemption? Yes Yes (Tenant may haul landlord’s share of grain.) (Tenant may haul landlord’s share of grain.) Does the exemption include for-hire transportation? Yes No What Parts of the FMCSA regulations are exempt? Part 395 – Hours of Service Part 382 – Drug and alcohol screening Part 383 – CDL [Illinois exemption not yet in place] Part 391 Subpart E – Driver Qualifications (e.g.: Medical Card) Part 395 – Hours of Service Part 396 – Vehicle Maintenance [Illinois law still applies] Do mileage limits apply to the exemption? Yes Depends on the size of the vehicle: (Limited to 150 airmiles from the distribution point, whether wholesale or retail.) If ≤ 26,001 pounds GVW or GVWR, then exemption is available anywhere in the USA with no mileage restriction. The above chart is based on a document provided by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administra on (FMCSA.) Revised 2014-02 B If > 26,001 pounds, then exemption is available in the state of registration OR (if outside the state) within 150 air-miles of the farm. This document prepared and provided by: Copyright 2014 © Illinois Farm Bureau®