Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors
advertisement
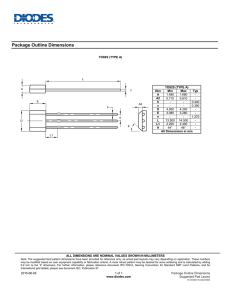
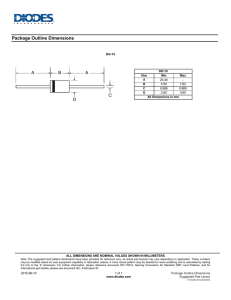
Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Program Support Notes by: Diane Krosby B.Ed © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producer: Simon Garner B.Ed, Dip Management To order or inquire please contact VEA: VEA (Video Education America) E-mail 6902 Hawthorn Park Drive Indianapolis, IN 46220 Phone: 1.866.727.0840 Fax: 1.866.727.0839 orders@veavideo.com Website www.veavideo.com Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors For Teachers Introduction This video explains what semiconductors are and how their use, and the invention of the integrated circuit and transistor, have revolutionized electronics. Types of semiconductors (n and p-type) are clearly explained including applications such as the operation of diodes and transistors. The program explains: • conductors, semiconductors and insulators (in terms of band structure theory, valence and conduction bands) • types of semiconductors (n and p-type) including the major features of each in terms of charge carriers and holes • pn diodes and npn transistors and how they work in terms of their semiconductor structure • forward and reverse biasing of diodes • the operation of transistors including MOSFETs • the widespread use and applications of semiconductors in our electronic society (diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, solar cells). Timeline 00:00:00 00:03:08 00:10:02 00:17:34 00:21:11 00:22:11 00:22:49 Development of electronics Semiconductors Diodes Transistors Summary Credits End program Related Titles Introduction to Electricity DC Electricity – Discovery and Developments Principles of Physics 2 Recommended Resources http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ENIAC http://www.howstuffworks.com/diode.htm http://virlab.virginia.edu/VL/MOS_kit.htm/state/0 http://www.pbs.org/transistor/science/info/diodes.html 2 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Student Worksheet Initiate Prior Learning 1. Name some electronic devices that you use every day. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How would your life be different without these electronic devices? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How has electronics changed in the last few years? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What electronic components do you know of? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Active Viewing Guide Chapter 1: The Development of Electronics 1. What advantages did transistors have over the diode valves used in early communication devices? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is an integrated circuit (IC)? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How have ICs changed since the 1960s? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 2: Semiconductors – Materials 4. Complete this table comparing conductors, semiconductors and insulators: Material Comparison of Valence & Conduction Bands Conductor Bands _______________ Result Many free _______________ to conduct electricity Electrons do not have enough energy to Large band _______________ Insulator cross the gap, so insulators do not _______________ electricity A small amount of energy can allow Semiconductor Small band _______________ electrons to cross the gap, so they can _______________ electricity 4 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors 5. What is doping? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Complete this table summarizing n-type and p-type semiconductors: Type of Semiconductor Material Doped with Majority Charge Carriers n-type p-type Chapter 3: Diodes 7. What does a diode do? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Why are diodes always connected in series with a limiting resistor? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Draw a diagram showing how the depletion layer forms at the p-n junction of a diode. 5 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors 10. What happens in a diode when it is: a) Forward biased? _________________________________________________________________________________ b) Reverse biased? _________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Fill the gaps: When forward biased, the point at which a diode starts to conduct is called the _______________ voltage, and is about _______________ V. 12. What is the difference between an LED and a photodiode? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is the difference between most diodes and a photodiode in terms of the way they are connected in circuits? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 4: Transistors 14. Label the following diagram of an npn transistor: n _______________ p _______________ n _______________ 6 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors 15. Fill the gaps: In a transistor, a small _______________current (through the base-emitter circuit) produces a much _______________ (_______________) current in the emitter-collector circuit. 16. Label the diagram showing the base and collector currents : BASE COLLECTOR EMITTER 17. Fill the gaps: In a MOSFET transistor, when a voltage is applied, making the gate _______________, electrons in the p-type are _______________ towards the gate, forming an electron channel between _______________ and _______________. If the gate is negative, _______________ current flows. Changes in the gate voltage _______________ the transistor _______________ or _______________. 