RBS
Rotational ball seat
Applications
■■
High-inclination wells
■■
Low-fracture pressure formations
■■
Well applications where liner string
consists of additional pressure-actuated
tools, such as external casing packers
(ECPs)
Benefits
■■
■■
■■
Minimizes risk of ball-seating failure in
horizontal sections
■■
■■
■■
Since the RBS is run in the setting string, it reduces formation pressure surges that are experienced when conventional liner toe ball seats shear. Once the liner hanger has been set and
the RBS sheared, a full-bore ID allows normal cementing operations, including the passage of
drillpipe wiper plugs.
Saves operation time in long liners
because ball does not have to reach
liner toe
Reduces risk of fracturing formation
because of sharp rise in equivalent
circulating density (ECDs) when conventional liner toe ball seats shear
Features
■■
The rotational ball seat (RBS) is a ball-type tubing-blockage device that is run in the liner setting
string. When pressure is required to set hydraulic liner systems, a drop-ball is released from
the surface and lands on the ball seat contained within the RBS. Increasing the pressure above
the predetermined shear value causes the ball seat to shear and rotate down. The drop-ball is
released, and a smooth and full ID is present through the tool.
Design that ensures that the ball is dislodged as the ball seat shears
Full-bore clearance after ball seat shears
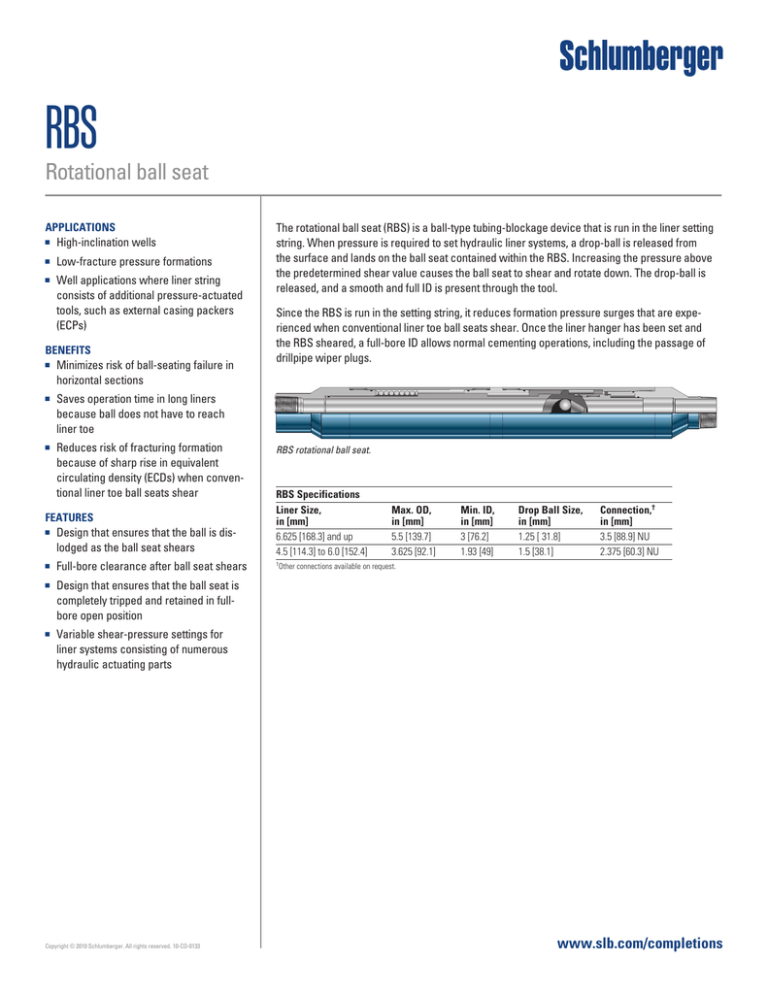
RBS rotational ball seat.
RBS Specifications
Liner Size,
in [mm]
6.625 [168.3] and up
4.5 [114.3] to 6.0 [152.4]
†Other
Max. OD,
in [mm]
5.5 [139.7]
3.625 [92.1]
Min. ID,
in [mm]
3 [76.2]
1.93 [49]
Drop Ball Size,
in [mm]
1.25 [ 31.8]
1.5 [38.1]
Connection,†
in [mm]
3.5 [88.9] NU
2.375 [60.3] NU
connections available on request.
Design that ensures that the ball seat is
completely tripped and retained in fullbore open position
Variable shear-pressure settings for
liner systems consisting of numerous
hydraulic actuating parts
Copyright © 2010 Schlumberger. All rights reserved. 10-CO-0133
www.slb.com/completions


