Atmosphere
advertisement

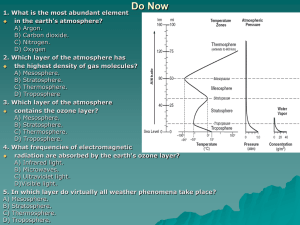
Bell Ringer 1) Which answer below is NOT a positive effect of volcanism? a) Source of geothermal energy b) Deposits minerals c) Creation of ‘new’ crust d) Results in fertile soils e) Creation of sedimentary rocks 2) Earthquakes and volcanoes are most alike because… a) Both can occur at the midlines of tectonic plates b) Both can occur as a result of transform plate boundaries c) Both can occur along fault lines d) Both can occur as a result of convergent plate boundaries e) Both are a result of convection currents in the earth’s mantle 3) A volcanic eruption with high silica content will… a) Produce very viscous lava, flowing slowly b) Produce very runny lava which flows quickly, covering a large amount of land c) Produce an interplate volcano d) Create a caldera, resulting in an underground volcano e) Produce new land such as the Hawaiian Islands 4) Which answer below describes subduction? a) Two plates slide past each other b) Two plates converge; the pressure pushes both plates upward c) Two plates converge; one plate moves below the other d) Two plates move apart from each other e) Two plates move perpendicular to each other The Atmosphere Chapter 17 pgs 474-476 The Atmosphere • Atmosphere – thin layer of gases which surround Earth. The Atmosphere • Atmosphere – thin layer of gases which surround Earth. • Jobs of the atmosphere include: • Providing oxygen • Absorbing solar radiation • Burning up incoming meteors • Transports and recycles water • Moderates climate Composition • The atmosphere is: – 78 % Nitrogen gas – 21% Oxygen gas – 1% Argon gas – Traces of several other gases Composition • These trace gases include: 1) Permanent gases – gases whose minute concentrations remain stable Gas Neon Helium Atmospheric Concentration 0.0018% 0.0005% Composition • These trace gases include: 1) Variable gases – gases whose concentrations vary, depending upon time of year or location. Gas Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide Atmospheric Concentration 0 – 4% 0 – 0.038% History • Throughout earth’s history, the composition of the atmosphere has changed dramatically. History • Throughout earth’s history, the composition of the atmosphere has changed dramatically. The atmosphere was mostly carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen until about 2.7 million years ago when photosynthetic organisms in the ocean began to produce oxygen. History • Throughout out earth’s history, the composition of the atmosphere has changed dramatically. History • Throughout out earth’s history, the composition of the atmosphere has changed dramatically. Today, human activity is greatly altering the quantities of certain gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane and ozone. 4 Layers • The atmosphere is composed of four distinct layers. • Each layer has specific characteristics which aid in the continuation of life on earth. Atmosphere Model • Each group must: – Make a beginning marker for their layer w/ elevation and temp – Make an ending marker for their layer w/ elevation and temp – Make an informational mini-poster about their layer highlighting any other important information (temperature, ozone levels, air density, etc.) – Hang the posters in the appropriate areas of the hallway When all the posters are hung, we are going to take a trip through the atmosphere. One person from each group will teach the rest of us about their layer. Bell Ringer 1) The atmosphere is primarily… a) Oxygen b) Hydrogen c) Nitrogen d) Argon e) Carbon Dioxide 2) Scientists are optimistic that the hole in the ozone layer may completely fix itself by 2050. Which international treaty is most responsible for leading to the improvement of the ozone layer? a) The Kyoto Protocol b) CITES c) The Clean Water Act d) The Clean Air Act e) The Montreal Protocol 3) New crust is created… a) At convergent plate boundaries as one plate is subducted beneath another. b) Along fault lines, as the movement of the earth causes magma to rise to the surface c) At divergent plate boundaries – as plates move apart magma rises to the surface d) As tectonic plates slide past each other, resulting in faults and fissures e) As old crust is recycled through the convection currents of the mantle. AP Practice 4) The Kyoto Protocol calls for all of the following except… a) Reductions in emissions of six greenhouse gases to below 1990 levels b) A global collaboration for a sustainable environment c) Allowances for carbon-credit training d) Money to clean up toxic waste sites e) Exemptions for developing nations Through the Atmosphere… Atmosphere Starting Ending Level Elevation Elevation Troposphere 0 ~20km Stratosphere 20km 50km Mesosphere 50 80-90 Thermosphere 90km beyond Important Information Atmospheric Properties Atmospheric Pressure: • Gravity pulls gas molecules toward Earth’s surface – air is most dense at the surface of the earth and decreases with altitude. Atmospheric Properties Atmospheric Pressure: • Gravity pulls gas molecules toward Earth’s surface – air is most dense at the surface of the earth and decreases with altitude. • Atmospheric pressure is a measure of the force per unit area of air. Atmospheric Properties Atmospheric Pressure: • At sea level, atmospheric pressure is 14.7lb/in2 (psi) or 1 atmosphere (atm) Atmospheric Properties Atmospheric Pressure: • Kala Patthar, a mountain near Everest, has an altitude of 18,000 ft. On the peak, atmospheric pressure is 0.43 atm. • About half of the Earth’s air molecules are below the hiker at this elevation. Atmospheric Properties Atmospheric Pressure: • On the summit of Everest - 29,035 feet – the atmospheric pressure is just over 0.29 atm. • A climber on the peak is standing above 2/3 of the Earth’s air molecules. Atmospheric Properties Atmospheric Pressure: • Commercial airlines cruise at about 36,000 feet – at that point the passengers are roughly above 80% of the Earth’s air molecules. • This is located about midway into the stratosphere military airlines fly higher on average. NASA is even higher Atmospheric Properties Relative Humidity: Atmospheric Properties Relative Humidity: • Humidity is a ratio of water vapor a given volume of air contains to the maximum amount it could contain. Atmospheric Properties Relative Humidity: • Humidity is a ratio of water vapor a given volume of air contains to the maximum amount it could contain. If the relative humidity is 33%, then the air contains about one-third of the water vapor it could hold at that temperature. Atmospheric Properties Relative Humidity: • When the humidity is high (say, 88%), then the air is already holding most of the water vapor that it can – as a result, sweat evaporates slowly and the body can not cool itself sufficiently. Atmospheric Properties Relative Humidity: • When the humidity is high (say, 88%), then the air is already holding most of the water vapor that it can – as a result, sweat evaporates slowly and the body can not cool itself sufficiently. • Low humidity has more “space” for water vapor, so sweat evaporates quickly and the body feels much cooler. Exit Slip 1) Moving toward the surface of the earth, which answer shows the correct order of the atmospheric layers? a) Troposphere, Stratosphere, Thermosphere, Mesosphere b) Mesosphere, Stratosphere, Thermosphere, Troposphere c) Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere d) Thermosphere, Mesosphere, Stratosphere, Troposphere e) Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Troposphere 2) Which answer below is NOT a job of the earth’s atmosphere? a) Recycling water b) Absorbing hazardous solar radiation c) Creating weather patterns d) Providing oxygen e) Moderating climate 3) The ozone layer… I) Is found in the Stratosphere II) Is found in the Troposphere III) Reduces the amount of dangerous UV solar radiation reaching earth’s surface IV) Reduces the amount of IV radiation reaching earth’s surface a) I and III b) I and IV c) II and III d) II and IV 4) Which location would have the highest atmospheric pressure? a) Lexington, KY – 1000 feet above sea level b) Georgetown, KY – 846 feet above sea level c) Harlan, KY – 1,191 feet above sea level d) Elizabethtown, KY – 731 feet above sea level e) Louisville, KY – 466 feet above sea level