LC Oscillators
advertisement

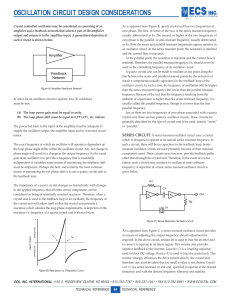
LC Oscillators • LC parallel resonant circuit • used for high frequency domain • frequency selective feedback network Zech Z C || Z L Zech L/C 1 j L C 1 ZC jC Z L jL Resonance frequency: Thompson’s relation f0 1 2 LC The parallel LC circuit connected in series with a load acts as a band-stop filter having infinite impedance at the resonant frequency of the LC circuit. 1/7 How the LC circuit and the basic amplifier will be connected ? Three points oscillator, one transistor amplifier vo Principle scheme, for variable signals The basic amplifier is an inverting one (CE), so the divider Z2, Z3 must introduce a -180o phase shift; Z2, Z3 will have opposite signs. Z3 and Z1 should be similar to obtain an LC parallel resonant circuit between collector and base. 2/7 Small-signal equivalent circuits for three points oscillators vo vo C1C3 C C1 C3 f0 1 2 L2C L L1 L3 f0 1 2 LC2 3/7 Optional +VPS +VPS Colpitts Hartley 4/7 Quartz-crystal oscillator C p C s R very low value can be neglected • Series resonance fs symbol equivalent circuit • Parallel resonance C Cs C p Cs C p Cs 1 2 LCs range: tens of KHz … hundreds of MHz fp 1 2 LC fs 5/7 Optional +VPS quartz-crystal sinusoidal oscillator • advantage: very stable frequency, high quality factor • disadvantage: oscillates on a fixed frequency (quartz frequency) 6/7 Quartz is amongst one of the most common minerals in the Earth's continental crust. It has a hexagonal crystal structure made of trigonal crystallized silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) The crystal oscillator circuit sustains oscillation by taking a voltage signal from the quartz resonator, amplifying it, and feeding it back to the resonator. The rate of expansion and contraction of the quartz is the resonant frequency, and is determined by the cut and size of the crystal. During startup, the circuit around the crystal applies a random noise (ac)signal to it, and purely by chance, a tiny fraction of the noise will be at the resonant frequency of the crystal. The crystal will therefore start oscillating in synchrony with that signal. As the oscillator amplifies the signals coming out of the crystal, the crystal's frequency will become stronger, eventually dominating the output of the oscillator. Natural resistance in the circuit and in the quartz crystal filter out all the unwanted frequencies. 7/7