INDUCED VOLTAGES AND INDUCTANCE
advertisement

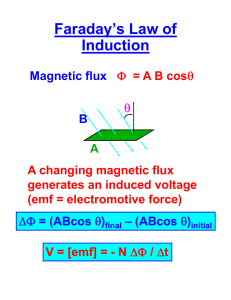
INDUCED VOLTAGES AND INDUCTANCE A Summary from College Physics by Raymond. Serway Induced Emf And Magnetic Flux The magnetic flux ∅B through a closed loop is defined as where B is the strength of the uniform magnetic field, A is the cross-sectional area of the loop, and θ is the angle between B and a direction perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The value of the magnetic flux is proportional to the total number of lines passing through the loop Faraday’s experiment. When the switch in the primary circuit at the left is closed, the ammeter in the secondary circuit at the right measures a momentary current. Conclusion: • The emf in the secondary circuit is induced by the changing magnetic field through the coil in that circuit. • An electric current could be produced by a changing magnetic field. Faraday’s Law of Induction Principle: a current is set up in the circuit as long as there is relative motion between the magnet and the loop. Faraday’s law of magnetic induction: If a circuit contains N tightly wound loops and the magnetic flux through each loop changes by the amount ∆∅B during the interval ∆t, the average emf induced in the circuit during time ∆t is Lenz’s law Lenz’ Law describe the polarity of voltage: The current caused by the induced emf travels in the direction that creates a magnetic field with flux opposing the change in the original flux through the circuit. If the magnetic flux through a loop is becoming more positive, say, then the induced emf creates a current and associated magnetic field that produces negative magnetic flux. An example of Lenz’s law. Applications of EMF Induced Electric Guitar: Vibration of magnetized string at a frequencies → varies the magnetic flux → changing the induced voltage → sent to amplifier → loudspeaker Applications of EMF Induced Tape Recorder: • A magnetic tape moves past a recording and playback head. • The tape is a plastic ribbon coated with iron oxide or chromium oxide. Example process to record a sound: • A sound wave sent into a microphone is transformed into an electric current, amplified, and allowed to pass through a wire coiled around a doughnut-shaped piece of iron, which functions as the recording head. • The iron ring and the wire constitute an electromagnet, in which the lines of the magnetic field are contained completely inside the iron except at the point where a slot is cut in the ring. • Here the magnetic field fringes out of the iron and magnetizes the small pieces of iron oxide embedded in the tape. • As the tape moves past the slot, it becomes magnetized in a pattern that reproduces both the frequency and the intensity of the sound signal entering the microphone. Applications of EMF Induced AC Generator An emf is induced in a coil, which rotates by some external means in a magnetic field Applications of EMF Induced DC Generator The emf fluctuates in magnitude, but always has the same polarity. The output voltage always has the same polarity and the current is a pulsating direct current Self-inductance What is the self-induction? As the current increases with time towards its equilibrium value → the magnetic flux through the loop due to this current also increases→ induces an emf in the circuit that opposes the change in magnetic flux. By Lenz’s law, the induced emf is in the direction indicated by the dashed battery in the figure. The net potential difference across the resistor is the emf of the battery minus the opposing induced emf. As the magnitude of the current increases → the rate of increase lessens and hence the induced emf decreases. This opposing emf results in a gradual increase in the current. For the same reason, when the switch is opened, the current doesn’t immediately fall to zero. Self-inductance The self-induced emf must be proportional to the rate of change of the current with time L is a proportionality constant called the inductance of the device. The SI unit of inductance is the henry (H) The negative sign indicates that a changing current induces an emf in opposition to the change. This means that if the current is increasing (∆I positive), the induced emf is negative, indicating opposition to the increase in current, VICE VERSA RL Circuit A circuit element that has a large inductance, such as a closely wrapped coil of many turns, is called an inductor 1. at t = 0: The current begins to increase, but the inductor produces an emf that opposes the increasing current. As a result, the current can’t change from zero to its maximum value of ε/R instantaneously. 2. As the current approaches its steady-state value, the back emf of the coil falls off because the current is changing more slowly. 3. Finally, when the current reaches its steady-state value, the rate of change is zero and the back emf is also zero. Energy Stored In A Magnetic Field