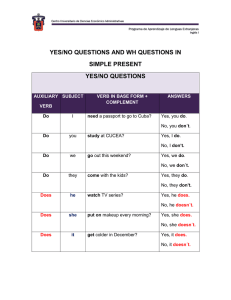
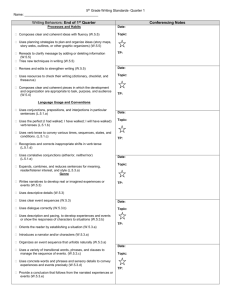
English Language Learners` Reference Guide Past Tenses
advertisement
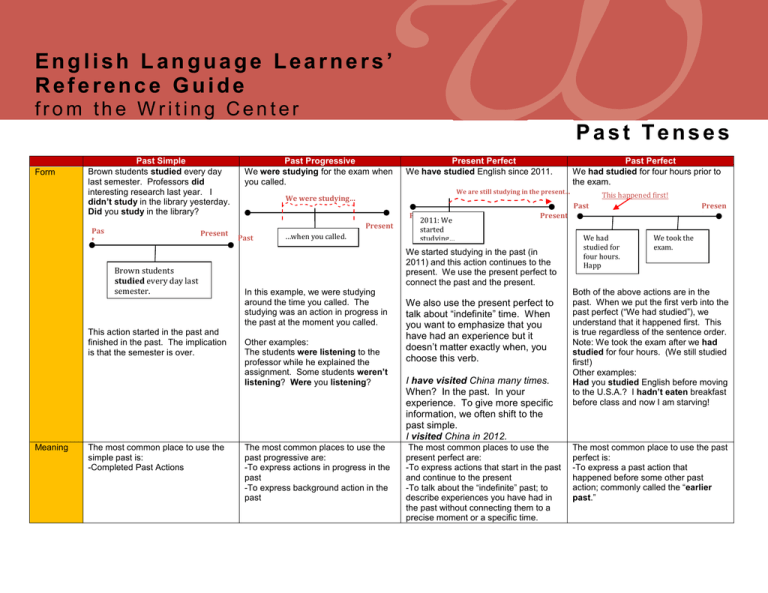
English Language Learners’ Reference Guide from the Writing Center Past Tenses Form Past Simple Brown students studied every day last semester. Professors did interesting research last year. I didn’t study in the library yesterday. Did you study in the library? Pas t Present Brown students studied every day last semester. This action started in the past and finished in the past. The implication is that the semester is over. Meaning The most common place to use the simple past is: -Completed Past Actions Past Progressive We were studying for the exam when you called. Present Perfect We have studied English since 2011. We are still studying in the present… We were studying… This happened first! Past Present Past Past Perfect We had studied for four hours prior to the exam. …when you called. Past 2011: We started studying… We started studying in the past (in 2011) and this action continues to the present. We use the present perfect to connect the past and the present. In this example, we were studying around the time you called. The studying was an action in progress in the past at the moment you called. Other examples: The students were listening to the professor while he explained the assignment. Some students weren’t listening? Were you listening? The most common places to use the past progressive are: -To express actions in progress in the past -To express background action in the past Presen t Present We also use the present perfect to talk about “indefinite” time. When you want to emphasize that you have had an experience but it doesn’t matter exactly when, you choose this verb. I have visited China many times. When? In the past. In your experience. To give more specific information, we often shift to the past simple. I visited China in 2012. The most common places to use the present perfect are: -To express actions that start in the past and continue to the present -To talk about the “indefinite” past; to describe experiences you have had in the past without connecting them to a precise moment or a specific time. We had studied for four hours. Happ We took the exam. Both of the above actions are in the past. When we put the first verb into the past perfect (“We had studied”), we understand that it happened first. This is true regardless of the sentence order. Note: We took the exam after we had studied for four hours. (We still studied first!) Other examples: Had you studied English before moving to the U.S.A.? I hadn’t eaten breakfast before class and now I am starving! The most common place to use the past perfect is: -To express a past action that happened before some other past action; commonly called the “earlier past.” Past Tenses Continued How to use it Past Simple The affirmative uses the base form of the verb +-ed. There are many irregulars which also must be memorized.* I You We They walked. He She It walked. *See the Irregular Verb Reference Guide for a list of the most common irregulars. Negatives Use the auxiliary verb did + not. -I did not walk. (I didn’t walk.) -She did not walk. (She didn’t walk.) *Note the use of the past on do means you don’t need it on the verb! Past Progressive When creating any progressive tense, BE is the auxiliary. In the present progressive, be is in the past form: WERE, and WAS. The verb must always been in the gerund (-ing) form. I was walking. was walking. were walking. They Use NOT between be and the verb. -I was not walking to class in the rain. (I wasn’t walking…) -She was not walking to class in the rain. (She wasn’t walking…) I You have walked. We They He She has walked. I You Subject Verb you live? you living last year at this time? you lived in the U.S.A.? you lived before coming to Brown? Yes/No Questions Auxiliary Subject Verb Did you eat lunch on campus? Were you eating at the Ratty at noon today? Have you eaten in the Ratty? had walked. We They had walked. It Use NOT between had and the verb. -I had not walked to school before I bought a warm jacket. (I hadn’t walked…) -She had not walked to school because she preferred the bus. (She hadn’t walked…) Asking questions in the Past Tenses Basic questions follow a specific formula in English. You can use this formula across verb tenses as long as you update the auxiliary and verb form. Key Terms Auxiliary Verbs: “Grammatical” verbs which do a job in the sentence but don’t carry meaning. Because they “help” create a tense, a negation, or a question, they are often called “helping verbs.” Past Participle: For regular verbs, the past participle is the verb+ed. For irregular verbs, the past participle form is found in the third column. For example, the verb to speak is irregular and its breakdown is: SPEAK SPOKE SPOKEN. Spoken is the past participle to be used with simple perfect tenses. Note that the second column form, Spoke is to be used in the simple past. Need more help: Email Rachel Toncelli, ELL Director, at ellwriting@brown.edu for a schedule of English Language Seminars. He She It Use NOT between have/has and the verb. -I have not walked to school this year. (I haven’t walked…) -She has not walked to school this year. (She hasn’t walked…) Information Questions Question Word Auxiliary Where did Where were How long have What had Question Word Past Perfect Use the past of HAVE to create the past perfect. Use HAD in all persons. He She It You We Present Perfect When creating any perfect tense, HAVE is the auxiliary. In the present perfect have is in the present form: HAVE or HAS. The verb must always be in the past participle.