Hydraulic Transient Analysis
advertisement

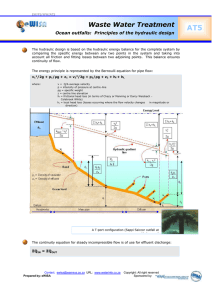
DHI SOLUTIONS Hydraulic Transient Analysis Simulating system behaviour under various operating conditions for more reliable and safer operations Pressure waves can have dramatic effects Hydraulic transients (HT), also called pressure surge or water hammer, are planned or accidental changes of conditions in a water distribution network, e.g. by opening or closing a pump or valve. As a result, a pressure wave is generated which travels through the pipe network. Sudden changes resulting in extensive pressure waves can have dramatic effects, ranging from pump defects to catastrophic pipeline failures. Transient events can also have significant water quality and health implications. SUMMARY Client Water Utilities Industrial Pipeline Systems Hydropower Problem HT analysis is essential for system design HT are dangerous in operation HT analysis is difficult Solution Analysis of system behaviour under HT conditions; identification of particularly dangerous conditions; establishing safe operating environment Benefits Safe design and operation under standard and emergency scenarios Specifically tailored solutions Pipe networks can suffer major damage from hydraulic transients, at the worst resulting in catastrophic pipeline failures Establishing a safe operating environment Surge modelling provides the most effective means of identifying weak spots in the network and predicting possible effects of hydraulic transients under different standard and emergency scenarios. Moreover, the models evaluate possible precautions and countermeasures to establish a safe operating environment. Model analyses are designed to predict extremes of pressure, both maximum and minimum, which may potentially develop within the system during its operating lifetime and the probability of occurrence of each extreme event, as well as its consequences. The transient analysis is best used in conjunction with a hydraulic network model and includes additional information such as the operating time for equipment or the time for quiescent conditions to develop after flow changes. Hydraulic transients in the cooling water system of nuclear power plants require thorough investigation Design and operations DHI carries an enormous library of various hydraulic and surge protection devices as well as a variety of transient sources to be included in the models. Hydraulic transient analysis will be done using MIKE Hydraulic Transient Analysis Simulating system behaviour under various operating conditions for more reliable and safer operations URBAN FGDHT (Flow Gradient Hydraulics) Solutions Software. DHI accurately analyses hydraulic behaviour of your pipeline system under pressurized, transitional or cascading flow conditions. Benefits of DHI hydraulic transient analysis are safe design and operation of the pipeline systems. Moreover, you will be provided with a detailed report, recommendations and assistance in field tests. The key information at your fingertips is specifically tailored to your needs based on dialogue and needs assessment. MIKE URBAN FGDHT provides the following analysis and methods: Built-in steady-state engine Transient force computation engine Pump and turbine modeling for fixed and variable speed units using four quadrant curve characteristics Rule-based control analysis Simulation of numerous surge mitigation and protection devices Simulation of multiple transient sources including gate and valve movements, pump and turbine activities, and others MIKE URBAN FGDHT can model the following transient sources: valve closure (open to close, close to open, any position, and to partial), valve opening, pump, controlled shutdown, pump start-up, pump trip-off, rapid demand change, rapid pressure change, single source, multiple sources, turbine (speed, no load), turbine (load rejection), turbine (load acceptance), turbine (demand change), turbine (start-up), turbine (shut down), rupture disk, pipe or a valve break MIKE URBAN FGDHT can model the following surge protection devices: open surge tank, spilling surge tank, one way surge tank, gas vessel (air chamber), surge tank with orifice, surge tank with bladder, variable area surge tank, differential surge tank, pressure relief valve, anti-slam valve for air release/vacuum valve, surge anticipation valve, surge attenuating air. Consequences of hydraulic transients Our software was developed to analyse system behaviours under various unsteady flow conditions and to help you to understand the consequences of hydraulic transients. These consequences include maximum and minimum pressures in the system, occurrences of local vacuum conditions and/or cavitations at specific locations. These occurrences can be either within specific devices or within a pipe. Additional behaviours that are analysed are hydraulic vibration of a pipe, string oscillations or rapid movement of the water masses, and risk or occurrence of contamination at cross-connections. Accurate modelling helps to identify and isolate conditions that deserve particular attention. Illustration of the MIKE URBAN FGDHT software – user interface. DHI’s software analyses hydraulic system behaviour under various conditions, allowing for safe and reliable design and operation of your pipeline system DHI provides specifically tailored solutions for proper pipework design Contact: Petr Ingeduld - pi@dhigroup.com September 2011© DHI Hydraulic Transient Analysis in Project Design: from beginning to end Hydraulic transient studies are especially important in the design of water distribution systems. The severity of transient pressures must be determined so that the pipework can be properly designed to withstand these additional loads. The studies are commonly included in the Basis of Design Report to help decide upon the required facilities and to identify differences between alternative operating parameters. Hydraulic transient studies are generally completed during the Preliminary Design as their results on pressures, flows and performance estimates are utilized in the later design stages. Design modifications in the Final Design stage may require repetition of transient runs to verify or modify results. DHI will provide you with a range of tools for time efficient model adjustments and modifications.