Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells PEMFC
advertisement

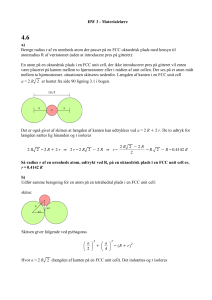
Extraction of the energy Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells PEMFC H2 → 2H+ + 2eJens Oluf Jensen Energy and Materials Science Group, Department of Chemistry, Technical University of Denmark, Kemitorvet 207, DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark Summer School on Materials for the Hydrogen Society, Reykjavik, June 19.-23. in 2008 Negative electrode Anode (oxidation) Building up a MEA Anode (H2, negative) (½O2 + 2e- → O2-) ½O2 + 2H+ + 2e→ H2O Positive electrode Cathode (reduction) Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) Cathode: Proton conducting membrane H+ → Electrode Electrode Electrolyte Pt on carbon ½O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → H2O Electrolyte: H+ conducting polymer Perfluorosulphonic acid (e.g Nafion) Cathode (O2, positive) Anode: MEA = Membrane Electrode Assembly Pt on carbon H2 → 2H+ 2e- 1 Single cell Channel plate Diffusion layer Catalyst layer Electrolyte Electrode structure Channel plate Rip Electrode substrate Microporous Catalyst layer layer Electrolyte Electrons, Heat Ions Gas Gas diffusion layer (GDL) An MEA Single cell e lat lp +) ne n e( a Ch thod lyte o e Ca (-) ctr lat Ele ode el p An ann C 2 Stacking Transport paths Electrons and heat Reactants and products Bipolar plate Diffusion layer Catalyst layer Electrolyte + Channel plates (bipolar plates) Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) Nexa from Ballard 1200 W 3 Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) GM/Opel Fuel Cell Marathon 2004, 10 000 km HydroGen3 (Opel Zafira) 260 kW PEMFC with 205 kW motor, Ballard http://www.gmeurope.com/marathon/ Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) Reykjavik German submarine U - 212 Siemens PEM fuel cell GfE metal hydride storage tank 4 Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) 2kW CHP Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) Advantages: • Compact construction • Large current density • Solid electrolyte • Low working temperature • Fast start-up 6kW CHP Disadvantages: • Water management • Noble metal catalyst From IRD Fuel Cells • CO sensitive (must be < 20 ppm) • Cooling issues Perfluorosulfonic acid polymers (Nafion®) Nearly all PEMFC’s based on PFSA polymers (perfluorosulphonic acid) Teflon Developed by DuPont Proton conduction Vehicle mechanism Proton carried by water as H3O+, H5O2+ etc Grotthus mechanism Proton jumping from H3O+ to H2O (Then another H+ can take the next jump) PFSA (Nafion) 5 Water drag Cooling in cars Anode Membrane Cathode e- e- H2O H2 H7O3+ H2O O2 From DaimlerChrysler Conductivity depends strongly on water content Water management - a technical challenge Too little water => drying out, loss of conductivity Too much water => condensation, flooding of electrodes Water ΔT(40 ºC) 60-70ºC 20-30ºC 90-100ºC 50-60ºC Cooling a FC car requires a larger cooling system (radiator) Reformer / Reformer Brændselscelle / Fuel cell How can a higher working temperature help ? El Nat. Gas, Methanol Advantages: • Higher CO tolerance • No water management • No liquid water • Higher value of excess heat • Easier cooling CO-oprensning til 0,001 % Varme/heat H2 CO2 CO H2 CO2 Befugtning af luften Humidification of the air CO clean-up to 0,001 % Luft ind Air in Luft ud Air out 6 Reformer / Reformer Brændselscelle / Fuel cell Other attempts El Nat. Gas, Methanol CO-oprensning til 0,001 % Varme/heat H2 CO2 CO H2 CO2 Befugtning af luften Humidification of the air CO clean-up to 0,001 % Luft ind Air in Luft ud Air out Almindelige PEM-celler er baseret på membraner som Nafion Ny membran af PBI og phosphorsyre Maksimal temperatur: ca. 80°C Conventional PEMFC are based on Membranes like Nafion Maksimal temperatur: ca. 200°C Maximum temperature ca. 80°C New membrane of PBI and phosphoric Replacement of sulphonic acid - Phosphonic acid - Other side chains - Other acceptor/donors Replacement of water -H2SO4 -H3PO4 -CF3SO3H Direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) (A special PEMFC) Anode: CH3OH + H2O → 6H+ +6e- + CO2 Cathode: 1.5O2 + 6H+ + 6e- → 3H2O acid Maximum temperature: ca. 200°C Nafion PBI H N H N N N Electrolyte: Ion conducting polymer (e.g. Nafion) Catalysts: Noble metals (Pt and Pt alloys) n Poly (2,2´-m-(phenylene)-5,5´-bibenzimidazole) 7 Direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) Size: DMFC < 1W - 1 kW Applications: • Portable electronics (laptops, phones, MP3...) • Small/medium UPS systems • Remote power DMFC DMFC Toshiba DMFC for 1) a laptop 2) an MP3 player DMFC IRD Fuel cells 8 DMFC DMFC Direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) Example System (bus) Advantages: • Liquid fuel • Easy and fast fuelling • Easy and compact fuel storage 193 kW 180 kW Work 166 kW 30% Motor etc. 14 kW DC/DC 13 kW Losses: Cooler 20 kW • MeOH poisonous Power 213 kW Compr 47 kW • Expensive catalyst (10xPt amount) FC el. 260 kW FC heat 285 kW Disadvantages: • Low efficiency • Fuel crossover Fuel 545 kW 9 Some of the problems Polymer fuel cell (PEMFC) • Cost • Hydrogen storage in vehicles • Efficient hydrogen production • Durability of cells • Noble metals supply • Infrastructure • Numerous technical details From IRD Fuel cells 10