product dissection 3/1/2015
PRODUCT
DISSECTION/UNDERSTANDING
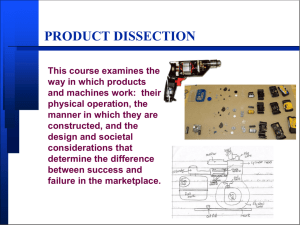
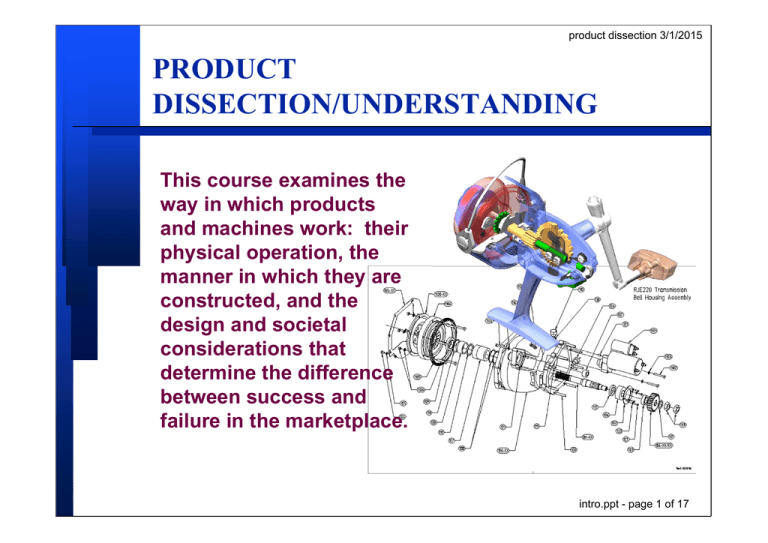
This course examines the
way in which products
and machines work: their
physical operation, the
manner in which they are
constructed, and the
design and societal
considerations that
determine the difference
between success and
failure in the marketplace.
intro.ppt - page 1 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
Course Philosophy
Not a traditional lecture class
Hands-on Experience:
I hear, I forget
I see, I remember
I do, I understand
intro.ppt - page 2 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
Retention versus Method how much do we retain?
Reading
Hearing Words
Looking at Picture
Watching Movie
Looking at Exhibit
Watching Demonstration
Seeing it Done
Participation in Discussion
Giving a Talk
Simulating Real Experience
Doing the Real Thing
10%
20%
30%
50%
50%
50%
50%
70%
70%
90%
90%
intro.ppt - page 3 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
Course Objectives
The primary objective of this course is to learn about
engineering and product design by:
• Dissecting existing consumer and industrial products to
determine how they function, how they were made and
how they might be improved
• Explaining that function by applying appropriate physical
principles
• Communicating that function effectively - oral, written,
electronic, graphic
• Developing visual reasoning skills and basic mechanical
knowledge
intro.ppt - page 4 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
Course Content
1.Product dissection, reverse engineering and
competitive analysis as a design tool
2.Team building
3.Materials and selection
4.The product design process
and the product life cycle
5.History of technology
The Design Process
ref . Engineering Design Graphics, J. H. Earle, pg 18,
used by permisison of Addison Wesley, ©1990, all rights reserved
intro.ppt - page 5 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
Course Content - continued
6. Consumer-product interaction issues: aesthetics,
ergonomics, “good design”, codes and standards,
safety, product liability, ethics, green design
7. Basic mechanical and electrical components and
measurements
8. Introduction to manufacturing processes and design
for manufacturability
9. Documenting and communicating a design
intro.ppt - page 6 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
Engineering knowledge ?!!!
Synthesis
Analytical Knowledge
Statics
GRADUATE ENGINEER
Design
Project
Math
Physics
Thermodynamics
Chemistry
Concurrent Eng.
Adv Mfg Processes
Mfg Processes
Product Dissection
Graphics and Design
Material Science
Dynamic
Engineering drawing
PRODUCT REALIZATION
intro.ppt - page 7 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
What will you get from this course?
1. Increased knowledge for mechanical and electrical
devices
2. Awareness of the “big picture” of the product design
process and the product life cycle
3. A greater awareness of how things are made
4. An appreciation of good design
5. Effective verbal, graphical and written
communication skills
6. A better idea of what engineers really do
intro.ppt - page 8 of 17
product dissection 3/1/2015
The Difference between an
Engineer and a Scientist
“The scientist seeks to understand the world and operates
against an absolute standard. His findings either describe
nature accurately or they do not. By contrast, the
engineer is problem oriented. He seeks not to describe
the world but to change it... The engineer also lives in the
world where science and values meet.” - Edward B. Fiske,
1989
“Scientists discover what is, engineers create what has
never been.” - Theodore von Karman, 1911
intro.ppt - page 9 of 17