Beats (lecture 10) The Doppler Effect – Moving Listener
advertisement
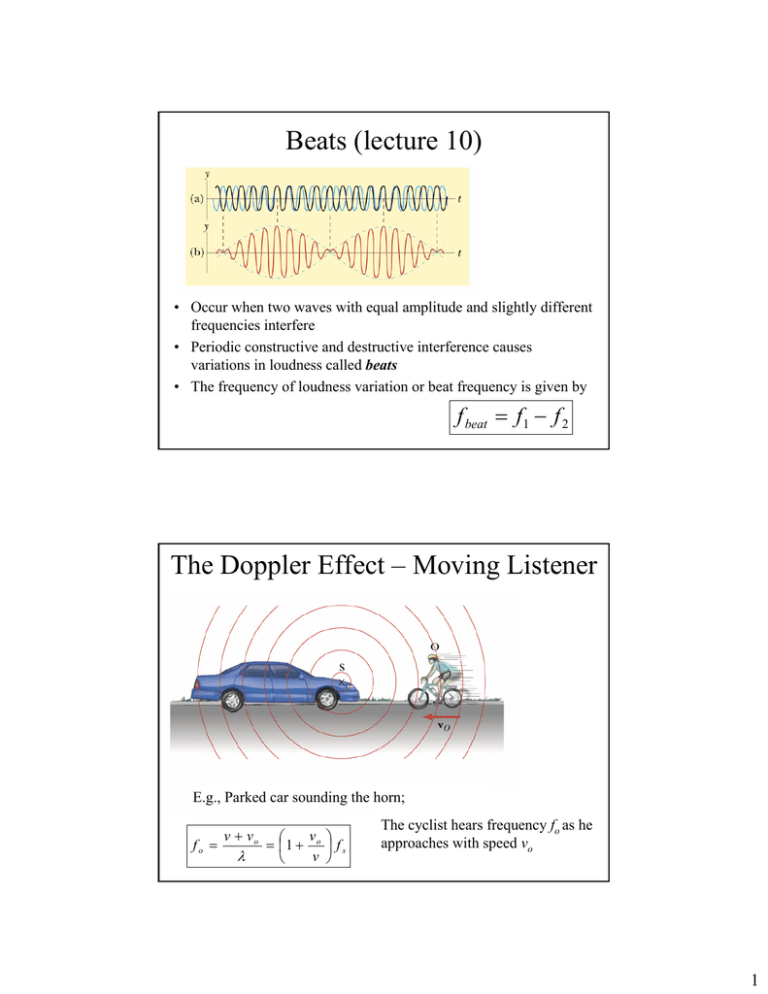
Beats (lecture 10) • Occur when two waves with equal amplitude and slightly different frequencies interfere • Periodic constructive and destructive interference causes variations in loudness called beats • The frequency of loudness variation or beat frequency is given by f beat = f1 − f 2 PHYS 1901: Waves (Y&F Ch 13) 1 The Doppler Effect – Moving Listener E.g., Parked car sounding the horn; v + vo v fo = = 1 + o f s PHYS 1901:λWaves (Y&F Ch 13)v The cyclist hears frequency fo as he approaches with speed vo 2 1 Moving Source and Moving Listener fL = v + vL fS v + vS This expresses the frequency heard by the listener in terms of the frequency of the source It includes all possibilities for motion of source and listener (relative to the medium) along line joining them PHYS 1901: Waves (Y&Fthe Ch 13) 3 Shock Waves PHYS 1901: Waves (Y&F Ch 13) 4 2


