Photo Detector - Stanley Electronic Components
advertisement

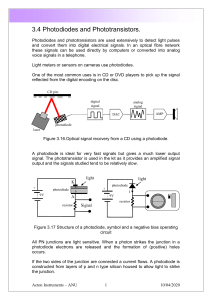
Photo Detector Ip Photodiode Electron Conduction band Incident light Features 2. n RL A photodiode is a semiconductor device which converts the light to electric energy when exposed to light. It comes in a package for use as an electronic component. 1. VR p hν Excellent linearity of the output current with respect to incident light Eg(eV) hν Depletion layer P-layer Quick response I-layer h: Planck’s constant Eg: Energy gap Hole Band gap Valence band N+-layer v: Frequency of light 3. Wide spectral response 4. Long life Fig. 1: Action of a PIN photodiode 5. Small output change with respect to temperature changes 6. Small output current up to the conduction band, thus leaving holes in the valance band and generating carriers. The carriers thus generated in the depletion layer separate due to electrical field conductivity, so that the electrons move to the N region, and the holes move to the P region. At this time, the number of carriers generated is basically in proportion to the luminance of the light, and a photocurrent flows through the photodiode. The size of the photocurrent is roughly proportional to the intensity of the light. Phototransistor A phototransistor is designed to amplify the output from a photodiode using a transistor. Compared to the photodiode, it provides higher output signal levels. Characteristics of a phototransistor 1. Large photocurrents 2. Slow response 3. Long life 4. Poor output current linearity with respect to incident light A PIN photodiode is a device that has a significantly thick I-layer between the PN junction. This widens the depletion layer when a reverse bias is applied, and allows the diode to be used at a high reverse bias voltage. The high electrical field conductivity in the wide depletion layer prompts the carriers to move, and has the effect of increasing response. 5. Large output changes temperature changes Phototransistor with respect to The phototransistor amplifies a photocurrent using the amplification function of a transistor, to compensate for the low sensitivity of photodiodes and PIN photodiodes. It has a structure that basically combines a photodiode and a transistor (see Fig. 2). When light strikes the depletion layer between the base and collector and its surrounding area, the photocurrent that is generated becomes the base current for the transistor and is amplified by the transistor’s amplification factor ß. However, the photocurrent between the base and collector flows slowly, because it flows with the diffusion of the carriers. It also has a slower response than a photodiode or PIN photodiode, because the large diffusion of the carriers causes the Principle of Operation Photodiode The photodiode has a PN junction consisting of a P-type semiconductor region on the light receiving side and an N-type semiconductor region on the substrate side (see Fig. 1). Applying a reverse bias to the PN junction creates a depletion layer between the P-layer and N-layer, so-called because it has no mobile carriers. When light that has greater energy than the semiconductor band gap energy strikes the region near the junction of the photodiode (the depletion layer and the area surrounding it), the electrons in the valance band absorb the light and rise 2008 年 10 月、Oct 2008 スタンレー電気株式会社 Stanley Electric Co., Ltd 1/3 high frequency component inside the photocurrent to short-circuit. Reverse voltage [VR] The allowable amount of reverse voltage that can be applied from the cathode to the anode side of a photodiode. [V] Incident light Base hν Emitter Collector-emitter voltage [VCEO] n The allowable amount of voltage that can be applied from the collector side to the emitter side of a phototransistor. [V] p n Emitter-collector voltage [VECO] The allowable amount of voltage that can be applied from the emitter side to the collector side of a phototransistor. [V] Collector Fig. 2: Structure of a phototransistor Collector current [IC] Glossary of Terms The allowable amount of current that can flow from the collector side to the emitter side of a phototransistor. [mA] Vertical PIN photodiode Vertical phototransistor Collector loss [PC] A type of photodiode and phototransistor that is mounted on a printed substrate by inserting the leads through holes on the substrate. The photo detector is mounted on the lead frame and sealed with resin. The allowable amount of power that can be consumed by the photocurrent and collector voltage in a phototransistor. [mW] Dark current [ID] The current that flows through a photodiode when a reverse voltage is applied with light blocked out. [nA] Dark current [IC] The current that flows through a phototransistor when a positive voltage is applied with light blocked out. [µA] Vertical lamp types Chip phototransistor Photocurrent [IP] A type of phototransistor that is mounted on the surface of a printed substrate, or substrate-type phototransistors. The current that flows from the cathode to the anode side of a photodiode when incident light is applied under prescribed conditions. [µA] Photocurrent [IC] Substrate types The collector current that flows through a phototransistor when incident light is applied under prescribed conditions. [mA] Power dissipation [Pd] Radiation luminance [Ee] The radiant flux that is applied per unit area. [W/cm2] The allowable amount of power that can be consumed by the photocurrent and reverse voltage in a photodiode. [mW] 2008 年 10 月、Oct 2008 スタンレー電気株式会社 Stanley Electric Co., Ltd 2/3 Peak sensitivity wavelength [λP] The wavelength at which photosensitivity is greatest. [nm] Inter-terminal capacity [CT] The capacitance between the cathode and anode terminals of a photodiode. [pF] Collector-emitter saturated voltage [VCE(sat)] The voltage between the collector and emitter of a phototransistor under prescribed saturation conditions. [V] Response speed [tr⋅tf] The amount of time it takes for a photocurrent to rise from 10% to 90% or fall from 90% to 10% of its maximum value with respect to a pulsed light input. [ns or µs] Half intensity angle [Δθ] The distribution characteristic of photosensitivity in the direction of the optical axis of a lens. It is expressed as the range of angle through which the response is 50% of its peak value. [deg] Sensitivity [S] The amount of current that flows per energy of radiation from a single wavelength of light. [A/W] 2008 年 10 月、Oct 2008 スタンレー電気株式会社 Stanley Electric Co., Ltd 3/3