Optical Theremin
advertisement

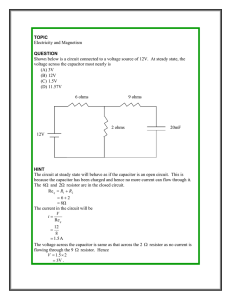
Optical Theremin Kevin Tang Rachel Rotman Kyle Morin Tim Hewitt Technical Communications 400 Professor Stevens October 1, 2009 Table of Contents Table of Contents............................................................................1 Definition.........................................................................................2 Function..........................................................................................2 Parts................................................................................................3 Specifications..................................................................................4 Operating Principle.........................................................................4 Index................................................................................................5 Glossary...........................................................................................6 1 Definition The Optical Theremin is a light‐sensitive electronic musical instrument (Figure 1). It produces sounds of varying pitches depending on the amount of light that enters a series of photodiode light sensors. Function The Optical Theremin is easily portable and will run for months off a single 9‐volt battery. The instrument has a momentary on‐off switch on its side. The instrument can be used to create sound effects similar to those of R2D2 from the “Star Wars” movie franchise. Experimenting with different light sources can produce a wide variety of sounds at different pitches and volumes. 2 Parts (see Figure 2) 1. 555 Time Integrated Circuit (IC) 2. 10Ω Resistor 3. 20Ω Resistor 4. 100µF Capacitor 5. 500µF Capacitor 6. Perforated Bread Board Other parts not shown below include the battery, photodiode light sensors, and black plastic enclosure. 6 3 Specifications The Optical Theremin is a small plastic box with the electrical components contained inside. It measures 4.5 inches long, 2.5 inches wide, and 2.5 inches high, and weighs 1 pound. It has an input voltage of 9V and an input amperage of 50mA. The Optical Theremin is available for $20 per unit. Operating Principle Shining a flashlight at either one of the photodiodes will activate the Optical Theremin and trigger it to produce sounds. To achieve different notes, flashlights may be shone at different angles. This will allow more or less light into the photodiode, resulting in varying output frequencies. One photodiode controls output pitch while the other controls the output volume. High frequencies can be obtained by shining a flashlight directly at the ‘pitch’ photodiode. The lowest frequencies produced by the instrument are produced when the instrument is placed in a dark room. 4 Index B Bread board, 3 C Capacitor, 3 D Definition, 2 F Flashlight, 4 Frequencies, 4 Function, 2 G Glossary, 6 I Input Amperage, 4 Input Voltage, 4 O Operating principle, 4 Optical Theremin, 2, 3, 4 P Parts, 3 Photodiode Light Sensors, 2, 4 R Resistor, 3 S Specifications, 4 T Time Integrated Circuit, 3 5 Glossary Amperage – the strength of an electric current expressed in amperes Bread board – a construction base for a one of a kind electronic circuit Capacitor – a device for gathering and holding a charge of electricity, made up of two equally charged conducting surfaces and separated by a dielectric Frequencies – periodic vibration whose pitch is audible to a human Photodiode light sensors – a type of photo detector, capable of converting light into either current or voltage depending on the form of operation Resistor – a device used to control current in an electric circuit by providing resistance Time Integrated circuit – a miniaturized electronic circuit of transistors, resistors and capacitors, in which the components are interconnected to perform a certain operation Voltage – an electromotive force or electric potential, expressed in volts 6