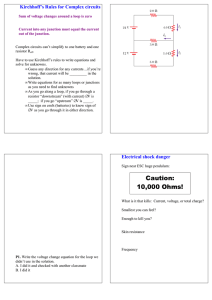
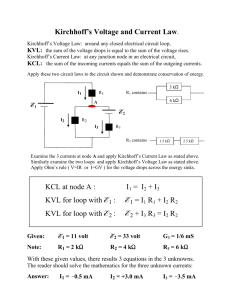
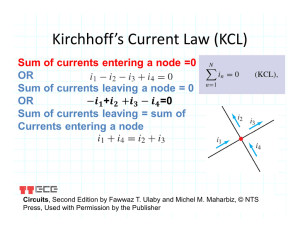
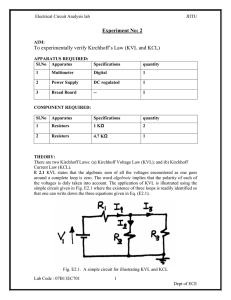
Kirchhoff`s Laws
advertisement

Chapter Kirchhoff’s Laws Topics Covered in Chapter 9 9-1: Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) 9-2: Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) 9-4: Node-Voltage Analysis 9-5: Method of Mesh Currents 9 9-1: Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) The sum of currents entering any point in a circuit is equal to the sum of currents leaving that point. Otherwise, charge would accumulate at the point, reducing or obstructing the conducting path. Kirchhoff’s Current Law may also be stated as IIN = IOUT Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Fig. 9-1: Current IC out from point P equals 5A + 3A into P. 9-2: Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) Loop Equations A loop is a closed path. This approach uses the algebraic equations for the voltage around the loops of a circuit to determine the branch currents. Use the IR drops and KVL to write the loop equations. A loop equation specifies the voltages around the loop. 9-2: Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) Loop Equations ΣV = VT means the sum of the IR voltage drops must equal the applied voltage. This is another way of stating Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law.