7 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Extension Activities 1. Find out about ENIAC, the world’s first electronic computer – how it worked, and how it compared to modern computers. 2. Write about how your life would be different if the transistor and silicon chip had not been invented. 3. How do you think electronics may change in the future? 8 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Suggested Student Responses Initiate Prior Learning 1. Name some electronic devices that you use every day. Answers will vary but could include: Computers Mobile phones Game consoles 2. How would your life be different without these electronic devices? Answers will vary 3. How has electronics changed in the last few years? Electronic devices are now much smaller, more complex, more sophisticated and faster. 4. What electronic components do you know of? Answers will vary but may include: Transistors Resistors Diodes LEDs 9 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Active Viewing Guide Chapter 1: The Development of Electronics 1. What advantages did transistors have over the diode valves used in early communication devices? Transistors were smaller, cheaper, reliable and used minimal power compared to their diode valve predecessors. 2. What is an integrated circuit (IC)? An integrated circuit (IC) is an entire electronic circuit built into a single piece of silicon (silicon chip). 3. How have ICs changed since the 1960s? Since the 1960s, ICs have become smaller, more complex and faster. Chapter 2: Semiconductors – Materials 4. Complete this table comparing conductors, semiconductors and insulators: Material Comparison of Valence & Conduction Bands Result Conductor Bands overlap Many free electrons to conduct electricity Insulator Large band gap Electrons do not have enough energy to cross the gap, so insulators do not conduct electricity Semiconductor Small band gap A small amount of energy can allow electrons to cross the gap, so they can conduct electricity 5. What is doping? Doping is adding small amounts of other substances (such as arsenic or phosphorus) to boost the conductivity of a semiconductor. 6. Complete this table summarizing n-type and p-type semiconductors: Type of Semiconductor Material Doped with Majority Charge Carriers n-type Elements with 5 outer electrons negatively charged electrons p-type Elements with 3 outer shell electrons positively charged holes 10 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Chapter 3: Diodes 7. What does a diode do? A diode only allows current to flow in one direction. 8. Why are diodes always connected in series with a limiting resistor? Diodes are always connected in series with a limiting resistor to protect the diode from large voltages and currents which could damage it. 9. Draw a diagram showing how the depletion layer forms at the p-n junction of a diode. 10. What happens in a diode when it is: a) Forward biased? The depletion layer shrinks and current flows b) Reverse biased? The depletion layer is large and no current flows 11. Fill the gaps: When forward biased, the point at which a diode starts to conduct is called the threshold voltage, and is about 0.6-0.7V. 12. What is the difference between an LED and a photodiode? LEDs use an electric current to emit light. Photodiodes detect light, and produce an electric current. 13. What is the difference between most diodes and a photodiode in terms of the way they are connected in circuits? The main difference between most diodes and a photodiode is that a photodiode is connected and operates in reverse bias. Chapter 4: Transistors 14. Label the following diagram of an npn transistor: n emitter p base n collector 11 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors 15. Fill the gaps: In a transistor, a small base current (through the base-emitter circuit) produces a much larger, (amplified) current in the emitter-collector circuit. 16. Label the diagram showing the base and collector currents : BASE COLLECTOR EMITTER 17. Fill the gaps: In a MOSFET transistor, when a voltage is applied making the gate positive, electrons in the ptype are attached towards the gate, forming an electron channel between source and drain. If the gate is negative, no current flows. Changes in the gate voltage switch the transistor on or off. 12 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968. Semiconductors, Diodes and Transistors Extension Activities 1. Find out about ENIAC, the world’s first electronic computer – how it worked, and how it compared to modern computers. ENIAC was the world’s first general-purpose computer, built from 1943-1946. It contained 17,468 vacuum tubes, 7,200 crystal diodes, 1,500 relays, 70,000 resistors, 10,000 capacitors and around 5 million hand-soldered joints. It weighed more than 30 short tons (27t), was roughly 8 by 3 by 100 feet (2.4m × 0.9m × 30m), took up 1800 square feet (167m2), and consumed 150kW of power. 2. Write about how your life would be different if the transistor and silicon chip had not been invented. Answers will vary. 3. How do you think electronics may change in the future? Answers will vary, but may include: further miniaturization of technology (down to the nanoscale), and quantum computers. 13 © Video Education Australasia Pty Ltd 2011 Reproducing these support notes You may download and print one copy of these support notes from our website for your reference. Further copying or printing must be reported to CAL as per the Copyright Act 1968.