π π π
advertisement

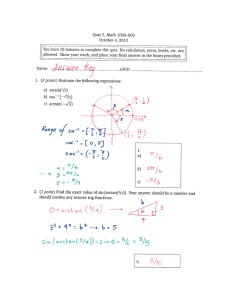
3/5/2012 Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions f ( x ) = arcsin x or f ( x ) = sin −1 x sin −1 x ≠ 1 sin x arcsin ( sin x ) = x sin ( arcsin x ) = x Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions −π π Definition : y = arcsin x is the number in , for which sin y = x 2 2 3 π Find arcsin = 3 2 3 when plugged into the sine function. 2 π π 3 Find the angle b / w − and on the unit circle that goes with a point with a y − value of . 2 2 2 Find the angle that gives −1 −π Find arcsin = 6 2 π π −1 Find the angle b / w − and on the unit circle that goes with a point with a y − value of . 2 2 2 Find arcsin ( −1) = −π 2 π π Find the angle b / w − and on the unit circle that goes with a point with a y − value of − 1. 2 2 1 3/5/2012 What is the derivative of y = arcsin x? from before: f ( x ) = sin x 1 ′ ( f −1 ) ( x ) = f ′ f −1 ( x ) f ′ ( x ) = cos x ( ) 1 ( f )′ ( x ) = cos ( arcsin x) 1 −1 ( f )′ ( x ) = ′ x = ( ) (f ) ( )( ) this is better written as 1 − sin ( arcsin x ) 2 1 −1 −1 f −1 ( x ) = arcsin x f −1 ′ x = ? since cos x = 1 − sin 2 x , we have −1 ( f )′ ( x ) = Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions remember sin ( arcsin x ) = x 1 − sin ( arcsin x ) 2 y = arcsin x 1 y′ = 1 − x2 1 1 − x2 Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions Let y = arcsin ( 3x ) . 3 Find y ′ . 6 y′ = 1 1 − ( 3x ) 2 ⋅ ( 3) 3⋅ 3 = 6 3 2 2 3 3 3 = y ′ = 1 3 6 1− 4 4 3 3 y ′ = 6 1 2 3 3 = 4 2 1 1 = 2 4 3 y ′ = 6 6 2 3/5/2012 Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions f ( x ) = arccos x or f ( x ) = cos −1 x cos −1 x ≠ 1 cos x arccos ( cos x ) = x cos ( arccos x ) = x Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions Definition : y = arccos x is the number in [ 0, π ] for which cos y = x −1 2π Find arccos = 3 2 Find the angle ( b / w 0 and π ) on the unit circle that goes with a point with a x − value of −1 . 2 3 π Find arccos = 6 2 Find the angle ( b / w 0 and π ) on the unit circle that goes with a point with a x − value of 3 . 2 Find arccos ( −1) = π Find the angle ( b / w 0 and π ) on the unit circle that goes with a point with a x − value of − 1. 3 3/5/2012 What is the derivative of y = arccos x? from before: f ( x ) = cos x 1 ′ f −1 ( x ) = f ′ ( x ) = − sin x f ′ f −1 ( x ) ( ) ( ) 1 ( f )′ ( x ) = − sin ( arccos x) 1 −1 f −1 ( x ) = arccos x f −1 ′ x = ? ( )( ) since sin x = 1 − cos 2 x , we have −1 ( f )′ ( x ) = Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions − 1 − cos ( arccos x ) this is better written as 2 ( f )′ ( x ) = −1 −1 remember cos ( arccos x ) = x 1 − cos ( arccos x ) 2 y = arccos x ( f )′ ( x ) = −1 −1 y′ = 1 − x2 Fall 2010 y′ = −1 ⋅ x −3/ 2 2 1 1− x ⇒ y′ ( 4 ) = −1 2 −1 ⋅ 1 2 ⋅ 43/ 2 1− 4 −1 ( ) −1 1 − x2 g= 1 = x −1/ 2 x g′ = −1 −3/2 x 2 2 1 1 since = x x y′ = Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions −1 ⋅ 3/2 1 2x 1− x −1 3/ 2 −1 −1 = ⋅ since 43/ 2 = 2 2 = 8 3 2 ⋅8 4 = 1 −1 −1 ⋅ = 3 16 8 3 2 y′ ( 4 ) = 1 8 3 4 3/5/2012 f ( x ) = arctan x or f ( x ) = tan x −1 lim arctan x = x→− ∞ Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions −π 2 lim arctan x = x →∞ 1 tan −1 x ≠ tan x π 2 arctan ( tan x ) = x tan ( arctan x ) = x Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions −π π Definition : y = arctan x is the number in , for which tan y = x 2 2 Find arctan ( −1) = −π 4 tan ( π2 ) = undef tan ( π3 ) = 3 tan ( π4 ) = 1 Find arctan ( 3 ) = π3 1 3 tan ( π6 ) = tan ( 0 ) = 0 −1 −π Find arctan = 6 3 tan ( −6π ) = −1 3 tan ( −4π ) = −1 tan ( −3π ) = − 3 tan ( −2π ) = undef 5 3/5/2012 What is the derivative of y = arctan x? from before: f ( x ) = tan x 1 ′ f −1 ( x ) = f ′ ( x ) = sec 2 x f ′ f −1 ( x ) ( ) ( ) 1 ( f )′ ( x ) = sec ( arctan x) Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions f −1 ( x ) = arctan x f −1 ′ x = ? ( )( ) since sec2 x = 1 + tan 2 x, we have −1 2 ( f )′ ( x ) = 1 + tan (1arctan x ) −1 this is better written as 2 ( f )′ ( x ) = 1 −1 1 + tan ( arctan x ) remember tan ( arctan x ) = x 2 y = arctan x ′ x = ( ) (f ) −1 1 1 + x2 Why is the word arc used? y′ = 1 1 + x2 Math 103 – Rimmer 3.9Inverse Trig. Functions arclentgh s = rθ On the unit circle r = 1,so s = θ 6