Radiation Pattern Definitions Normalized field pattern: Power pattern
advertisement

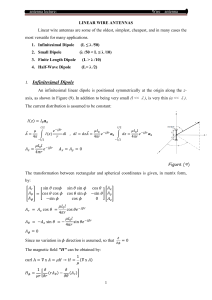
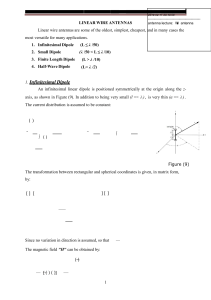
1 Radiation Pattern Definitions Normalized field pattern: Power pattern: In dB scale Examples Ideal dipole: Line current: Main lobe (major lobe, main beam) Side lobe (minor lobe) Maximum side lobe level: Half-power beamwidth: Pattern types: Broadside, Intermediate, Endfire. 2 Directivity Solid angle: Radiation intensity: where Directivity: Beam solid angle: Power Gain (Gain) 3 or Radiation efficiency: Referenced Gain: dBi: referenced to isotropic antenna. dBd: referenced to dipole antenna. The origin of radiation – short dipoles. Phasor retarded potential and , Consider an infinite small short dipole pointing in z direction and located at origin, where is a line current, and is the length, i.e., or at then, , since . 4 In spherical coordinate and that is Near Field: The same as the static magnetic field calculated by Biot-Savart’s law 5 since . The same as the static electric field generated by dipole moment . Far field: Spherical TEM wave , Propagating in In general, Summary: , 6 1. All radiation of finite current distribution is spherical TEM wave at far field. 2. Both and Half-wave dipole varies as at far field. 7 Poynting vector: Power radiated: Radiation resistance: Importance of half-wave dipole: 1. consider the dipole as an open transmission line, then . At , ,..., . Which means zero reactance. In reality, the length is a little be shorter. Since a good transmission’s intrinsic impedance is near pure real, this allows matching to transmission lines. 2. The efficiency is the best at . 8 Antenna Arrays Suppose there are N identical antennas each located at location , then where Thus, 9 where is called array factor, is the vector potential of single element located at origin. General Uniform Linear Arrays Let , and where then the normalized array factor, , then 1. Main-beam direction. Maximum occurs when a. Broadside array, b. Endfire array, , i.e., 10 2. Null locations: 3. Side lobe locations: Pattern Multiplication Example: Two-Collinear, Half-Wavelength Spaced Short Dipoles Parameters: 11 12 Example: Two Parallel, Half-Wavelength Spaced Short Dipoles Since 13 Antenna in Communication Systems Open circuit voltage: polarization match. for ideal dipole receiving antenna and When Maximum power transfer: Power density: Maximum effective aperture For a dipole In general, Effective aperture: Available power: In general, or 14 Aperture efficiency: , where is the physical aperture size. Communication Links Power delivered to the load : polarization mismatch factor, : impedance mismatch factor, In dB form or where dBm is power in decibels above a milliwatt. EIRP: effective (equivalent) isotropically radiated power ERP: effective radiated power by a half-dipole 15 Other Antenna Types 1. Traveling wave antennas 16 2. Helix 17 3. Yagi-Uda 18 19 20 4. Broadband antennas a. Spiral b. log-periodic 5. Aperture 21 6. Patch