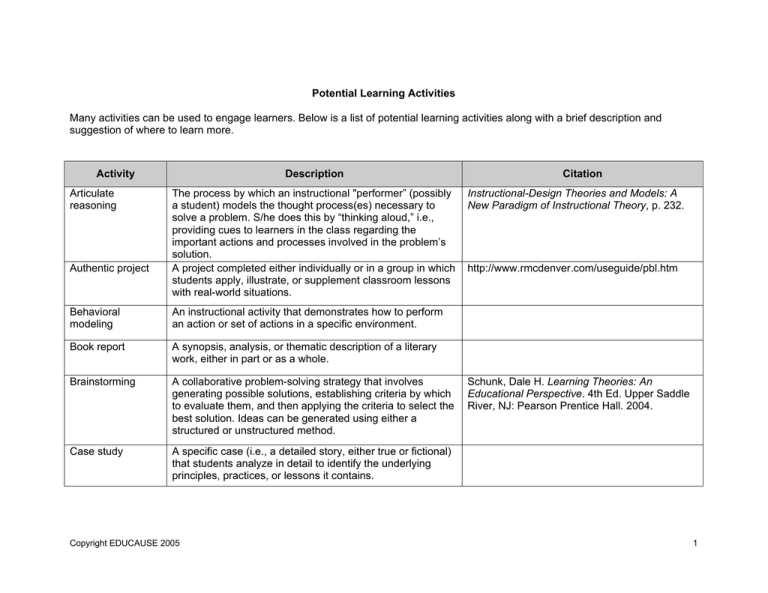
Potential Learning Activities
Many activities can be used to engage learners. Below is a list of potential learning activities along with a brief description and
suggestion of where to learn more.
Activity
Articulate
reasoning
Authentic project
Description
The process by which an instructional "performer” (possibly
a student) models the thought process(es) necessary to
solve a problem. S/he does this by “thinking aloud,” i.e.,
providing cues to learners in the class regarding the
important actions and processes involved in the problem’s
solution.
A project completed either individually or in a group in which
students apply, illustrate, or supplement classroom lessons
with real-world situations.
Behavioral
modeling
An instructional activity that demonstrates how to perform
an action or set of actions in a specific environment.
Book report
A synopsis, analysis, or thematic description of a literary
work, either in part or as a whole.
Brainstorming
A collaborative problem-solving strategy that involves
generating possible solutions, establishing criteria by which
to evaluate them, and then applying the criteria to select the
best solution. Ideas can be generated using either a
structured or unstructured method.
Case study
A specific case (i.e., a detailed story, either true or fictional)
that students analyze in detail to identify the underlying
principles, practices, or lessons it contains.
Copyright EDUCAUSE 2005
Citation
Instructional-Design Theories and Models: A
New Paradigm of Instructional Theory, p. 232.
http://www.rmcdenver.com/useguide/pbl.htm
Schunk, Dale H. Learning Theories: An
Educational Perspective. 4th Ed. Upper Saddle
River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall. 2004.
1
Activity
Description
Charting
Creation of graphs, tables, images, etc., to represent and/or
organize data.
Coaching
Peers analyze, provide feedback and encouragement on
each others' performance.
Cognitive modeling
"Reflection-in-action,” i.e., a demonstration of the reasoning
behind what is happening in a given activity.
Concept mapping
A graphical representation of related information in which
common or shared concepts are linked together.
Debate
A verbal activity in which two or more differing viewpoints on
a subject are presented and argued.
Discussion
A formal or informal conversation on a given topic. Also
called “dialogue.”
Dramatization
Acting a play, novel, or situation.
Drawing /art /
sculpture
Illustrating concepts through the use of images/likenesses.
Drill and practice
A learning activity in which students are presented with a
problem/task and asked to provide the answer; may be
timed or untimed.
Essay
A brief, written thesis on a specific issue or topic.
Copyright EDUCAUSE 2005
Citation
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 205.
2
Activity
Description
Citation
Schunk, Dale H. Learning Theories: An
Educational Perspective. 4th Ed. Upper Saddle
River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall. 2004.
Experiment
A learning strategy by which a study is designed so that the
learner becomes the investigator who systematically varies
conditions (independent variables) and observes changes in
outcomes (dependent variables).
Facilitator
Someone (e.g., a faculty member or student) who uses
structured inquiries and activities to help learners
collaboratively identify/attain the desired learning outcomes.
Field trip
An excursion that explores an authentic setting (e.g., a
museum, farm, different culture, etc.).
Chiseri-Strater, Elizabeth and Bonnie Stone
Sunstein. Field Working: Reading and Writing
Research. Upper Saddle River New Jersey:
Prentice Hall Blair Press. 1997. P 43.
Game
Undirected play or “playing around” (informal play), or a
contest to achieve an objective using an agreed-upon set of
equipment and procedural rules (formal play).
Salen, Katie and Eric Zimmerman. Rules of
Play: Game Design Fundamentals. MA: MIT
Press. 2004.
Guest speaker
An invited presenter who shares feelings, thoughts, and
ideas.
