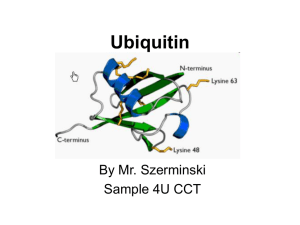
Introduction Conclusion References Contact Information Methods
advertisement

Network and Pathway Analysis of Post-translationally Modified Peptides Identified by Immunoaffinity-based Proteomics Jeffrey C. Silva1; Stuart Tugendreich2; Hongbo Gu1; Charles L. Farnsworth1; Kimberly A. Lee1; Xiaoying Jia1; Jian Min Ren1; Matthew P. Stokes1 1 Introduction Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA USA 01923; 2Ingenuity Systems, Redwood City, CA 94063 IPA® Canonical Pathways: Mapping identified proteins onto pre-defined signaling networks Post-translational modification of proteins provides critical regulation of protein activity, stability, and localization in nearly all aspects of cellular signaling. We have developed antibodies that recognize specific post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, methylation), consensus kinase substrate motifs, or peptides from proteins that reside in the same signaling pathway or pathways. The antibodies are used to immunoaffinity purify post-translationally modified peptides from cell lines, tissues, xenografts, or other biological materials which are then identified using LC-MS/MS, enabling identification of thousands of post-translationally modified peptides in a single LC-MS/MS run. Ingenuity® Systems pathway analysis software IPA® has been applied to these large datasets in order to facilitate interpretation of the LC-MS/MS data and provide a biological context to the results. A Acetyl Methyl Methods Ubiquitin PTMScan analysis (Rush et al. 2005, Lee et al. 2011, Kim et al. 2011) was performed on HCT-116 human colon carcinoma and mouse liver tissue peptides with the Acetyl-Lysine, Mono-Methyl-Arginine, or Ubiquitin Branch Antibodies from Cell Signaling Technology. Samples were run on LTQ-Orbitrap VELOS™ or Elite LC-MS/MS instruments and searches were performed using Sorcerer™ software (Lundgren et al. 2009). Results from each study were combined and imported into the Ingenuity® Systems IPA® software package. Core analyses were run on all proteins identified as well as proteins unique to each antibody using the Ingenuity Knowledge Base of genes and endogenous chemicals limited to direct interactions with experimental and high confidence predicted relationships. Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer B ® Acetyl Acetyl Methyl Methyl Ubiquitin Ubiquitin Figure 3: A. Bar graphs of the highest scoring canonical pathways for each antibody. B-D. Selected canonical IPA® Signaling Pathways are color-coded for each antibody (Acetyl = Red, Methyl = Blue, Ubiquitin = Green). A composite pathway is shown for each (Yellow highlights). IPA®-Generated Networks: De novo pathway assembly from identified proteins A A PI3K-Akt Signaling D Acetyl Methyl Ubiquitin Figure 1: PTMScan Method: Immunoaffinity purification workflow using motif antibodies for enrichment of acetylated (AcetylScan®), methylated (MethylScan™), and ubiquitinated (UbiScan®) peptides. Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency C Acetyl B Methyl C Ubiquitin B Sites Proteins Acetyl 10,191 3,195 Methyl 3,058 1,099 Ubiquitin 14,977 4,453 Ubiquitin Acetyl 4453 164 C 192 DNA Binding/Repair/Replication Enzyme 16.1 Ubiquitin 12.3 2.6 7.2 6.0 0.0 Methyl 8.2 12.8 15.0 0.2 1.4 Receptor/Transporter/Cell Surface 1099 16.5 7.7 Adhesion/Extracellular 100 38.9 6.7 Transcription Acetyl Methyl 13.4 1.9 RNA Processing Mitochondrial Protein 25.7 3.3 3195 1030 6.6 4.6 11.2 10.0 20.0 30.0 Percent of Total 40.0 Figure 2: PTMScan® results using Acetyl-lysine, Mono-methyl-Arginine, and Ubiquitin Branch motif antibodies. A. Number of nonredundant sites/proteins identified for each antibody. B. Area proportional Venn diagram showing the number of proteins identified using each antibody (black numbers) and overlap between antibodies (white numbers). C. Top seven most highly represented protein classes identified with each antibody. Protein type information from the PhosphoSitePlus® database. Figure 4: The top three IPA®-generated networks are shown for each antibody (A = Acetyl, B = Methyl, C =Ubiquitin). The overlap of the networks created for each antibody are shown with the selected networks displayed in detail. Conclusion References Ingenuity® Systems IPA® software provides in-depth analysis of the complimentary biological networks assembled using the Acetyl-Lysine, Mono-Methyl-Arginine, and Ubiquitin-Branch motif antibodies in PTMScan®. 1. Rush, J. et. al. (2005) Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 94–101. 2. Lee, K. A. et. al. (2011) J. Biol. Chem. 286(48):41530–41538. 3. Kim, W. et. al. (2011) Mol. Cell. 2011 Oct 21;44(2):325–340. 4. Lundgren, D. H. et. al. (2009) Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics Chapter 13, Unit 13 13. Contact Information © 2013 Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. / Cell Signaling Technology®, PhosphoScan®, PhosphoSitePlus®, PTMScan®, AcetylScan®, UbiScan®, and MethylScan™ are trademarks of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. / LTQ-Orbitrap® is a registered trademark of THermo Fisher Scientific. / IPA® is a registered trademark of Ingenuity Systems, Inc. / Sorcerer™ is a trademark of Sage-N Research. Jeffrey C. Silva, Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. Email: jsilva@cellsignal.com PTMScan® Services Department Email: ptmscan@cellsignal.com • web: www.cellsignal.com/services