Scenario #1: Light Emitting Diodes
advertisement

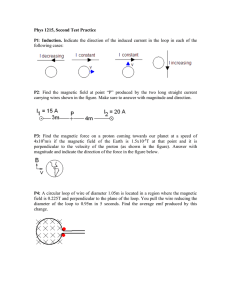
Scenario #1: Light Emitting Diodes In the circuit at right, a power supply sends current through a light-emitting diode (LED). As electrons pass through the LED, they drop to a lower energy level, emitting a photon in the process. Very little energy is lost; to create 2.0 eV photons requires a voltage of approximately 2.0 V. The power supply is adjusted to provide the exact voltage needed by the LED. Multiple Choice Questions (3 points): 1) One circuit runs a red LED; another runs a blue LED. What can you say about voltage in the two circuits? A. The red LED requires higher voltage. B. The two LEDs require the same voltage. C. The blue LED requires higher voltage. D. Two LEDs are better than one. 2) One circuit runs a red LED; another circuit runs a blue LED. Each circuit carries exactly 20.0 mA. What can you say about the number of photons emitted each second by the two LEDs? A. The red LED emits more photons. B. The two LEDs emit the same number of photons. C. The blue LED emits more photons. D. Led Zeppelin emits more photons than either. Short Answer Question (6 points): A coil of copper wire has 1200 turns, and an area of 0.0040 m2. The coil of wire is connected to a light emitting diode that emits 620 nm photons. A cow magnet with field strength 0.050 T is quickly thrust into the coil. What is the approximate minimum time for the magnet to go from being outside the coil to being inside the coil in order to light the LED? ! ! © 2014 Brian Jones, all rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced without the express written consent of the author. Scenario #2: Light Emitting Filaments Halogen bulbs have filaments like regular incandescent bulbs, but the filaments are much hotter, the bulbs are physically smaller, and they work at lower voltages. The small bulbs can be used at the focal point of a mirror to create a tight beam of light; they are used for spotlights, projectors and desk lamps. Multiple Choice Questions (3 points): 3) Increasing the temperature of a bulb’s filament ______________ the energy radiated from the filament, _____________ the peak wavelength of the emitted radiation. A. increases, increases B. increases, decreases C. decreases, increases D. decreases, decreases 4) Light from a halogen desk lamp is focused into a circle 40 cm across. A student using the lamp needs brighter light; she moves the lamp closer to the desktop to focus the light into a circle 20 cm across. This increases the intensity by a factor of A. 2 B. 4 C. 6 D. 8 Short Answer Question (6 points) A halogen bulb runs at 24 V provided by a transformer connected to the standard 120 V electricity supply. The transformer draws 20 W from the outlet and has 500 turns of wire on the primary. Find: • The number of turns on the secondary of the transformer • The current drawn from the outlet • The current in the bulb ! ! ! © 2014 Brian Jones, all rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced without the express written consent of the author. The test has 4 scenarios, each with 2 multiple choice questions (3 points each) and 1 short answer question (6 points). That’s 12 points possible per scenario. 4 scenarios at 12 points each plus 2 points for putting your name on your paper makes 50 points. The scenarios below are those from last year’s exam. Solutions will be posted on Tuesday, April 13. Scenario #3: The Right Hand Rules Scenario #1: The Right Hand Rules Multiple Choice Questions (3 points): Multiple Choice Questions (3 points) 5) Two wires carry equal and opposite currents, as in the cross section diagram 1) right. Two wires equalfield and opposite currents, in the cross at The carry magnetic at a point exactlyasbetween thesection two wires is diagram at wires is right. In this diagram, the magnetic field at a point exactly between the two A. Directed down, toward thethe bottom A. directed down, toward bottomofofthe thepage. page B. Directed up, toward the top of the page. B. directed up, toward the top of the page C. Directed to the right. C. directed to the right D. Zero. D. zero 6) A isismoving current-carryingwire wire diagram 2) proton A proton movingabove above aa current-carrying as as in in thethe diagram at at right. The wire and the proton are in the plane of the paper. In this The wire and the proton are in the plane of the paper. In this diagram, the diagram, the magnetic forceis on the proton is magnetic force on the proton ! right. A. directed down, toward bottomofofthe thepage. page A. Directed down, toward thethe bottom B. directed up, toward the top of the page B. Directed up, toward the top of the page. C. directed to the C. Directed out of theright paper. D. zero D. Zero. Short Answer Question (6 points): Short Answer Question (6 points): A proton moves to the right through a region of space with electric and magnetic ! A proton the right through a region of space fields moves at right to angles to each other, as in the diagram at with right. aFor just the right E electric field the traverse top of the field ! speed, thetoward proton will thispage fieldand withthe no magnetic net deflection. B directed out of the page, as in the diagram at right. The electric • What is the direction of the electric force on the proton? field magnitude 1500 V/m ; the magnetic field • Whatisis! Ethe= direction of the magnetic force on the proton? magnitude is ! B = 50 mT. • For what speed will the net force be zero? • isDescribe the path proton force if it moves at proton? twice this speed. • What the direction of of thetheelectric on the • What is the direction of the magnetic force on the proton? Scenario #2: What’s the Flux? • For what speed will the net force be zero, so the proton Multiple Choice Questionsas(3shown? points) moves with no deflection transformer the this following • AIfparticular the proton moves athas twice speed,specifications: will the proton’s path curve upward or curve Vp =downward? 120 V Primary voltage: Secondary voltage: Vs = 6.0 V ! v Power output: P = 10 W 3) 1) If this transformer has 800 turns of wire on the primary, how many turns of wire are on the secondary? A. B. C. D. 40 400 1600 16,000 4) When the transformer is running at its full rated power, how much current is in the primary? A. B. C. D. 0.083 A 0.60 A 1.7 A 10 A © 2009 Brian Jones, all rights reserved No part of this document may be reproduced without the express written consent of the author. © 2014 Brian Jones, all rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced without the express written consent of the author. Scenario #4: Rad Medicine Lung ventilation can be measured with ! 133 Xe , a radioactive isotope of xenon with a 5.2 day half-life. A patient breathes using a sealed system containing the radioactive gas. Xenon atoms undergo beta-minus decay, emitting a 350 keV electron; the daughter nucleus then emits a gamma ray that can be detected with a gamma camera. Multiple Choice Questions (3 points): 7) What is the daughter nucleus of the beta-minus decay? A. ! 131 Te B.! 133 I C.! 133 Xe D.! 133 Cs 8) The ! 133 Xe is supplied to hospitals in sealed vials with a rated activity. After 3 weeks, the activity has dropped to _______ of the initial value. A. 1/2 B. 1/4 C. 1/8 D. 1/16 Short Answer Question (6 points) A patient has xenon gas with total activity 740 MBq in his lungs for 2 minutes. The radiation dose to the lungs is primarily due to the beta radiation. If 50% of the energy of the emitted electrons is absorbed in 1.2 kg of lung tissue, what is the dose equivalent in Sv? © 2014 Brian Jones, all rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced without the express written consent of the author.