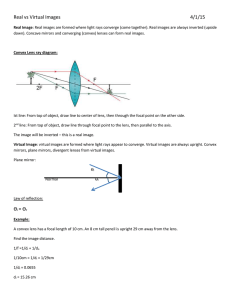
Lenses Review Question: Lens Operation: Convex Lens Convex
advertisement

Review Question: Lenses Which way will the light beam refract? Ray refracted towards normal Ray refracted away from normal air glass 1 2 Lens Operation: Convex Lens A lens bends light through refraction. You can think of a lens as many pieces of glass assembled together: object Principle axis Focal point 2f Focal Pt. Focal point Image Convex Lens viewed as several pieces. 3 Object past 2 focal points away. 2 or more rays converge to show real, inverted, and smaller 4 image. Convex Lens Convex Lens image object object Principle axis Principle axis 2f Focal point 2f Focal point Focal point Focal point Object between f and lens Image Object between 2f and f gives an inverted, real, larger image. 5 The rays don’t seem to actually converge. But if they are traced backwards to their apparent origin, a virtual, upright, and larger image is 6 formed!! Mirror / Lens Equation: Questions: Q: Where must an object be placed with a convex lens so that it acts as a magnifying glass? A: Inside the focal point Q: Where must an object be placed with a convex lens so that it projects a larger image onto a screen (slide projector)? If an object is placed 12 cm from a convex lens with a focal length of 10 cm, where does the image appear? 1 1 1 f do d i 6 5 1 60 60 di A: Between 2f and f 1 1 1 10 12 di 1 1 60 di 6 5 1 60 60 di di 60 cm 7 Mirror / Lens Equation: Lens Combinations If an object is placed 10 cm from a convex lens and an image is clearly projected onto the Board 100 cm away, what is the lens’ focal length? 1 1 1 f do d i 1 1 1 f 10 100 11 1 100 di 100 di 11 8 A refracting telescope uses one large objective convex lens in the front. 1 10 1 f 100 100 Another small convex lens is used as an eyepiece that you look through. di 9.1 cm 9 Refracting Telescope Light from a distant planet goes through the front convex lens and forms a small, real image. In reality, many optical devices use more than one lens or mirror. 10 Optical Devices: Obviously, many devices employ the principles learned today: Telescope tube The image is inside the focal point of the second convex lens, the eyepiece. The image acts as an object that then forms a much11 larger virtual image that the person sees. 12