Field Effect Transistors (FETs)
advertisement

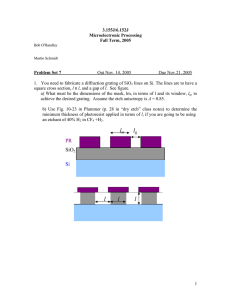
Field Effect Transistors (FETs) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) A junction field effect transistor is made up of a gate region diffused into a channel region. When control voltage is applied to the gate, the channel is depleted or enhanced, and the current between the source and the drain is thereby controlled. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET construction n-channel JFET – A junction field effect transistor having an n-type channel between the source and the drain. p-channel JFET – A junction field effect transistor having a p-type channel between the source and the drain. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET construction (continued) Gate – One of the field effect transistor’s electrodes (also used for thyristor devices [chapter 20]) Source – One of the field effect transistor’s electrodes. Drain – One of the field effect transistor’s electrodes. Channel – A path for a signal. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Junction field effect transistor (JFET) types Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET operations Drain Supply Voltage (+VDD) – The bias voltage connected between the drain and the source of the JFET, which causes current to flow. Gate-Source Bias Voltage (VGS) – The bias voltage applied between the gate and the source of a field effect transistor. Drain Current (ID) – A JFET’s source-to-drain current. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Relationship between a JFET’s DC supply voltage and output current. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Differences between BJT and JFET Current-Controlled Device (BJT) – A device in which the input junction is normally forward biased and the input current controls the output current. Voltage-Controlled Device (JFET) – A device in which the input junction is normally reverse biased and the input voltage controls the output current. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Unipolar Device (JFET) – A device in which only one type of semiconductor material exists between the output terminals and therefore the charge carriers have only one polarity (unipolar). Bipolar Device (BJT) – A device in which there is a change in semiconductor material between the output terminals (NPN or PNP between the emitter and the collector), so the charge carriers can be one of two polarities (bipolar). Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET characteristics Drain Characteristic Curve – A plot of the drain current (ID) versus the drain-to-source voltage (VDS). Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET characteristic curve Pinch-off Voltage – The value of VDS at which further increases in VDS will cause no further increase in ID. Constant-current Region – The flat portion of the drain characteristic curve. In this region ID remains constant despite changes in VDS. Breakdown Voltage (VBR) – The voltage at which a damaging value of ID will pass through the JFET. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET characteristics Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET characteristic curve (cont.) Drain-to-Source Current with Shorted Gate (IDSS) – The maximum value of drain current achieved by holding VGS at 0 volts. Gate-to-Source Cutoff Voltage or VGS(off) – The negative VGS bias voltage that causes ID to drop to approximately zero. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Transconductance Transconductance – Also called mutual conductance, it is the ratio of a change in output current to the initiating change in input voltage. ∆I D δm = ∆VGS δ m = transconduc tan ce in Siemens(S ) ∆I D = Change in drain current ∆VGS = Change in gate − source Voltage Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Voltage gain AV = δ m x R D Where AV = Voltage gain δm = Transconductance RD = Drain Resistor Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET data sheet Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET biasing Gate Biasing Self Biasing Voltage Divider Biasing Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Gate biasing VGS = VGG Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Gate biasing (Continued) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Self-biasing VG = 0 Volts Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Voltage divider biasing Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET circuit configurations Common-Source Common-Gate Common-Drain Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Common-Source (C-S) circuits An FET configuration in which the source is grounded and common to the input and output signal. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Common-Gate (C-G) circuits An FET configuration in which the gate is grounded and common to the input and the output signal. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Common-Drain (C-D) circuits An FET configuration in which the drain is grounded and common to the input and the output signal. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Source follower Another name used for a common drain circuit configuration. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen JFET applications Digital JFET Circuits Analog JFET Circuits Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Digital JFET circuits Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Analog JFET circuit Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Testing JFETs A transistor tester will test BJTs and JFETs. An ohmmeter can be used to test a JFET. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) The MOSFET has a metal gate that is insulated from the semiconductor channel by a layer of silicon dioxide. The input voltage at the gate will generate an electric field which will have the effect of changing the channel’s size. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen D-type MOSFET construction and types Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Types of MOSFETs Depletion-Type MOSFET – A field effect transistor with an insulated gate that can be operated in either the depletion or enhancement mode. n-Channel D-Type MOSFET – A depletion type MOSFET having an n-type channel between its source and drain terminals. p-Channel D-Type MOSFET – A depletion type MOSFET having a p-type channel between its source and drain terminals. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Operating Modes of MOSFETs Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen D-MOSFET biasing Zero Biasing – A configuration is which no bias voltage is applied at all. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen D-MOSFET application Cascode Amplifier Circuit – An amplifier circuit consisting of a self-biased common-source amplifier in series with a voltage-divider biased common-gate amplifier. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Dual Gate D-MOSFET A metal oxide semiconductor FET having two separate gate electrodes. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Enhancement-Type (E-Type) MOSFET Enhancement-Type MOSFET or E-MOSFET – A field effect transistor with an insulated gate that can only be turned ON if the channel is enhanced. n-Channel E-Type MOSFET – An enhancement-type MOSFET having an n-type channel between its source and drain terminals. p-Channel E-Type MOSFET – An enhancement-type MOSFET having a p-type channel between its source and drain terminals. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen E-type MOSFET construction and type Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen E-type MOSFET operation and characteristics Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen E-MOSFET biasing Drain-Feedback Biasing – A configuration in which the gate receives a bias voltage feedback from the drain: VGS =VDS Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Vertical-channel E-MOSFET An enhancement type MOSFET that, when turned ON, forms a vertical channel between source and drain. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Testing MOSFET with an ohmmeter Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen End of Field Effect Transistors (FETs) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen