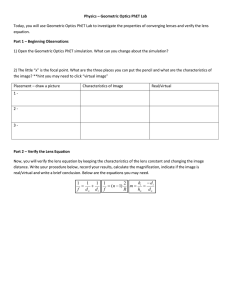
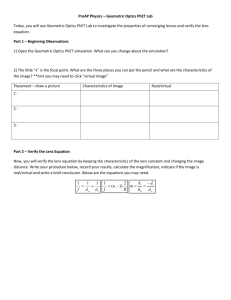
AG Geometric Optics Expanded
advertisement
Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Learning Expectation: We are learning: 1. We are learning to identify and describe four ways that light interacts with matter Students may be given… Students may be asked to… An object or a description of an object Classify it as opaque, translucent, or transparent, or luminous or nonluminous Dates of Applicable Lessons Knowledge and Skills • Define the terms given above • Provide several examples of each type of material Resources • Textbook reading, Hsu p 500 • http://www.ioncmaste.ca/homepage/resources/web_resources/CSA_Astro9/files/multimedia/unit3/phases _moon/phases_moon.html This applet helps to explain why we see the phases of the moon. 1 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Learning Expectation: We are learning: 2. We are learning to use the Ray Model of Light to understand the optics of shadows and apertures Students may be given… Students may be asked to… An object or a description of an object Classify it as opaque, translucent, or transparent, or luminous or nonluminous A drawing or description of a light source, mask or block, screen Find the location and size of the bright spot or shadow Dates of Applicable Lessons Identify the umbra, penumbra, and region of light Determine the orientation and shape of the resulting bright spot Knowledge and Skills • Describe the differences in the behavior of light in transparent, translucent, and opaque objects • Identify examples of transparent, translucent, and opaque objects • Provide evidence supporting the view that light travels in rays • Draw light rays emanating from point and extended sources • Draw lab setups of light sources, masks, and screens from top, side, and perspective viewpoints • Use the ray model to show how moving the light source, mask, and/or screen would affect what one sees on the screen 2 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics • • • • Use the ray model to show how changing the size and shape of the aperture would affect what one sees on the screen Use the ray model to show how changing the size and shape of the light source would affect what one sees on the screen Explain penumbra formation in your own words Use a ray diagram to explain the difference between solar and lunar eclipses Resources • Pinhole applet: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=38 Applet allows students to manipulate a light source and a pinhole mask. Your computer must have Java in order to run the applet. • Shadow applet: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=42 Applet allows students to manipulate a light source and an opaque mask to investigate the formation of shadows. Your computer must have Java in order to run the applet. • Solar and Liunar Eclipses: http://www.ioncmaste.ca/homepage/resources/web_resources/CSA_Astro9/files/multimedia/unit3/solar_e clipses/solar_eclipses.html. Interactive web site allows students to see ray diagrams for eclipse formation • Eclipse formation: http://www.scienceu.com/observatory/articles/eclipses/eclipses.html 3 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Learning Expectation: We are learning: Students may be given… 3. Understand how light interacts with reflective surfaces A ray of light approaching a mirror Determine the direction in which the light ray reflects A drawing or description of an object, mirror, and observers Determine the region (field of view) where an observer must be located to see the image of an object in a mirror Students may be asked to… Dates of Applicable Lessons Locate the image of the object Knowledge and Skills • Identify the angle of incidence and reflection when a light ray strikes a surface • Use a protractor to measure or construct an angle • Use a protractor to construct a line that is perpendicular (“normal”) to a surface • Contrast specular reflection with diffuse reflection, and cite examples of each • Use the law of reflection to find the image location and field of view when an object is near a mirror • Explain the difference between real and virtual images Resources • Textbook reading: Hsu, pp. 442, 482, 500-502, 508 4 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics • • • • • • • Physics Classroom Tutorial: http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/Class/refln/reflntoc.html Lesson 1 parts a-d, Lesson 2 parts a-d. Multimedia Physics Studio animations: http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/mmedia/optics/lr.html and http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/mmedia/optics/ifpm.html How to use a protractor animation: http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/protractor-using.html Law of reflection movie: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9aWE4rDw_ks Mirror and image applet: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/oldjava/optics/mirror_e.html Creating an image with a Plane Mirror simulation http://web.phys.ksu.edu/vqm/laserweb/Java/MirrImge/Imageme1.htm Mirror game: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/oldjava/optics/mirrorgame_e.html 5 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Learning Expectation: We are learning: 4. We are learning how light changes direction at a boundary between two transparent materials Students may be given… Students may be asked to… A light ray approaching a boundary between two materials Draw the correct path of a ray of light when it crosses a boundary between two media A physical situation in which light is refracted Determine which material has a greater index of refraction Dates of Applicable Lessons Determine in which material light is traveling with a greater speed Describe how refraction can cause phenomena such as optical illusions and dispersion Knowledge and Skills • Use a protractor to construct a line that is perpendicular (“normal”) to a surface where a light ray enters or exits a material • Identify the angles of incidence and refraction for a given light ray • Use a protractor to measure angles of incidence and refraction • Know the speed of light in a vacuum • Calculate the speed of light in a medium given the medium’s index of refraction • Provide examples of situations when refraction occurs 6 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Resources • Textbook reading: Hsu, pp. 442, 482, 500, 503-506. 525 • Physics Classroom Tutorial: http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/Class/refrn/refrntoc.html see especially Lesson 1 parts a-f • Multimedia Physics Studio animation (“The Broken Pencil”) http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/mmedia/optics/bp.html • Refraction of light applet http://www.physics.uoguelph.ca/applets/Intro_physics/refraction/LightRefract.html • Refraction of light applet. Another way to visualize light striking a boundary http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=16 • Examples of refraction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8ZxG_vyZWCw • Dispersion animation: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wKO5vfu8Gns 7 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Learning Expectation: We are learning: Students may be given… 5. We are learning to apply the concept of refraction to understand lens optics A drawing or description of an object (or an image) and a lens Students may be asked to… Dates of Applicable Lessons Locate the image of the object using a ray diagram and the thin lens equation Describe the characteristics of the image Knowledge and Skills • Identify a convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lens • Draw the principal axis for a lens • Define the focal point, focal length, object distance, and image distance • Draw the three “principal” rays for concave and convex lenses • Use the principal rays to determine where a lens will form an image • Interpret a ray diagram to determine whether an image is real or virtual • Distinguish between upright and inverted images • Distinguish between enlarged and reduced images • Use the thin lens equation to calculate where a lens will form an image • Describe how a screen helps an observer to see an image. 8 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Resources • Textbook reading: Hsu, pp. 498-99, 507-513 • Physics Classroom Tutorial: http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/Class/refrn/refrntoc.html Lesson 5, parts a-f • Graphics of three principal rays: http://acept.asu.edu/courses/phs110/expmts/exp11a.html • Lens applet by Fu-Kwun Hwang; click + button to change the lens type: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=48 • Lens applets by Kiselev; shows image formation by principal and non-prncipal rays: http://www.physics.uoguelph.ca/applets/Intro_physics/kisalev/java/clens/index.html (converging lens) and http://www.physics.uoguelph.ca/applets/Intro_physics/kisalev/java/dlens/index.html (diverging lens) • Optics Bench applet from Davidson; allows parallel beams of light in addition to objects http://webphysics.davidson.edu/Applets/optics/intro.html 9 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics Learning Expectation: We are learning: 6. What affects our perception of color Students may be given… Students may be asked to… Differently colored lights shining on a white screen Explain the color of light that is perceived Differently colored lights shining through a transparent filter or on a colored object Explain the color of light that is perceived A beam of white light approaching a transparent object Explain the effect the object has on the light Dates of Applicable Lessons Knowledge and Skills • Describe how the parts of the eye allow us to see light and interpret color • Describe the additive color process • Draw diagrams showing how additive primary colors of light can be combined to make other colors • Describe the subtractive color process • Draw diagrams showing how subtractive primary colors of pigments can be combined to make other colors • Understand how relative light intensity can affect color perception Resources 10 Assessment Guide – Geometric Optics • • • • • • Textbook reading: Hsu, pp. 483-491 Physics Classroom Tutorial: http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/Class/light/lighttoc.html Lesson 2, parts a-f Shockwave Physics Studio: http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/shwave/lights.html (color addition lighting activity) and http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys/shwave/paints.html (color subtraction painting activity) Three color applets from University of Texas (mixing light, mixing pigments, color printing) http://pdukes.phys.utb.edu/PhysApplets/Colors/TabbedcolorBox.html Color subtraction applet using filters http://mc2.cchem.berkeley.edu/java/absorption/java%20classes/absorption.html Two colo perception applets from University of Colorado (color addition using three bulbs; color subtraction using a single bulb and a filter): http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim=Color_Vision 11