Potential and Kinetic Energy
advertisement
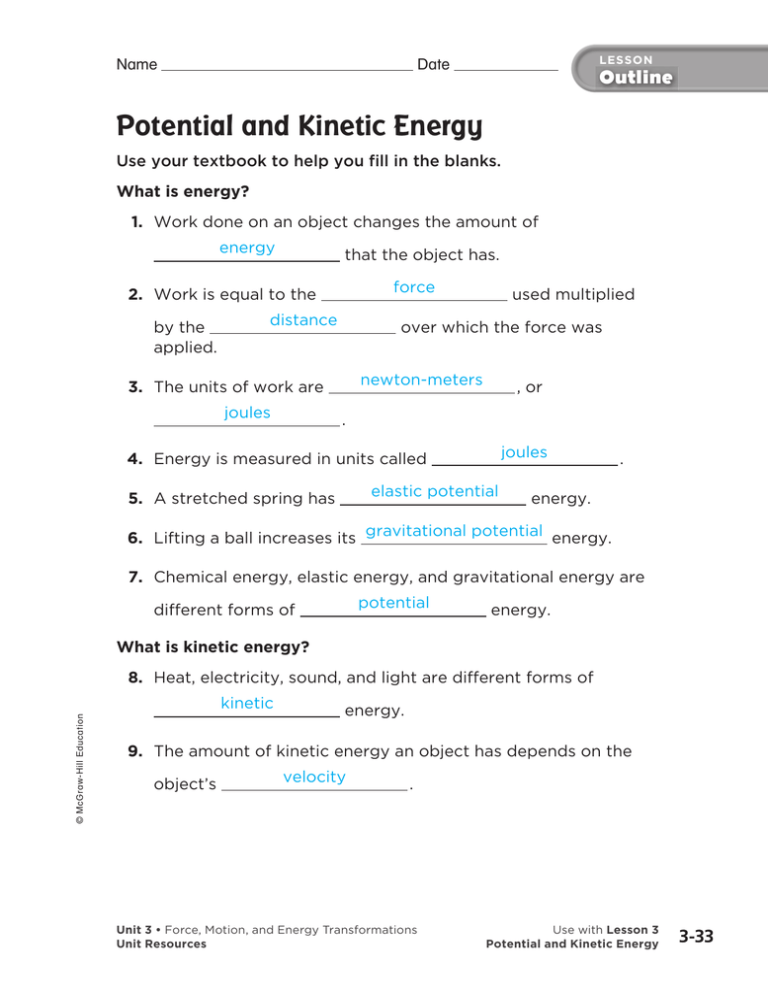
Name LESSON Date Outline Potential and Kinetic Energy Use your textbook to help you fill in the blanks. What is energy? 1. Work done on an object changes the amount of energy that the object has. force 2. Work is equal to the by the applied. distance over which the force was newton-meters 3. The units of work are joules used multiplied , or . joules 4. Energy is measured in units called elastic potential 5. A stretched spring has . energy. 6. Lifting a ball increases its gravitational potential energy. 7. Chemical energy, elastic energy, and gravitational energy are potential different forms of energy. What is kinetic energy? 8. Heat, electricity, sound, and light are different forms of © McGraw-Hill Education kinetic energy. 9. The amount of kinetic energy an object has depends on the object’s velocity . Unit 3 • Force, Motion, and Energy Transformations Unit Resources Use with Lesson 3 Potential and Kinetic Energy 3-33 LESSON Outline Name Date How can energy change? created 10. Energy cannot be destroyed ; it can only or change form . 11. Whenever energy is used to do work, energy changes form . 12. Electricity does work in an oven by moving particles around and changing into heat . Critical Thinking 13. Trace the energy changes that occur in a toaster, in a radio, and in a windmill used to generate electricity. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it does change form. In a toaster, electrical energy is changed into heat and light. In a radio, electrical energy is changed into the kinetic energy of the vibrating speaker, sound energy, and a little heat. In the windmill, kinetic energy of moving air turns the blades, which spin a generator that turns energy of motion into electrical energy. © McGraw-Hill Education 3-34 Unit 3 • Force, Motion, and Energy Transformations Unit Resources Use with Lesson 3 Potential and Kinetic Energy
