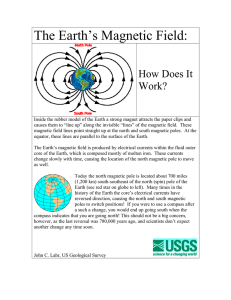
) William Gilbert (1544-1603) 1600 – The Earth is a Big Magnet
advertisement

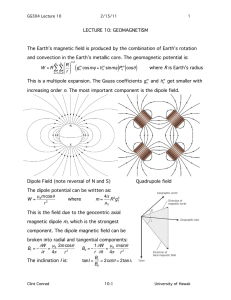
Week 38 Lecture 9: • Internal magnetic field • Magnetic elements • Dipole description • Spherical harmonic analysis of B-field Lecture 10: • Magnteosphere shape/modified by external currents • Stand-off distance • L-shell mapping • Chapmann Ferraro current • Tail currents History 221-206 BC : Probably first compass made in China (during Qin dynasty) 800-1050 AD: Compass seems to have become a usual tool for navigation 1596 : Barentz makes the first measurements of declination in Norway after it became clear that compass does not point exactly north 1600 : Gilbert suggested that the source of the Earth’s magnetic field lies inside the Earth & published ”De magnete” 1838 : Gauss introduced spherical harmonic analysis. History cont. ~1820 : Hans Christian Ørsted discovered the relationship between electric currents and Bfields 1896-1903 : Kristian Birkeland organized major campaigns to map the impact of solar activity on the Northern Light & Earth magnetic field ) William Gilbert (1544-1603) 1600 – The Earth is a Big Magnet Drift of the Magnetic North Pole from 1831 to 2006 Will the MNP be in Sibir in 40 years? B- Vector Field Which Pole is Which? • Field line perpendicular at Dip Pole (Dip=90°) • Dipole Axis (Dip<90°) Mathematical fit to observations is dipole with quadropole, octopole components • Eccentric Dipole Axis (Dip<90°) minimizes higher order poles by moving away from Earth’s center. Dip-polen (N1)-Dipol-polen (N2) omkring 1980