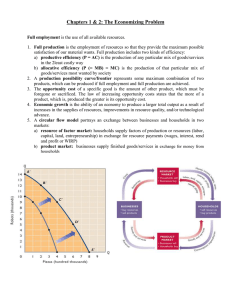
1 Indonesia 89/1 (Simplified schematic social accounting matrix
advertisement

1 Indonesia 89/1 (Simplified schematic social accounting matrix) Source: H.A. Khan, E. Thorbecke, Macroeconomic effects of technology choice: Multiplier and structural multiplier analysis within a SAM framework, Journal of Policy Modeling 11, 1989, 131-156 Total flows of transactions is represented by a 4 by 4 social accounting matrix, which can be elaborated as given on the next page. Expenditures Endogenous Accounts Exogenous Accounts Institutions, i.e., HouseSum of holds and Production Other Factors Companies Activities Accounts 1 2 3 4 Totals 5 Receipts Endogenous Accounts Factors 1 Institutions, i.e., Households and Companies 2 Production Activities 3 0 0 T 13 x 1 y 1 T 21 T 22 0 x 2 y 2 0 T 32 T 33 x 3 y 3 y x Exogenous Accounts (FOF, Sum of Other Accounts 4 l' 1 l' 2 l' 3 t Totals 5 y' 1 y' 2 y' 3 y x NIA, INPUT-OUTPUT, SAM) 2 Format of SAM-TECH Indonesia, 1975. (Numbers under each account represent the various sectors appearing in the SAM, e.g., 23 different factors, 10 households, etc.) Expenditures Endogenous Accounts Institutions Factors Receipts Endogenous Accounts 1 ... 23 Households Companies 34 24 ... 33 1 ... 23 Institutions Allocation Households of labor and uninc 24 ... 33capital income to households 34 Production Activities Government 75 35 ... 74 Capital Account 76 Allocation of labor and capital value added to factors Factors Companies Exogenous Accounts Current transfers among households Profits and dividends distributed to households Allocation of inc operating surplus to companies Production Activities 35 ... 74 Net Indirect Rest of the World Taxes 77 Factor Total inincome comes of received factors from abroad Current transfers to households Nonfactor Total income of income received households from abroad Current transfers to domestic companies Household consumption expenditures on domestic commodities Domestic intermediate input requirements Total 78 Total incomes of domestic companies Government Investment current exexpendpenditures onitures on domestic domestic commodities goods Exports Aggregate demand =gross output Exogenous Accounts Government 75 Capital 76 Direct taxes Household savings Direct taxes on companies Net Net Total govindirect nonfactor ernment taxes incomes receipts received from abroad Undistributed Profits after tax Net Indirect Taxes Government current expenditures on imports Net capital Aggregate received savings from abroad Net indirect taxes Net indirect taxes on export 77 Nonfactor Rest of the Factor pay- Household ment abroad consumption payment World expendabroad itures on 78 imported good Total Imports of intermediate inputs Total exTotal ex- Total expendTotal penditures penditures itures of costs of of domestic of house- companies gross factors of holds output production Government current expenditures on imports Imports of capital goods Total expend-Aggregate Total Total itures of investment indirect foreign government taxes exchange receipts Total indirect taxes Total foreign exchange expenditures