Schunk, Dale H. Learning Theories: An
Educational Perspective. 4th Ed. Upper Saddle
River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall. 2004.
Interview
Research conducted by questioning individuals in order to
answer a question, highlight an issue, or develop a
perspective.
Chiseri-Strater, Elizabeth and Bonnie Stone
Sunstein. Field Working: Reading and Writing
Research. Upper Saddle River New Jersey:
Prentice Hall Blair Press. 1997. p15.
Journaling
Learners keep written records of their intellectual and
emotional reactions to assignments and material on a
regular basis (e.g., weekly, after each class).
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 143.
Copyright EDUCAUSE 2005
3
Activity
Description
Citation
Lecture
Conveying material verbally, sometimes with visual aids, to
a group of learners.
Literature review
One-minute paper
A survey and summary of the literature on a specific topic.
Could be brief (only citations and brief synopses) or global
(including contexts, authors’ major purposes, and opposing
author viewpoints).
Learners summarize the "most important" or "most useful"
point(s) from a lecture, assignment, experiment, etc. Helps
students "process" an activity from short-term to mid-term
memory. Students could be assigned a "five minute paper"
to summarize a week’s lessons or identify the one item that
remains confusing.
On the spot
questioning
The instructor asks a question about learning material and
randomly calls on specific students for answers.
Panel discussion
A group of students (e.g., 4-5 people) give presentations on
the same topic but from different points of view. Another
option is for each panelist to take the role of a different
historical figure.
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 120.
Peer exchange
Students swap their work, motivating them to think more
about the material and discuss it among themselves.
Brown, D. (ed.) (2000) Teaching with
Technology. Massachusetts: Anker Publishing
Co.
Performance
modeling
Demonstration of an activity by a skilled performer via live
performance or video; may be recorded so the learner can
access the performance/presented material later.
Copyright EDUCAUSE 2005
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 93-95.
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 143
4
Activity
Description
Citation
Puzzles
A question, problem, or tool designed to test ingenuity or
recall.
Salen, Katie and Eric Zimmerman. Rules of
Play: Game Design Fundamentals. MA: MIT
Press. 2004. P 80-81.
Research paper/
report
A written document that includes a review of literature and
provides one perspective of the subject. A research report
includes multiple perspectives.
Scaffolding
Temporary support that allows a learner to perform a
complex task. As the learner becomes more proficient,
support is reduced until the student can stand on their own.
Leedy, Paul and Jeanne Ellis Ormrod. Practical
Research: Planning and Design. 8th Ed. Upper
Saddle River NJ: Prentic Hall Press. 2005. P.
36.
http://lester.rice.edu/browse/lstkeywordbrowse.a
spx?ord=181&Mid=61&tabIndex=0&tabid=1
Scavenger hunt
Learners working in pairs or groups must search to answer
a series of questions, collect material, etc. Learners may
bring back answers to the group, enabling the group to
answer a larger contextual question that requires answers
to the individual questions.
Service learning
A form of experiential education in which students engage in
activities intentionally designed to address community and
human needs while promoting student learning and
development.
Jacoby, Barbara and Associates. ServiceLearning in Higher-Education: Concepts and
Practices. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
1996.
Simulation
A replica or representation of a real-world phenomenon that
enables relationships, contexts, and concepts to be studied.
Salen, Katie and Eric Zimmerman. Rules of
Play: Game Design Fundamentals. MA: MIT
Press. 2004. P 423.
Socratic instruction
Also called “teaching by questioning”; questions and
answers are used to build a logical argument or reveal flaws
in reasoning.
Perelman, Ch. And L. Olbrechts-Tyteca. The
New Rhetoric: A Treatise on Argumentation.
Notre Dame, IN: U of Notre Dame Press. 1969.
Copyright EDUCAUSE 2005
5
Activity
Description
Citation
Student
presentation
Typically taking the form of an oral report, the presentation
involves researching a topic, taking a position and/or a role,
and studying a school of thought on the topic.
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 199-121.
Study session
Students work together to compare and discuss class notes,
diagrams, equations, etc., to improve understanding.
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 199-121.
Test/quiz
An exercise to determine the level of a student’s
understanding. Questions can take multiple forms (multiple
choice, essay, etc.).
Nilson, Linda. Teaching at Its Best: A ResearchBased Resource for College Instructors. 2nd
Ed., MA: Anchor Pub Co. 2003, p. 199-121.
Tutorial
Tutorials are secondary learning sessions, usually one-toone or small group, designed to help a student learn
material. They can be computer-mediated or face-to-face.
http://lester.rice.edu/Browse/lstprojectbrowse.as
px?ord=591&Mid=0&tabIndex=7&tabid=43
Web search
Students are assigned a topic to be researched on the Web,
which provides an opportunity to reinforce research
standards and source validity.
Faigley, Lester. The Longman Guide to the
Web. New York: Longman. 2000. P 135.
Working session
Time during class when learners are given a specific
project; resources are made available and the instructor
provides assistance, as needed.
Based on research conducted by 2004 NLII Fellow Jean Kreis.
Copyright EDUCAUSE 2005
6

